| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
CT Pulmonary angiogram (CTPA)
Related Subjects: |Assessing Breathlessness |Pulmonary Embolism |Deep Vein Thrombosis |DVT/PE in pregnancy |CTPA
📖 Introduction
- CT Pulmonary Angiogram (CTPA) is the gold standard test to confirm or exclude pulmonary embolism (PE) in suspected cases (after Wells / Geneva score risk stratification).
- Typical diagnostic pathway: Wells score → D-dimer (if low/intermediate risk) → CTPA (if high risk or D-dimer positive).
- Uses rapid IV iodinated contrast injection → should fully opacify pulmonary arteries.
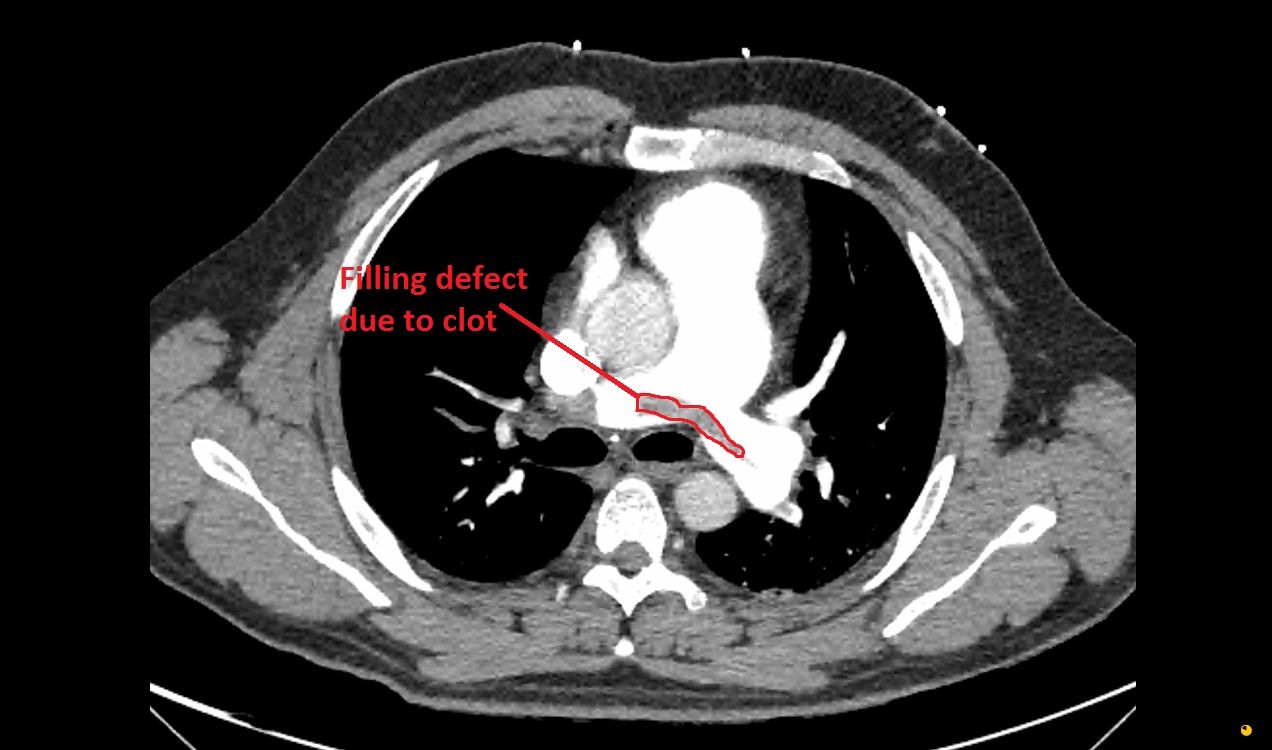
- PE = filling defect: contrast fails to fill the lumen, seen as a darker intraluminal area ± vessel cut-off.
- CTPA may also reveal alternative diagnoses (pneumonia, malignancy, pleural effusion, pneumothorax, aortic dissection).
🖥️ CT Pulmonary Angiography (CTPA)
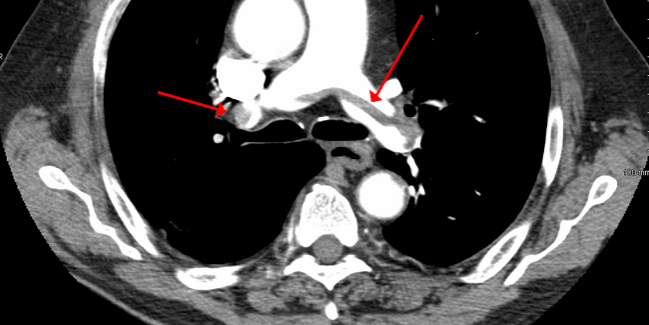
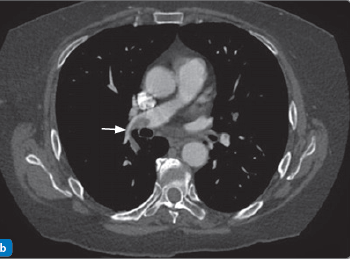
- CT pulmonary angiography (CTPA) is the gold-standard imaging test for confirming pulmonary embolism in most adults. After intravenous iodinated contrast is administered, the pulmonary arterial tree becomes opacified. An acute pulmonary embolus appears as a low-attenuation intraluminal filling defect within the contrast-filled artery. The thrombus may be centrally located, producing the classic “polo mint” or “railway track” sign on cross-sectional imaging, or it may be eccentrically adherent to the vessel wall. In complete occlusion, the affected artery may appear abruptly cut off.
