@About this App Makindo
@Contributers
@Developer and Author
@Privacy and Data Policy
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) Testing
AIDS (HIV) Neurological Disease
AIDS (HIV) Respiratory disease
AIDS Dementia Complex (HIV)
AIDS HAART Antiretroviral Drugs
AIDS HIV Infection
AIDS(HIV) Gastrointestinal Disease
APGAR Scoring (Children)
APTT and Coagulation
Abacavir
Abatacept
Abbreviated Mental Test Score (AMTS)
Abciximab
Abdominal Anatomy and Physiology
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
Abdominal Distension
Abdominal Mass (Child health)
Abdominal Masses: Clinical Approach and Considerations
Abdominal X Ray Collections
Abdominal X-Ray (AXR)*
Abdominal paracentesis for ascites
Abducent Nerve (Cranial Nerve VI)
Abetalipoproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig Syndrome)
Abnormal Cervical Smear Results
Abnormal Involuntary Movements
Abnormal eating exercising behaviour (Children)
Abnormal urinalysis
Abscess - General
Absence Seizure
Acamprosate
Acanthocytes
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acarbose
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
Accessory Nerve (Cranial Nerve XI)
Acetazolamide
Acetylcholine Receptor Antibodies
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Achalasia
Achenbach’s syndrome
Achilles Tendon rupture
Achondroplasia
Aciclovir
Acid Base Abnormality
Acid maltase deficiency (Pompe disease)
Acne Rosacea
Acne Vulgaris
Acoustic Neuroma
Acquired Long QT syndrome (LQTS)
Acrodermatitis enteropathica (Children)
Acromegaly and Giantism
Acromio-clavicular joint
Actinic Keratosis
Actinomyces israeli
Action Potential Neuron Versus Cardiac Ventricular Myocyte
Activated Charcoal
Active Proctitis
Actrapid (Insulin)
Acute (Ascending) Cholangitis
Acute Abdomen - Perforation of a Viscus
Acute Abdominal Pain - Adults
Acute Abdominal Pain - Children
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis
Acute Airway Obstruction
Acute Anaphylactoid Reactions
Acute Anaphylaxis
Acute Appendicitis
Acute Appendicitis in Children
Acute Bacterial Meningitis (Adults)
Acute Bacterial Meningitis in Children
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute Blepharitis
Acute Bronchitis
Acute Change in Vision or Vision Loss
Acute Chest Syndrome (Sickle Cell)
Acute Colonic Pseudo-obstruction
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) NSTEMI USA
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) STEMI
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): Complications
Acute Coronary Syndrome (Cardiac Troponins)
Acute Coronary Syndrome Arrhythmias
Acute Coronary Syndrome Grace score
Acute Coronary Syndrome TIMI Score
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Cardiac Thrombolysis
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Myocardial infarction
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Sgarbossa Criteria
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Unstable Angina
Acute Coronary: Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Acute Disc Prolapse
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
Acute Dystonic Reaction
Acute Encephalitis
Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Acute Epiglottitis
Acute Exacerbation of COPD
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Acute Glaucoma
Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children
Acute Heart Failure and Pulmonary Oedema
Acute Hydrocephalus
Acute Hypotension
Acute Inflammation
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)
Acute Interstitial nephritis
Acute Joint Pain and Swelling (Children)
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Limb Ischaemia
Acute Liver Disease
Acute Liver Failure
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL)
Acute Mastoiditis
Acute Monoarthritis
Acute Myeloblastic Leukaemia (AML)
Acute Myocarditis
Acute Neck Injury (no fracture)
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute Pericarditis
Acute Phase reactants
Acute Porphyrias
Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia (APML)
Acute Psychosis
Acute Pyelonephritis and Urosepsis (UTI)
Acute Radiation Syndromes
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute Retroviral Syndrome (HIV)
Acute Rhabdomyolysis
