Related Subjects:
|Metabolic acidosis
|Lactic acidosis
|Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) / Acute Renal Failure
|Renal/Kidney Physiology
|Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
|Anaemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
|Analgesic Nephropathy
|Medullary Sponge kidney
|IgA Nephropathy (Berger's disease)
|HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)
|Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN)
|Acute Rhabdomyolysis
|Autosomal Dominant Polycystic kidney disease
🔎 Always investigate for acute kidney injury (AKI) by checking serum creatinine (and comparing with baseline), urine dip for nephritis, and assessing fluid status.
Most cases are supportive, but some need urgent intervention (e.g., catheter, stent, dialysis).
🚑 General Management Summary (Hyperkalaemia First!)
| Emergency Management of AKI |
|---|
- ABC, O₂ if hypoxic, IV access, ECG monitoring.
- 📉 Treat hyperkalaemia ≥ 6.0 mmol/L immediately.
- 🌡️ Treat systemic infection or urosepsis with IV antibiotics.
- Send bloods: FBC, U&E, Ca/P/ALP, CRP, Lactate.
Do ECG, CXR, VBG/ABG.
- Prerenal: Fluids, sepsis treatment, stop BP-lowering drugs (ACEI, ARB, CCB). Consider inotropes if shocked.
- Renal: Stop nephrotoxins (ACEI/ARB/NSAID/Gent). Order ANCA/ANA/anti-GBM if nephritis suspected. Renal referral.
- Postrenal: Catheterize. If oliguria/anuria, urgent renal USS (<12h).
- Consider dialysis if:
– Refractory hyperkalaemia
– Pulmonary oedema
– Severe uraemia (encephalopathy, pericarditis)
– Severe acidosis unresponsive to fluids/bicarb.
|
📖 About AKI
- AKI has replaced the older term “acute renal failure.”
- Defined as a sudden fall in renal function → ↑ urea/creatinine, ↓ urine output.
- Often reversible if identified and treated early.
- eGFR is unreliable in acute illness — use creatinine and urine output instead.
📊 KDIGO Definition & Staging
| Stage | Criteria |
|---|
| 1 | Creatinine 1.5–1.9× baseline OR ↑ ≥26 µmol/L in 48h OR urine <0.5 ml/kg/hr for 6–12h |
| 2 | Creatinine 2–2.9× baseline OR urine <0.5 ml/kg/hr ≥12h |
| 3 | Creatinine 3× baseline OR RRT started OR anuria ≥12h |
⚡ Renal Functions Affected
- Water/electrolyte control
- Excretion of toxins & drugs
- Acid–base regulation
- BP control (RAAS)
- EPO & Vitamin D activation
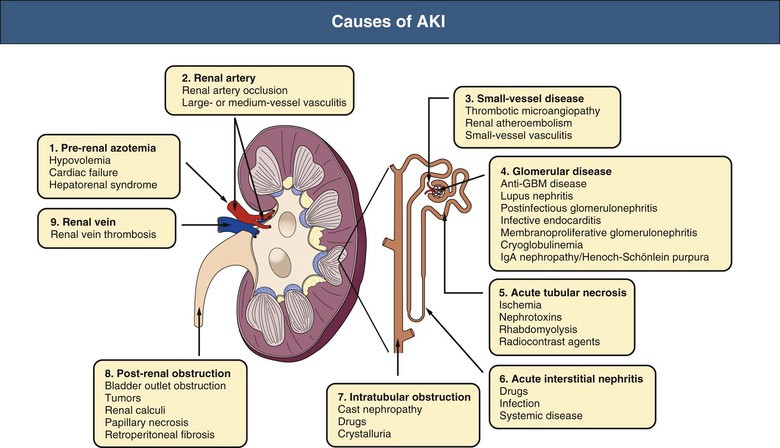
🧾 Causes of AKI
| Site | Examples | Actions |
|---|
| Prerenal |
Hypovolaemia (bleeding, burns, sepsis), hypotension, ACEI/ARB/NSAIDs, PPIs |
Fluids, sepsis control, stop offending drugs, vasopressors if needed |
| Renal (Intrinsic) |
ATN (45%), RPGN, GN, vasculitis, interstitial nephritis, HUS/TTP |
Nephrology input, send ANCA/ANA/anti-GBM, stop nephrotoxins, consider biopsy |
| Postrenal |
Stones, strictures, malignancy, prostate obstruction |
Catheterize, USS (<12h), consider stent/nephrostomy, urology input |
🔬 Prerenal vs Intrinsic Renal (Urine Features)
- Urine SG: Prerenal > 1.020 vs. Renal < 1.010
- Urine Osmolality: Prerenal > 500 vs. Renal < 350 mOsm/kg
- Urinary Na⁺: Prerenal < 20 vs. Renal > 40 mmol/L
🧍 Clinical Presentation
- Malaise, lethargy, anorexia, nausea, vomiting
- Oliguria/anuria OR polyuria (if concentrating defect)
- Confusion, delirium, seizures, coma in severe cases
- Fluid overload → pulmonary oedema, raised JVP
- Skin pallor, pruritus; bruising (platelet dysfunction)
- Uraemic pericarditis → friction rub, tamponade
