Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome)
Related Subjects: |Adrenal Physiology |Addisons Disease |Phaeochromocytoma |Adrenal Adenomas |Adrenal Cancer |Cushing's Syndrome |Cushing's Disease |Congenital Adrenal hyperplasia |Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome) |ACTH |McCune Albright syndrome
Aldosterone induces sodium and water retention, but this is followed within a few days by a spontaneous diuresis called aldosterone escape. This process returns excretion to the level of intake and partially lowers the extracellular fluid volume toward normal, thus avoiding any clinically significant edema.
📖 About
- Excess production of aldosterone may cause up to 5% of cases of hypertension (HTN).
🧬 Aetiology
- High aldosterone → suppressed renin → sodium retention, potassium (K⁺) and hydrogen (H⁺) loss.
- Main clues: hypertension, hypokalaemia, metabolic alkalosis.
⚡ Causes of Primary Hyperaldosteronism
- Conn’s Adenoma (~75%)
- Benign adrenal adenoma (<25 mm), yellow on imaging (cholesterol-rich).
- Age 30–60, more common in women.
- 🔧 Treatment: laparoscopic adrenalectomy (HTN cured ~70%). Spironolactone pre-op may be used.
- Bilateral Adrenal Hyperplasia (~25%)
- Usually in >50 years, bilateral (macro- or micronodular).
- 🔧 Treatment: medical management with spironolactone or eplerenone. Surgery not usually indicated.
- Adrenal Carcinoma (rare)
- More common in elderly; tumours >4 cm, invasive.
- May co-secrete cortisol, androgens, or oestrogens.
- 🔧 Treatment: surgical resection ± adjuvant mitotane. Prognosis poor.
- Glucocorticoid-Remediable Hyperaldosteronism (rare, genetic)
- Autosomal dominant; early-onset HTN in childhood.
- Family history; bilateral zona glomerulosa hyperplasia.
- ↑ 18-hydroxycortisol & 18-oxocortisol.
- 🔧 Treatment: low-dose glucocorticoids (e.g., dexamethasone) + MR antagonists/amiloride.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Hypertension (often resistant).
- Headaches, general weakness.
- Muscle weakness, cramps, myopathy (from hypokalaemia).
🧾 Indications for Screening
- HTN with hypokalaemia (not diuretic-induced).
- Resistant HTN (uncontrolled on ≥3 agents).
- HTN + adrenal incidentaloma.
- Severe HTN (>160/100 mmHg).
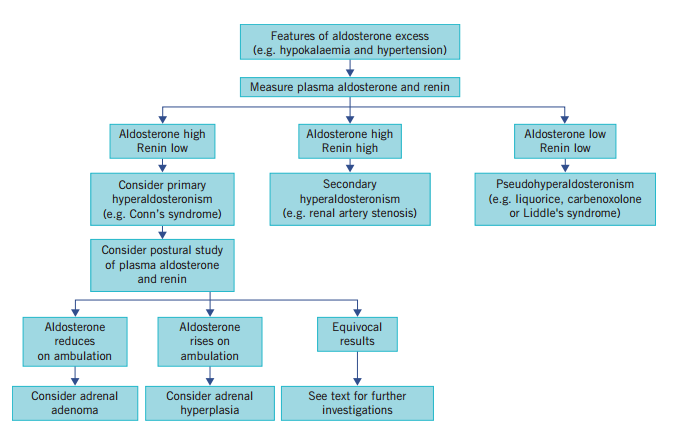
🔍 Investigations (off diuretics, ACEi, ARBs)
ARR (aldosterone:renin ratio) >30 with aldosterone >300 pmol/L = highly suggestive (99% sensitive, 79% specific).
- Electrolytes: mild hypernatremia, hypokalaemia, hypomagnesemia; metabolic alkalosis (but >50% normokalaemic).
- Plasma renin & aldosterone: high aldosterone, suppressed renin. ARR >20–30 diagnostic.
- Saline suppression test: 2L saline over 4h. Normal → aldosterone <200 pmol/L; failure to suppress = primary hyperaldo.
- Imaging: adrenal CT/MRI to localise adenomas or hyperplasia.
- Adrenal venous sampling: differentiates unilateral vs bilateral disease.
- 131-Iodocholesterol scan: may help localise adenomas.
- Echocardiogram: LVH from longstanding HTN.
- Genetic testing: for glucocorticoid-remediable hyperaldosteronism.
🧾 Differential Diagnosis
- Glucocorticoid-remediable hyperaldosteronism.
- Apparent mineralocorticoid excess (licorice ingestion).
- Liddle’s syndrome (low aldosterone, high ENaC activity).
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (enzyme defects).
- Gordon’s syndrome (HTN + hyperkalaemia).
💊 Management
- Surgical
- Conn’s adenoma → laparoscopic adrenalectomy (70% cure/improvement).
- Adrenal carcinoma → surgical resection ± mitotane (poor prognosis).
- Medical
- Bilateral hyperplasia or non-surgical → MR antagonists:
- Spironolactone 25–100 mg/day.
- Eplerenone 50–100 mg/day (more selective).
- Amiloride also an option.
- Glucocorticoid-remediable → low-dose dexamethasone ± MR antagonists.
- Bilateral hyperplasia or non-surgical → MR antagonists:
📚 References
Cases — Primary Hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s Syndrome)
- Case 1 — Hypertension with hypokalaemia 💊: A 42-year-old woman presents with resistant hypertension despite 3 antihypertensives. Bloods: K⁺ 2.7 mmol/L, metabolic alkalosis. Plasma aldosterone:renin ratio is raised. CT adrenal: left adrenal adenoma. Diagnosis: Conn’s syndrome due to adrenal adenoma. Managed with laparoscopic adrenalectomy.
- Case 2 — Bilateral adrenal hyperplasia 🧬: A 55-year-old man with long-standing hypertension develops muscle weakness and polyuria. Bloods: persistent hypokalaemia, suppressed renin, raised aldosterone. Adrenal vein sampling: bilateral secretion. Diagnosis: primary hyperaldosteronism due to bilateral adrenal hyperplasia. Managed medically with mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (spironolactone, eplerenone).
- Case 3 — Incidentaloma ⚠️: A 48-year-old woman investigated for an incidental adrenal mass found on CT for renal colic. She has mild hypertension but normal potassium. Screening shows elevated aldosterone:renin ratio. Diagnosis: subclinical primary hyperaldosteronism. Managed with further endocrine evaluation and treatment depending on lateralisation studies (surgery if unilateral, medication if bilateral).
Teaching Point 🩺: Primary hyperaldosteronism = autonomous aldosterone secretion, causing hypertension, hypokalaemia, and metabolic alkalosis. Causes: adrenal adenoma (Conn’s), bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, rarely carcinoma. Investigations: aldosterone:renin ratio (screening), confirmatory suppression tests, CT/MRI, adrenal vein sampling. Management: unilateral = surgery, bilateral = medical (spironolactone/eplerenone).
Categories
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology