| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
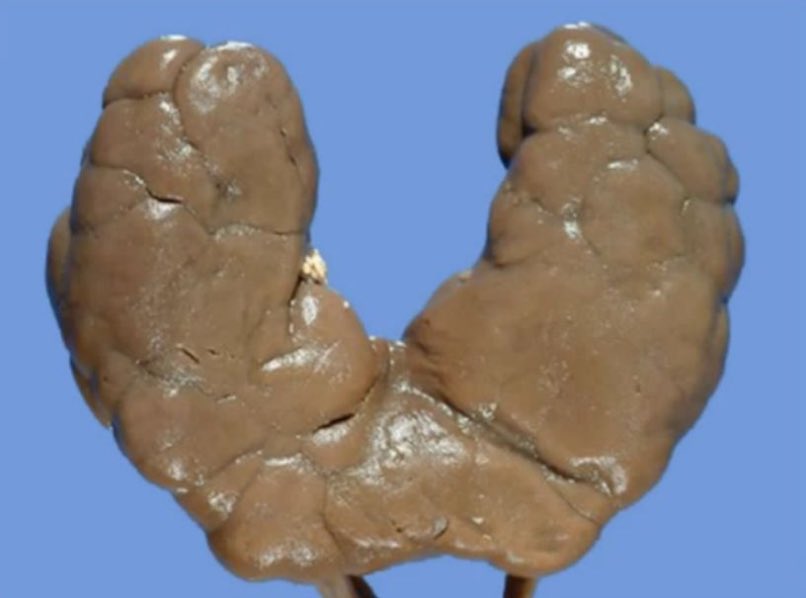
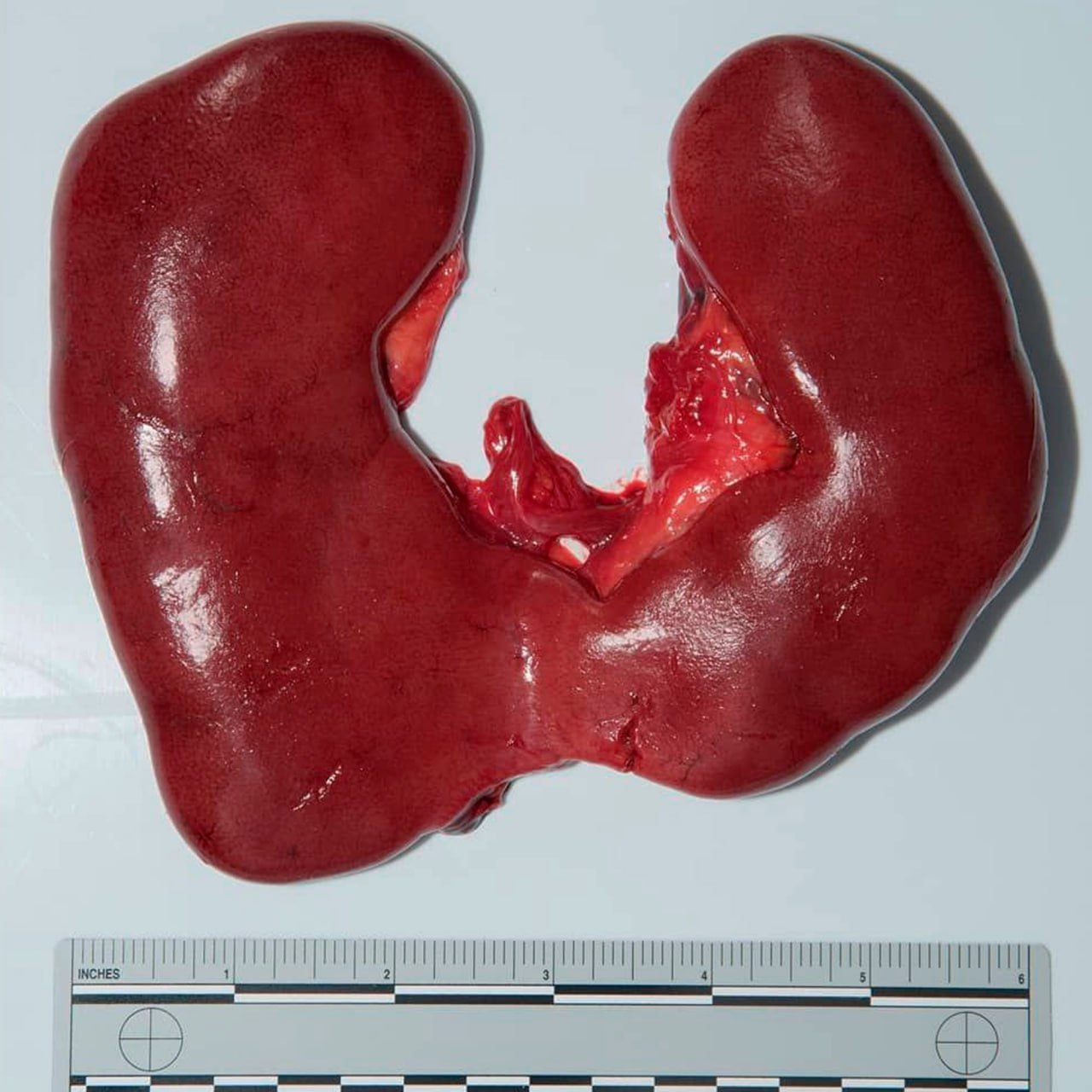
Horseshoe Kidney
🧩 Horseshoe kidney is the most common congenital renal anomaly. When found in isolation, it is usually benign ✅, but can predispose to obstruction, infection, and stones. Its anatomical relationship with the inferior mesenteric artery (IMA) has important surgical implications ⚠️.
ℹ️ About
- Characterised by fusion of the lower renal poles in ~90% of cases.
- The connecting isthmus may be fibrous or contain functioning renal parenchyma.
- Fusion occurs during embryogenesis when the kidneys ascend, becoming trapped under the IMA. 🧬
🧬 Aetiology
- Most common congenital renal anomaly (≈0.25% of the population).
- Genetic associations: Turner syndrome, trisomy 13, 18, 21. 🧪
- Other anomalies: hypospadias, uterine/vaginal malformations.
- More common in ♂ males.
👩⚕️ Clinical Features
- Often asymptomatic and detected incidentally on imaging.
- Symptoms may include vague lumbar pain, nausea, vomiting.
- Renal stones occur in up to 50% of cases (usually calcium oxalate). 💎
- Recurrent UTIs and hydronephrosis due to ureteropelvic junction obstruction.
- Can present across the lifespan (childhood ➝ late adulthood).
🔎 Investigations
- U&E: Assess baseline renal function and screen for AKI/CKD.
- Ultrasound: First-line for hydronephrosis, anatomy, and obstruction. 📡
- CT/MRI: Detailed anatomical assessment; essential for surgical planning and stone localisation.
- Nuclear renogram (MAG3/DMSA): May be used to assess drainage and split renal function.
🧫 Pathology & Anatomy Pearls
- Obstruction risk: Isthmus may cause ureteropelvic junction obstruction → recurrent infection/stone formation.
- Surgical risk: The isthmus lies just below the IMA → important during abdominal or vascular surgery. ⚠️
- Increased incidence of Wilms tumour and renal cell carcinoma compared with general population (though absolute risk is low).
💊 Management
- Asymptomatic: No specific treatment, but long-term surveillance may be advised. 👀
- Acute presentations: Manage with ABC, IV fluids, treat AKI if present.
- Infections: Antibiotics according to culture. 🦠
- Stones: ESWL (shockwave lithotripsy); percutaneous surgery or ureteroscopy if resistant. 💎
- Obstruction: Refer to urology; pyeloplasty may be considered in UPJ obstruction.
- Surgery: Extra caution required because of aberrant vessels and IMA position.
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