Acute Rotator Cuff Tear
Acute Severe Asthma (Status Asthmaticus)
Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS)
Acute Stroke Care Guidance UK Ireland 2023
Acute Tracheitis
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute and Chronic Diarrhoea
Acute and Chronic Gout
Acute on Chronic Liver Disease Decompensation
Acute rash (Child Health)
Acutely Ill Patient
Acutely Ill Patient with Parkinson's disease
Adalimumab
Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-Revised (ACER)
Addison Disease (Adrenal Insufficiency)
Adefovir
Adenocarcinoma of the Ampulla of vater
Adenosine
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
Administer IV Injection
Adrenal Adenomas
Adrenal Cancer
Adrenal Masses Incidentalomas
Adrenal Physiology
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Adrenocortical crises (Babies)
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenomyeloneuropathy
Adult Onset Stills Disease
Adult Polycystic kidney disease
Adverse Drug Effects
African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping sickness)
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD)
Aicardi syndrome
Air Embolism
Alberta Stroke program Early CT score (ASPECT) scoring system
Albumin
Albumin-Protein Creatinine Ratio (PCR)
Alcohol Metabolism
Alcohol Withdrawal (Delirium Tremens)
Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic Ketoacidosis
Aldosterone Physiology
Alendronate (Alendronic acid)
Alfacalcidol
Algorithms
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Alkalinisation of urine
Alkaptonuria
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic disorders
Allergies
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Allopurinol
Alogliptin (Vipidia)
Alopecia
Alopecia Areata
Alpha Thalassaemia
Alpha subunit (ASU) of TSH
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency
Alport's Syndrome
Alteplase
Altitude sickness / Acute Mountain sickness
Aluminium and Magnesium Antacids
Alveolar Gas Equation
Alzheimer disease (Dementia)
Amantadine
Amaurosis fugax
Amblyopia
Ameloblastoma
Amenorrhoea
American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease)
Amiloride
Amino acids
Aminoglycosides
Aminophylline
Aminosalicylates
Amiodarone
Amiodarone and Thyroid disease
Amitriptyline
Amlodipine
Ammonia Encephalopathy
Amnestic syndromes and Memory Disorders
Amoebiasis Amoebic (Entamoeba histolytica)
Amoxicillin
Amphetamine toxicity
Amphotericin B
Ampicillin
Amputations
Anaemia (Child Health)
Anaemia (Pregnancy)
Anaemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Anaemia of Chronic Disease
Anaemia: Assessment
Anagrelide 💊
Anakinra
Anal Cancer
Anal Fissure
Analgesic Nephropathy
Anatomy and Physiology of the Bone Marrow
Anatomy of Arteries
Anatomy of Cells and Physiology
Anatomy of Dentistry
Anatomy of Large Bowel
Anatomy of Male Genitalia
Anatomy of Neurons
Anatomy of Small Bowel
Anatomy of Spinal Column
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
Anatomy of the Biliary system
Anatomy of the Bladder
Anatomy of the Breast
Anatomy of the Cerebrum
Anatomy of the Cervical Spine Vertebrae C1 (Atlas) and C2 (Axis)
Anatomy of the Diaphragm
Anatomy of the Ear
Anatomy of the Eye
Anatomy of the Glomerulus
Anatomy of the Hand
Anatomy of the Inguinal and Femoral canal
Anatomy of the Larynx
Anatomy of the Liver
Anatomy of the Muscles
Anatomy of the Nose
Anatomy of the Oesophagus
Anatomy of the Ovary
Anatomy of the Pharynx
Anatomy of the Rectum
Anatomy of the Skin
Anatomy of the Spleen
Anatomy of the Stomach
Anatomy of the Thorax
Anatomy of the Uterus and Fallopian Tubes
Andexanet alfa
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Aneurysms, ischaemic limb and occlusions
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
Angiodysplasia
Angiomyolipoma
Angioneurotic Oedema
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Angiotensin Converting enzyme (ACE)
Angular Stomatitis - Cheilitis
Anion Gap
Ankylosing spondylitis
Anomalous Coronary Arteries
Anorexia Nervosa
Anosmia
Antacid medication
Anterior / Medial Medullary Infarct (Dejerine Syndrome)
Anterior Cruciate ligament injury
Anterior Horn Cell diseases
Anterior Spinal Cord syndrome
Anterior circulation Brain
Anthrax (Bacillus anthracis)
Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)
