| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
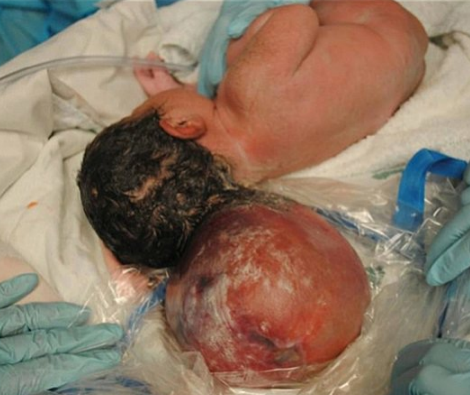
Encephalocoele
🧠 Encephalocele is a rare neural tube defect where sac-like protrusions of brain tissue and meninges extend through openings in the skull. ⚡ Early diagnosis and timely surgical repair are critical to reduce complications and improve neurological outcomes.
ℹ️ About
- Definition: Congenital defect where brain tissue, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), and meninges herniate through a skull defect.
- Location: 📍 Most commonly occipital, but can also appear frontally or nasofrontal (near nose/forehead).
🧬 Aetiology
- Genetic & Environmental: 🌍 Multifactorial, due to disrupted neural tube closure during early development.
- Folic Acid Deficiency: 🍃 Linked with higher risk of neural tube defects if maternal folate intake is inadequate.
- Associated Disorders: 🤝 May co-occur with syndromes or chromosomal abnormalities.
🗂️ Types
- Meningocele: Containing only CSF + meninges.
- Encephalocele: CSF + meninges + brain tissue.
- Hydroencephalocele: Includes CSF, meninges, brain tissue, and part of ventricular system.
⚙️ Pathophysiology
- ❌ Failure of neural tube closure within the first 3–4 weeks of gestation.
- 🪨 Skull defect allows brain/meningeal herniation → compression or dysfunction of neural tissue.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Visible Sac: 🎒 Protrusion on scalp (often occipital), containing CSF ± brain tissue.
- Neurological Symptoms: ⚡ Seizures, hydrocephalus, developmental delay, motor deficits.
- Craniofacial Abnormalities: 😷 Midline facial anomalies or skull deformities.
🔎 Investigations
- Prenatal Ultrasound: 📡 Detectable in 2nd trimester.
- MRI: 🖥️ Defines brain tissue involvement and defect extent.
- Genetic Testing: 🧬 Consider if syndromic features present.
🛠️ Management
- Pre-birth Counselling: 👨👩👧 Discuss prognosis, surgical options, and outcomes with parents.
- Surgical Repair: ✂️ Reduction of herniated tissue + closure of skull defect; timing depends on size, site, and symptoms.
- Supportive Care: ❤️ Includes hydrocephalus shunting, physio/OT, and seizure control if needed.
📈 Prognosis
- Variable: Depends on site, size, and brain tissue involved.
- Better Outcome: ✅ Small meningoceles (CSF + meninges only) often fare well; larger encephaloceles with brain tissue → poorer neurological prognosis.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
