| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Complement
Related Subjects: |Major Histocompatibility complex |Immune response |Complement |Opsonisation |Toll-like Receptors (TLRs) |Immunoglobulins |Immunology |X linked Agammaglobulinaemia (Bruton) |X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (Children) |Chediak Higashi syndrome |Common variable immunodeficiency |Severe combined immunodeficiency disorders |DiGeorge syndrome (thymic aplasia) |Selective IgA deficiency |Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (Children) |T lymphocytes
🛡️ The complement system is a tightly regulated cascade of plasma proteins that forms a central bridge between innate and adaptive immunity. It amplifies antibody function, enhances phagocytosis, recruits inflammatory cells, and can directly destroy pathogens through membrane pore formation. Physiologically, complement acts as a “biological alarm system” - rapidly triggered by microbes, immune complexes, or damaged tissue.
🔑 Core Principles
- System Architecture
- ⚙️ Comprises >30 circulating and membrane-bound proteins.
- Main effector components: C1–C9.
- Includes regulators (Factor H, CD55, CD59) and receptors (CR1–CR4).
- Proteins circulate in inactive pro-enzyme form → rapid amplification when triggered.
- Cascade Logic
- Each activation step cleaves the next component → exponential signal amplification.
- Small triggers generate large inflammatory and opsonic responses.
- Unchecked activation risks host tissue injury.
🛣️ Pathways of Complement Activation
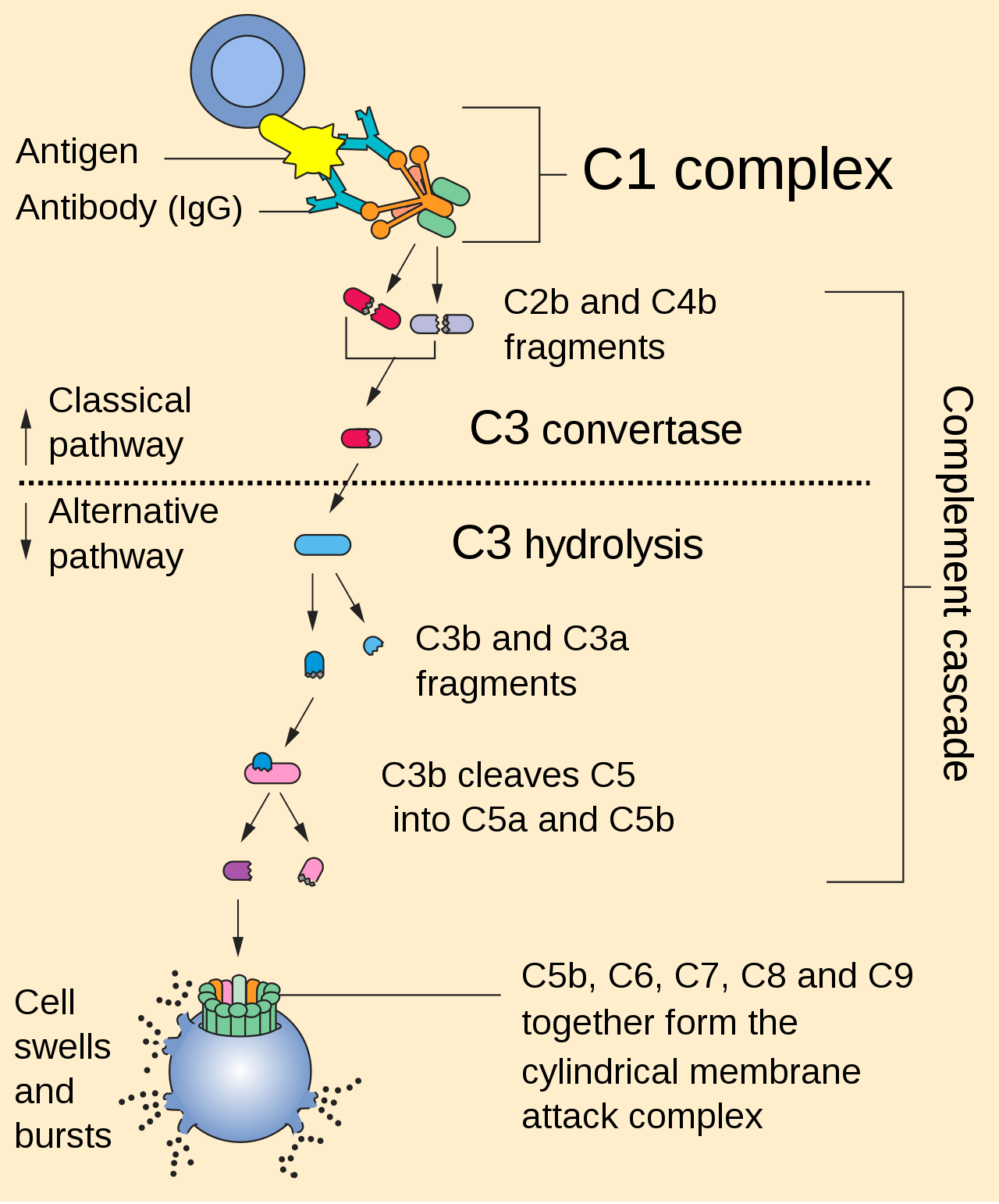
- 📘 Classical Pathway (Antibody-Dependent)
- Triggered by IgG or IgM bound to antigen.
- C1q binds Fc region → activates C1r and C1s.
- C4 and C2 cleavage → C3 convertase (C4b2a).
- Links adaptive immunity to innate effector mechanisms.
- 📗 Lectin Pathway (Pattern Recognition)
- Triggered by mannose-binding lectin (MBL) or ficolins.
- Recognises microbial carbohydrates.
- MASP activation → C4b2a formation.
- Functions independently of antibodies.