Anti-D immunoglobulin
Anti-Hu antibodies
Anti-NMDA (NMDAR) receptor encephalitis
Anti-OKT3 antibodies
Anti-RNP Antibody
Anti-Yo antibodies
Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Antiarrhythmic agents
Antibiotic Guidelines
Antibiotics Mechanisms
Antibiotics for Abdominal Infections
Anticholinergic Burden
Anticholinergic syndrome
Anticipation
Anticoagulation and Antithrombotic
Antidiuretic hormone (Vasopressin)
Antigen presenting cells
Antimicrobial Choices
Antimicrobial agents
Antimuscarinic drugs
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Antithrombin III deficiency (AT3)
Anuria and Oliguria
Anxiety Phobias and OCD
Anxiety disorder: generalised (GAD)
Aortic Dissection
Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic Sclerosis
Aortic Stenosis
Aortoenteric fistula
Apathetic thyrotoxicosis
Apixaban
Aplastic anaemia
Apomorphine
Apoptosis
Appendix Cancer Tumours
Approach to the Child with Respiratory Distress
Apraxia
Arnold Chiari malformation
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Artemisinins
Arterial blood gas sampling
Arterial thrombosis
Arteriovenous Malformations
Artery of Percheron stroke
Artery-to-artery embolic stroke
Artesunate
Arthrocentesis and Synovial fluid analysis
Asbestos Related Lung disease
Ascites
Aspergilloma
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspirin
Aspirin/Salicylate Toxicity
Assesment of Causes of Pain on inspiration
Assesment of the causes of Chronic Abdominal Pain
Assessing Abdominal Pain
Assessing Coma/Consciousness
Assessing Hearing Loss
Assessing Significance
Assessing a Patient who is Shocked
Assessing and Painful Red eye
Assessment of Causes of Nausea
Assessment of causes of Vaginal Discharge
Asteatotic eczema
Asthma
Asthma COPD overlap syndrome
Astigmatism
Astrocytomas
Ataxia Telangiectasia
Atazanavir
Atenolol
Atherosclerosis
Atorvastatin
Atracurium
Atrial Ectopic beats
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation and Rhythm Control
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Atrial flutter
Atrial myxoma
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia AVNRT
Atrophic vaginitis
Atropine Sulfate
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Auditory hallucinations
Autism spectrum disorder
Autism spectrum disorder
Autoimmune Haemolytic anaemia (AIHA)
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD)
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic neuropathy
Autosomal Dominant
Autosomal Recessive
Avascular Necrosis of Femoral head
Axillary Nerve
Azathioprine
Azithromycin
B lymphocytes
BRASH syndrome
BRCA genes (Familial Breast Cancer)
Bacillary Dysentery
Bacillus cereus poisoning
Back pain
Backpain / Backache
Baclofen
Bacteria and their Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacteroides fragilis
Baker's (Popliteal) Cyst
Balanitis (Adults)
Balanitis (Children)
Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN)
Balsalazide (Aminosalicylate)
Barrett's oesophagus
Barthel Index
Bartonella
Bartonella henselae (Cat Scratch Disease)
Bartters syndrome
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basic Anatomy: An overview
Basic Chemistry for Medicine
Basic Concepts of Pregnancy
Basic Neuroscience
Basic Physics for Medicine
Basic Statistics
Basilar artery thrombosis
Bayes' Theorem
Becker Muscular dystrophy
Beclometasone (Beclomethasone)
Beer Potomania
Behaviour/personality change
Behavioural and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia
Behavioural difficulties in Adults
Behavioural difficulties in childhood
Behcet's Syndrome
Bejel ( Treponema pallidum subspecies endemicum)
Belantamab mafodotin (Blenrep)
Bell's Palsy (Facial nerve palsy)
Bendroflumethiazide (Bendrofluazide) 💊
Benign Eyelid Conditions
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis
Benzodiazepine Toxicity
Benzodiazepines
Benzylpenicillin Sodium (Penicillin G)
Berg Balance Scale
Beriplex
Berylliosis
Beta Agonists
Beta Antagonists/Blockers
Beta Blocker toxicity
Beta Thalassaemia
Beta-2 Microglobulin
Beta-lactamases
Betahistine (Serc)
Bezafibrate
Bezafibrate
Biceps rupture
Bile salt malabsorption (BAM)
Biliary atresia
Bilirubin
Biochemical Lab values
Biochemistry and Physiology of Globins
Biological Agents