- Large emboli may lodge at the bifurcation of the main pulmonary artery, forming a saddle embolus that straddles both right and left pulmonary arteries. Segmental and subsegmental emboli appear as smaller filling defects within more distal branches. Acute thrombus often forms acute angles with the vessel wall, whereas chronic thrombus tends to appear eccentric with obtuse angles and may be associated with vessel narrowing or webs.
- Beyond directly visualising clot, CTPA provides important prognostic information. Signs of right ventricular (RV) strain include RV dilatation, typically assessed by an increased RV:LV diameter ratio (>1), interventricular septal flattening or bowing towards the left ventricle, reflux of contrast into the inferior vena cava or hepatic veins, and enlargement of the pulmonary artery. These findings reflect acute pressure overload and are associated with higher short-term mortality.
- CTPA may also demonstrate secondary complications such as peripheral wedge-shaped opacities consistent with pulmonary infarction, pleural effusions, or areas of atelectasis. Importantly, it frequently identifies alternative diagnoses when PE is excluded — such as pneumonia, pneumothorax, malignancy, or aortic pathology — which explains why it is often preferred over ventilation–perfusion scanning in routine practice.
- In summary, CTPA confirms PE by demonstrating intravascular filling defects and simultaneously risk-stratifies patients by assessing right heart strain and clot burden. The imaging findings must always be interpreted in the clinical context, particularly when small isolated subsegmental emboli are detected.
🧭 Systematic Approach: How to Read a CTPA
- ✅ Check contrast timing: are pulmonary arteries bright and well-opacified? If not, artefact or false negatives are likely.
- ✅ Follow the arteries: start centrally (main → right & left pulmonary arteries → lobar → segmental → subsegmental branches).
- ✅ Look for filling defects: sharply demarcated darker areas within contrast = thrombus. – Central clot: seen surrounded by contrast (“polo mint sign” on axial, “railway track sign” on sagittal/coronal). – Eccentric wall-adherent clot: partially obstructs lumen.
- ✅ Check lung parenchyma (lung window): infarcts appear wedge-shaped, pleural-based opacities. Don’t miss pneumonia or masses.
- ✅ Assess right heart strain: RV/LV ratio >1, septal flattening, reflux of contrast into IVC/hepatic veins → poor prognosis.
- ✅ Review mediastinum & pleura: aortic dissection, lymphadenopathy, effusions.
- ✅ Final sweep: scroll from lung apices to bases to avoid missed peripheral clots.
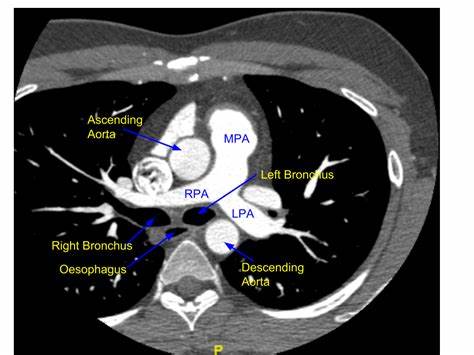
🫁 Pulmonary Artery Anatomy
- Main pulmonary artery bifurcates into: – Right pulmonary artery (RPA): horizontal, to right lung. – Left pulmonary artery (LPA): posterior, to left lung.
- Normal CTPA = uniform contrast filling throughout arterial tree.
⚠️ Contraindications
- 🤰 Pregnancy: radiation + contrast (consider V/Q if CXR normal).
- 💧 Renal impairment: risk of contrast nephropathy → check eGFR.
- ⚠️ Contrast allergy: avoid in severe iodine allergy; options = V/Q scan or MR angiography. Premedicate in mild allergy.
🩻 CTPA Images
📌 Practical Pitfalls
- ⏱️ Poor opacification: wrong contrast bolus timing → non-diagnostic study.
- 💨 Motion artefact: poor breath-holding may mimic PE (“pseudo-defect”).
- 📍 Subsegmental PEs: small, peripheral; clinical significance debated → always correlate with symptoms & discuss with respiratory/radiology team.
- 🧩 Non-thrombotic mimics: tumour emboli, fat emboli, artefacts → need correlation.
💡 Teaching Pearls
1️⃣ Always confirm contrast quality before interpreting.
2️⃣ Central → lobar → segmental → subsegmental search pattern.
3️⃣ Look for RV strain: prognostic marker.
4️⃣ Never forget to review lung windows and mediastinum → pneumonia, cancer, or dissection may explain the presentation.
5️⃣ If CTPA is negative but suspicion remains high → consider repeat CTPA, V/Q, or leg Doppler (for DVT).
🎥 Online Learning
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
