| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
Related Subjects: |Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS) |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Cancer and Stroke |Cardioembolic stroke |CT Basics for Stroke
🧠 Introduction
- Dural Arteriovenous Fistula (dAVF) = abnormal shunt between a dural artery (meningeal/occipital) and a dural venous channel.
- Acquired (unlike congenital AVMs) ➝ can cause intracerebral haemorrhage (ICH) or subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH).
- Account for ~10% of intracranial AVMs; more common in females.
⚙️ Aetiology
- Triggers: head trauma, previous cranial surgery, venous sinus thrombosis.
- Pathophysiology: direct arterial ➝ venous sinus connection ➝ high flow ➝ ↑ venous pressure ➝ venous congestion ➝ possible haemorrhage.
- Most often within the dura mater, especially the transverse sinus.
- Carotid–cavernous fistula: classically ➝ chemosis, scleral injection, pulsatile bruit.
- Without cortical venous reflux ➝ rarely cause neurological deficits.
📍 Common Sites & Presentations
- Cavernous sinus: 👁️ chemosis, proptosis, bruit, reduced vision.
- Transverse/sigmoid sinus: 👂 pulsatile tinnitus, headaches, seizures, stroke-like episodes.
- Vertebral artery/posterior fossa: 🌀 cerebellar or brainstem symptoms from venous congestion.
📑 Classification
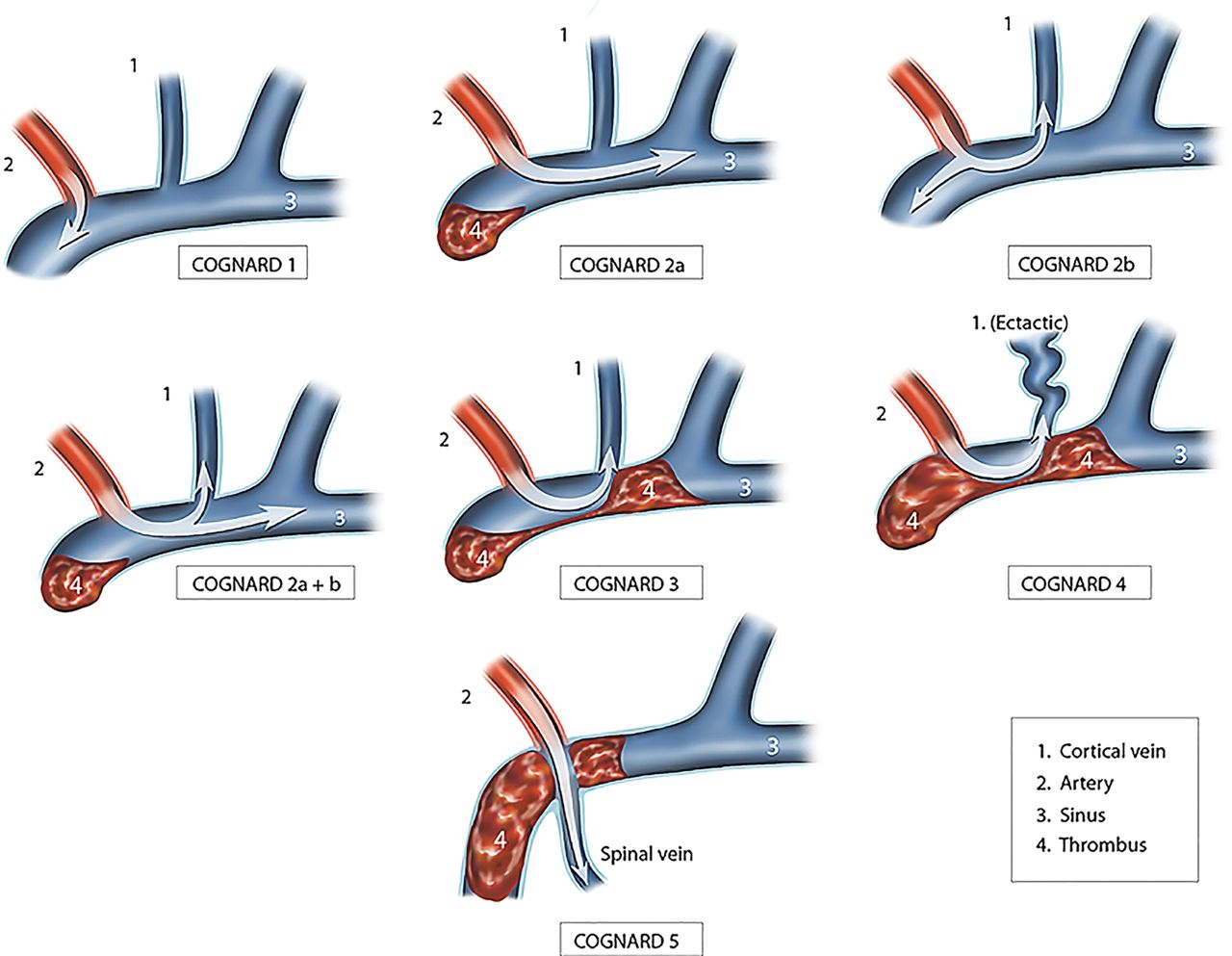
💡 Prognosis depends on presence of cortical venous reflux → high risk of haemorrhage and neuro deficits.
🔎 Clinical Features
- May be asymptomatic or cause chronic headache (dural pain fibre irritation).
- Seizures, bruit, headaches, stroke-like events are common presentations.
- Raised ICP, ICH, or SAH ➝ in severe cases.
🧪 Investigations
- Gold standard = Digital Subtraction Angiography (DSA).
- CTA/MRA may show venous congestion, dilated cortical veins, vasogenic oedema.
- Key finding: early venous filling from external carotid artery branches.
💉 Management
- Annual bleed risk <5% (higher with cortical venous reflux).
- Options:
- 🟢 Conservative (stable, low-risk lesions).
- 🟡 Endovascular embolisation (N-butyl cyanoacrylate, Onyx).
- 🔴 Surgery (disconnection of fistula, venous sinus occlusion) if embolisation not feasible.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
