| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Congenital
Related Subjects: |ECG-QT interval |Brugada Syndrome |Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Acquired |Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Congenital |Torsades de Pointes |Ventricular Fibrillation |Ventricular Tachycardia |Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm |Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD)
⚠️ Beta blockers (BBs) reduce sympathetic stimulation of cardiac ion channels and protect against arrhythmias, particularly in LQT1 and LQT2. They are first-line therapy for most congenital LQTS patients.
📌 About Long QT Syndrome (LQTS)
- A congenital cardiac channelopathy causing prolonged QT interval and risk of Torsades de Pointes or sudden cardiac death.
- Prevalence: ~1 in 2000; often under-recognised.
⚡ Torsades de Pointes
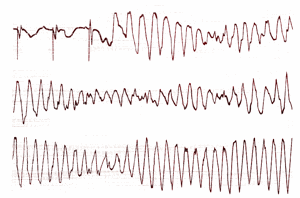
🧬 Aetiology
- Mutations in potassium, sodium, or calcium channels → delayed ventricular repolarisation.
- QT interval prolongation = substrate for polymorphic VT (torsades) and VF.
🔑 Types
- Romano-Ward: Autosomal dominant, QT prolongation + arrhythmias.
- Jervell & Lange-Nielsen: Autosomal recessive, associated with congenital deafness + higher arrhythmic risk.
📉 Risk Factors
- Increased sympathetic tone (exercise, stress, sudden loud noises).
- Electrolyte disturbance: ↓K⁺, ↓Mg²⁺, ↓Ca²⁺.
- QT-prolonging drugs (see CredibleMeds list).
🧪 Clinical Features
- Syncope (often during exercise, swimming, or emotional stress).
- Palpitations, cardiac arrest, or sudden unexplained death in family.
- May be asymptomatic and detected on ECG screening.
📊 Diagnostic Criteria (Schwartz Score)
- QTc >480 ms = +3 points
- Torsades de Pointes = +2
- Syncope with stress = +2; without stress = +1
- Congenital deafness = +0.5
- Family history of LQTS or sudden death <30 yrs = +0.5–1
- ≥4 points = high probability of LQTS
🧪 Investigations
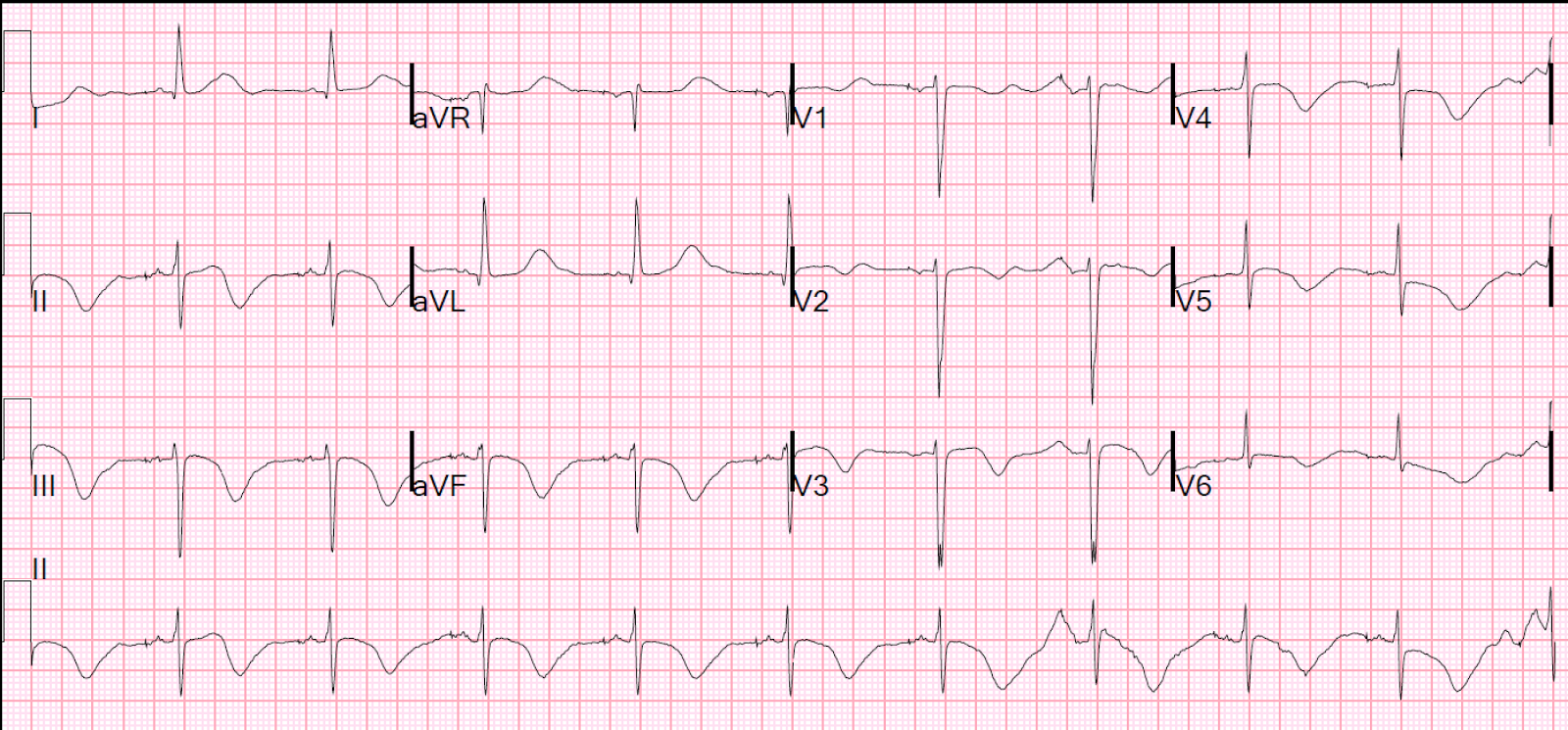
- ECG: QTc prolongation; repeat if borderline.
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, Ca²⁺, Mg²⁺ to exclude secondary causes.
- Genetic testing: if clinical suspicion strong.
🩺 Management
- Drug avoidance: Stop QT-prolonging drugs, avoid electrolyte disturbance.
- Beta blockers: (propranolol, nadolol, atenolol) = cornerstone, esp. in LQT1.
- ICD: For survivors of cardiac arrest, recurrent syncope despite BBs, or QTc >550 ms with high-risk features.
- LCSD (Left Cervicothoracic Sympathectomy): Considered if recurrent events despite BB therapy and ICD not suitable.
- Lifestyle advice:
- LQT1 → avoid swimming/strenuous exertion 🏊♂️
- LQT2 → avoid sudden loud noises / alarms 🔔
- All → avoid competitive sports unless risk-stratified by specialist
📚 Reference
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
