| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Supracondylar Femur Fractures
Related Subjects:
|Fractured Neck of Femur
|Fractured Shaft Femur
|Supracondylar Femur Fractures
|Femoral fractures
|Fractured Tibia and Fibula
Supracondylar Femur Fractures 🦴 occur just above the knee joint.
They are uncommon but serious, often from high-energy trauma (RTAs, falls) or low-energy in elderly/osteoporotic bone.
These fractures may involve the articular surface and carry a risk of knee stiffness, malunion, and post-traumatic arthritis.
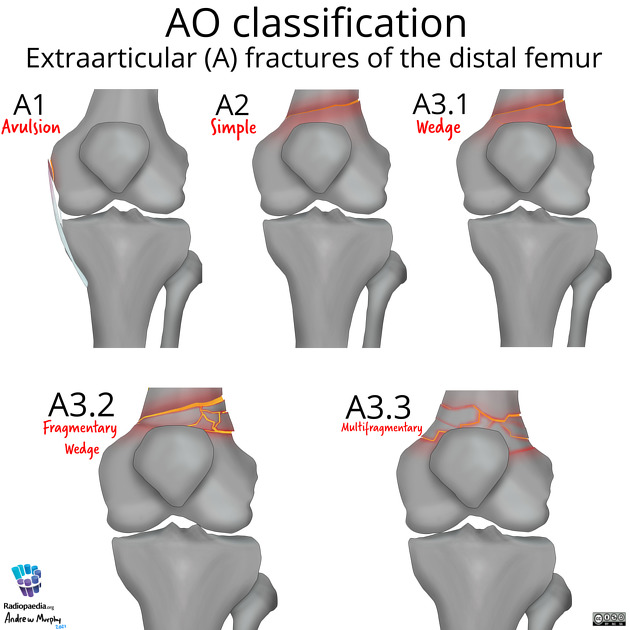
📖 About
⚙️ Aetiology
🩺 Clinical Features
🧪 Investigations
⚠️ Complications
💊 Management
📌 OSCE / Exam Pearls
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
