| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Behcet's Syndrome
|Monoarticular arthritis |Polyarticular arthritis |Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies |Ankylosing spondylitis |Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis |Reactive Arthritis |Psoriatic Arthritis |Adult Onset Still's Disease |Alkaptonuria |Behcet's Syndrome🧩 Behçet's syndrome is a chronic, relapsing, multisystem vasculitis of unknown aetiology, affecting both small and large vessels (arterial and venous). It classically presents with the triad of recurrent oral ulcers, genital ulcers, and uveitis.
🌍 Introduction
- Multisystem, chronic-relapsing inflammatory disorder
- Predominantly targets the venous system (thrombophlebitis, cerebral venous sinus thrombosis)
- Classic triad: recurrent oral ulcers + genital ulcers + uveitis
🧬 Aetiology
- Unknown cause; strong association with HLA-B51
- Most common in populations from the Middle East, Far East, and Mediterranean (“Silk Road distribution”)
- Neurological involvement in up to one-third (stroke, brainstem disease, venous sinus thrombosis)
🩺 Clinical Features
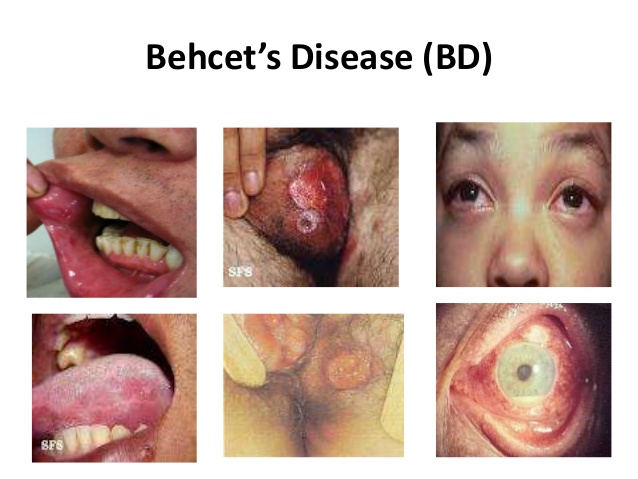
- 💋 Painful recurrent oral aphthous ulcers
- 🍑 Genital ulcers (scarring typical)
- 👁️ Ocular disease: anterior/posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis → risk of blindness
- 🦵 Musculoskeletal: arthritis, myalgia
- 🩸 Vascular: venous thrombosis, aneurysms
- 🩹 Skin lesions: erythema nodosum, pseudofolliculitis; positive pathergy test
- Diagnosis is clinical – no single confirmatory test
🧠 CNS Manifestations (Neuro-Behçet’s)
- Parenchymal (5–20%): Brainstem lesions → diplopia, ataxia, dysphagia, pseudobulbar speech, hemiparesis
- Meningoencephalitis: Headache, confusion, drowsiness progressing over days
- Cerebral venous thrombosis: Headache, raised ICP, haemorrhagic infarcts
- Psychiatric: Depression, paranoia, hallucinations (rare)
🔍 Differential Diagnosis
- Multiple sclerosis (relapsing neuro course)
- Neurosarcoidosis
- Stroke / vasculitis
🧪 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs; CRP/ESR may be ↑
- 🧷 Pathergy test: skin hyperreactivity at needle prick within 24–48h (not specific)
- IL-6 levels may correlate with disease activity
- MRI: Brainstem/basal ganglia T2 lesions, meningoencephalitis, venous thrombosis
- CTV/MRV if CVST suspected
- CSF: ↑ WCC (neutrophils often predominate) in parenchymal neuro-Behçet’s
📋 Diagnostic Criteria
Mouth sores ≥3 times in 12 months plus two of the following:
- Recurrent genital ulceration (± epididymitis/orchitis)
- Ocular inflammation (uveitis, retinal vasculitis)
- Skin lesions (erythema nodosum, pseudofolliculitis, papulopustules)
- Positive pathergy test
💊 Management
- Topical corticosteroids for ulcers; colchicine for mucocutaneous disease
- 👁️ Ophthalmology referral: steroid drops, azathioprine, biologics (infliximab, interferon)
- 🧠 Neurology: IV methylprednisolone for acute CNS disease ± long-term azathioprine, mycophenolate, or methotrexate
- 💉 Severe disease: cyclophosphamide, interferon-α, or biologics (anti-TNF, e.g. infliximab, etanercept)
- Anticoagulation for cerebral venous thrombosis (with caution if arterial aneurysms)
📚 References
- Diagnosis and management of Neuro-Behçet’s disease: international consensus recommendations
- Diagnosis and treatment of cerebral vasculitis – Peter Berlit, Ther Adv Neurol Disord (2010)
Cases — Behçet’s Syndrome
- Case 1 — Classic triad 👄👀: A 27-year-old Turkish man presents with recurrent painful oral ulcers, genital ulcers, and episodes of red, painful eyes. Ophthalmology exam: anterior uveitis. Diagnosis: Behçet’s syndrome. Managed with topical steroids for ulcers and systemic immunosuppression (colchicine, azathioprine).
- Case 2 — Vascular involvement 🫀: A 35-year-old woman presents with sudden leg pain and swelling. Doppler: femoral vein thrombosis. History reveals recurrent oral aphthous ulcers and erythema nodosum–like lesions on the shins. Screening: positive pathergy test. Diagnosis: Behçet’s with vascular involvement. Treated with anticoagulation and immunosuppressants.
- Case 3 — Neurological features 🧠: A 40-year-old man of Middle Eastern background presents with headache, unsteadiness, and double vision. MRI: brainstem lesions suggestive of neuro-Behçet’s. History of recurrent genital ulcers and past uveitis. Managed with high-dose steroids and cyclophosphamide under neurology and rheumatology teams.
Teaching Point 🩺: Behçet’s is a multi-system vasculitis most common along the Silk Road (Turkey, Middle East, East Asia). Key features: recurrent oral/genital ulcers, uveitis, skin lesions, vascular and neurological disease. Always consider in unexplained venous/arterial thrombosis in a young patient.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