- 📙 Alternative Pathway (Spontaneous Surveillance)
- Continuous low-level C3 hydrolysis (“tick-over”).
- C3b binds microbial surfaces.
- Forms C3bBb convertase.
- Stabilised by properdin.
- Key first-line defence mechanism.
⚔️ Effector Functions
- 🖇️ Opsonisation
- C3b/iC3b coat pathogens.
- Bind CR1/CR3 on phagocytes.
- Greatly enhances phagocytosis.
- 💥 Membrane Attack Complex (MAC)
- C5b–C9 assemble into transmembrane pores.
- Causes osmotic lysis.
- Especially effective against Neisseria species.
- 🔥 Inflammatory Signalling
- Anaphylatoxins: C3a, C4a, C5a.
- C5a is the most potent chemoattractant.
- Promotes mast cell degranulation and vascular permeability.
- 🧹 Immune Complex Clearance
- Complexes bind CR1 on erythrocytes.
- Transported to liver and spleen.
- Removed by macrophages.
- Prevents immune complex deposition.
🧯 Regulation and Host Protection
- Key Regulatory Proteins
- 🧩 Factor H → inhibits alternative pathway on host cells.
- 🚫 CD55 (DAF) → accelerates convertase decay.
- 🛑 CD59 (Protectin) → blocks MAC insertion.
- 🔒 C1 Inhibitor (C1-INH) → suppresses classical/lectin pathways.
🏥 Clinical Relevance
- 🧬 Complement Deficiencies
- C3 deficiency → severe recurrent infections.
- C5–C9 deficiency → Neisseria susceptibility.
- Early component deficiency → SLE risk.
- 🌙 Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria (PNH)
- PIGA mutation → loss of CD55/CD59.
- Uncontrolled MAC-mediated haemolysis.
- High thrombotic risk.
- 🤒 Immune-Mediated Injury
- SLE, vasculitis, RA, glomerulonephritis.
- Driven by immune complex–complement activation.
- 💊 Targeted Therapy
- Eculizumab/ravulizumab → C5 inhibition.
- Used in PNH, aHUS, C3 glomerulopathy.
📌 Summary
🧩 The complement system integrates innate surveillance with adaptive immunity.
Its core actions are opsonisation, inflammation, cytolysis, and immune complex clearance.
Clinical disease reflects imbalance: deficiency → infection; excess → autoimmunity and tissue damage.
Understanding regulation is central to modern immunotherapy.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