🧪 Investigations
- Bloods: U&E (↑ urea/creatinine, ↑ K⁺), Ca/P/ALP, CRP, FBC, film
- Urine: Dipstick (protein/haematuria), microscopy (casts)
- Serology: ANCA, ANA, Anti-GBM, complements
- Imaging: Renal USS (exclude obstruction), CXR (pulm oedema), ECG (K⁺)
- Special: Myeloma screen (high calcium/ESR), HIV, biopsy if unclear
🧪 Selected Targeted Tests
- Nephritis: ANCA, ANA
- Acidosis: ABG (HCO₃⁻ <19 mmol/L)
- Rhabdomyolysis: CK
- SBP <110 + sepsis: Lactate
- ENT bleed + renal: Anti-GBM
- High Ca²⁺ + ESR: Myeloma screen
|
💊 Management (With Renal/Urology Input)
- NEWS monitoring, fluid balance chart, daily U&E
- Prerenal: Hydrate (0.9% saline 1L over 2–4h, reassess). Pressors if shocked
- Renal: Stop nephrotoxins, treat vasculitis if confirmed, immunosuppression if needed
- Postrenal: Relieve obstruction (catheter/stent/nephrostomy)
- Acidosis: Consider IV bicarbonate (1.26%)
- Hyperkalaemia: Calcium gluconate + insulin/dextrose + salbutamol neb
- Dialysis indications (AEIOU):
– Acidosis (pH < 7.2)
– Electrolytes (K⁺ refractory)
– Ingestions (toxin)
– Overload (pulm oedema)
– Uraemia (encephalopathy, pericarditis)
🧾 Haemofiltration
- Preferred in unstable patients in ITU.
- Early discussion with renal + intensive care is essential.
📚 References
Cases — Acute Kidney Injury (AKI)
- Case 1 — Pre-Renal (Hypovolaemia) 🩸:
A 72-year-old man admitted with profuse diarrhoea and vomiting presents with hypotension and oliguria. Urea:creatinine ratio raised.
Diagnosis: AKI due to volume depletion.
Management: IV fluids, electrolyte correction, stop nephrotoxic drugs (e.g., NSAIDs, ACEi).
- Case 2 — Pre-Renal (Heart Failure) ❤️:
A 68-year-old woman with decompensated LV systolic failure presents with worsening breathlessness and reduced urine output. JVP elevated, bilateral crackles.
Diagnosis: Pre-renal AKI due to low cardiac output.
Management: Diuretics for pulmonary oedema, optimise heart failure therapy, careful fluid balance.
- Case 3 — Intrinsic Renal (ATN from Contrast Nephropathy) ⚡:
A 65-year-old man undergoes PCI with IV contrast. Two days later, he develops oliguria and rising creatinine. Urine microscopy: muddy brown casts.
Diagnosis: AKI due to acute tubular necrosis from contrast.
Management: Stop nephrotoxins, IV hydration, consider renal replacement therapy if severe.
- Case 4 — Intrinsic Renal (Acute Interstitial Nephritis) 💊:
A 54-year-old woman treated with antibiotics for UTI presents with rash, fever, and AKI. Urine: eosinophils present.
Diagnosis: Drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis.
Management: Stop offending drug; supportive care ± corticosteroids if severe.
- Case 5 — Post-Renal (Obstructive) 🚧:
An 80-year-old man with known BPH presents with anuria, lower abdominal pain, and bilateral hydronephrosis on ultrasound.
Diagnosis: Post-renal AKI due to bladder outlet obstruction.
Management: Immediate bladder catheterisation; urology referral; long-term BPH management.
Teaching Commentary 🧠
AKI is classified into:
- Pre-renal (hypoperfusion: dehydration, heart failure, sepsis),
- Intrinsic (tubular, glomerular, interstitial, vascular),
- Post-renal (obstruction).
Always look for reversible causes: hypovolaemia, sepsis, drugs, obstruction.
Initial management is ABCDE, stop nephrotoxins, check fluid status, catheterise, and correct potassium. Early nephrology input if severe or prolonged.