Bioterrorism
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome
Bisacodyl
Bisoprolol
Bisphosphonates
Bites and stings
Blackouts and faints (TLOC)
Bladder Cancer
Bladder Stones
Blank Templates
Bleeding Antepartum
Bleeding Postpartum
Bleeding or High INR on Warfarin or other Anticoagulation
Bleomycin
Blindness - global causes
Blood
Blood Pressure
Blood Transfusion Reactions
Blood cultures
Blood film interpretation
Blood transfusion
Blotting Techniques: Gel Electrophoresis
Body Mass Index
Bone Pain
Bone Physiology
Bone disease Lab results
Bone metabolism RANK RANKL OPG pathway
Bone scintigraphy (Bone scan)
Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough)
Borrelia burgdorferi
Borrelia recurrentis
Bortezomib
Botulism
Boxer's fracture
Brachial neuritis (neuralgic amyotrophy)
Brain Abscess
Brain CT Collection
Brain Embryology
Brain Herniation syndromes
Brain MRI
Brain MRI Collection
Brain Metastases
Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
Brain Physiology
Brain Tumours
Brain Tumours in Children
Brainstem Anatomy
Branchial cleft cyst
Breaking Bad News (OSCE)
Breast Cancer
Breast Cysts
Breast Fibroadenoma
Breast Lump
Breast abscess and Mastitis
Breast tenderness/pain
Breathlessness
Bretylium
Broad Complex Tachycardia
Bromocriptine
Bronchial adenoma
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiolitis
Bronchoscopy
Brown-Sequard Spinal Cord syndrome
Brucella
Brucellosis
Brugada syndrome
Bruising
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Budesonide
Buerger disease (Thromboangiitis obliterans )
Bulbar vs Pseudobulbar palsy
Bulimia Nervosa
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bumetanide
Bunions
Buprenorphine
Bupropion
Burkholderia cepacia
Burkitt's lymphoma
Burns Management Guide
Busulphan (Busulfan)
Byssinosis
C Programming
C# programming
C++ Programming
CADASIL
CARASIL
CHADS2 - VASc score
CMV retinitis
CNS fungal Infections
CNS infections
COVID 19
CSF Interpretation
CSF Rhinorrhoea
CT Basics for Stroke
CT Pulmonary angiogram (CTPA)
Cabergoline
Caesarean Section (CS)
Café-au-lait spots
Caisson Disease Decompression sickness (The Bends)
Calcific Uraemic Arteriolopathy (Calciphyalxis)
Calcitonin
Calcitriol (1,25 Dihydroxycholecalciferol)
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium Chloride or Gluconate
Calcium Physiology
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition (Pseudogout)
Calcium Resonium
Calcium channel blockers toxicity
Calot's triangle
Campylobacter jejuni
Canaliculitis
Cancer Frequency and Red flags
Cancer Pathology
Cancer and Stroke
Cancer of Unknown Primary
Candesartan
Candidiasis
Cannabis toxicity
Cannonball Metastases
Capacity in Older Adult
Capecitabine 💊
Caplacizumab
Capnocytophaga canimorsus
Capnography
Capreomycin
Capsular and Pontine Warning Syndromes
Captopri
Carbamazepine
Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae
Carbimazole
Carbohydrates
Carbon Monoxide Toxicity
Carbon Tetrachloride Toxicity
Carbon dioxide embolism
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
Carcinoid Heart Disease
Carcinoid Tumour Syndrome
Carcinoma of the Bile Duct
Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Cardiac Amyloid heart disease
Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology
Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy
Cardiac Catheter ablation
Cardiac Echocardiography: Basics and Uses
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Cardiac Embryology
Cardiac Failure
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac Physiology
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT) Pacemaker
Cardiac Syndrome X (Microvascular Angina)
Cardiac Troponins
Cardiac and Respiratory Rehabilitation
Cardioembolic stroke
Cardiogenic shock
Cardiological Emergencies
Cardiology Examination (OSCE)
Cardiopulmonary bypass
Cardiorespiratory Arrest
Caring for Patients with Dementia
Carmustine
Caroticocavernous Fistula
Carotid Artery Dissection
Carotid Body Tumour
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid Sinus Syncope
Carotid Web
Carotid sinus massage
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carvedilol
Caspases
Castleman's disease
Cataract
Catheter Related UTI
Catheter related Blood stream infection
Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES)
Cauda equina
Caudate Nucleus
Causes of Chronic Hepatitis
Causes of Eosinophila
Causes of Fatigue
Causes of Galactorrhoea
Causes of Gradual Visual Loss over weeks and months
Causes of Hypogonadism
Causes of Limp in Children
Causes of Neck Pain/Stiffness
Causes of Precious Puberty in Children
Causes of Ptosis
Causes of Short Stature in Children
Causes of Stroke
Causes of Tall Stature in Children
Causes of Tremor
Causes of Vertigo
Causes of a high Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate (ESR)
Causes of abnormal Vaginal bleeding
Causes of delayed Onset of Puberty in Children
Causes of high C reactive protein (CRP)
Cavernous angiomas (Cavernomas)
Cavernous sinus
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Cefaclor
Cefalexin
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Ceftriaxone
Cefuroxime
Celecoxib
Cell Adhesion Molecules
Cell Biology
Cell Cycle
Cell Response to Injury
Cellulitis
Central Pontine Myelinolysis (Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome)
Central Retinal Arterial Occlusion (CRAO)
Central Spinal Cord Syndrome
Central Venous line Insertion
Centronuclear Myopathy (CNM)
Cerebellar Examination (OSCE)
Cerebellar Haemorrhage
Cerebellar Ischaemic Stroke
Cerebellar Structure, Function, Physiology and Disease
Cerebral Amyloid angiopathy (CAA)
Cerebral Angiitis
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral Angiography and Perfusion
Cerebral Arterial Perfusion and Clinical Correlates
Cerebral Atrophy vs Hydrocephalus
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Palsy & HIE
Cerebral Radiation Vasculopathy
Cerebral Salt Wasting
Cerebral Vasculitis
Cerebral Veins 🧠
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (CVT)
Cerebral arteritis
Cerebral microbleeds
Cervical Cancer screening
Cervical Spine Immobilisation and Management
Cervical cancer
Cervical screening (HPV)
Cervical spondylosis
Cetirizine
Chalazion
Chancroid
Change in Bowel habit
Change in stool colour
Charcot Foot Syndrome (CFS)
Charcot Marie Tooth (CMT) disease
Chediak Higashi syndrome
Chemical Pathology
Chemosis
Chemotherapeutic Agents
Chest Abdomen anatomy
Chest Pain
Chest X Ray Collection
Chest X Ray Examples selection
Chest X Ray Interpretation
Chest drain Insertion
Chickenpox Varicella Infection
Child Abuse and Safeguarding NHS
Child abuse
Childhood Vaccination in the UK
Childhood Vaccination in the USA
Chlamydia Infections
Chlamydia psittaci
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Chlorambucil
Chloramphenicol
Chlordiazepoxide
Chloroquine
Chlorphenamine(Chlorpheniramine)
Chlorpromazine
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholecystitis
Cholera (Vibrio cholera)
Cholestatic Jaundice
Cholesteatoma
Cholesterol - Lipids
Cholesterol Embolisation Syndrome
Cholinergic crisis-syndrome
Chondrocalcinosis
Chorea - Ballismus
Choreoacanthocytosis
Chorioamnionitis
Choriocarcinoma - Malignant Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Chromatin
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Chronic Glaucoma
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating polyneuropathy
Chronic Interstitial Nephritis
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL)
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic Peritonitis
Chronic Radiation Enteritis
Chronic Rash (Adult/Child)
Chronic Urinary Retention
Chronic Vision Uni-Bilateral loss (Blindness)
Chronic abdominal pain
Chronic and recurrent Meningitis
Chronic joint pain/stiffness 🦴
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
Chronic stable angina
Ciclosporin
Cilia structure and function
Cimetidine
Cinacalcet
Ciprofloxacin
Circulatory Shock (Volume loss)
Cirrhosis
Cisatracurium
Cisplatin
Citalopram
Cladribine
Clarithromycin
Cleft lip or palate
Clindamycin
Clinical Appearance Collections
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) – First Demyelinating Event
Clonidine
Clopidogrel
Clostridioides difficile Infection
Clostridium botulinum Infection
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium tetani - Tetanus
Clotrimazole cream
Clotting pathways
Clozapine
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats CRISPR
Co Careldopa (Sinemet)
Co-Beneldopa (Madopar)
Co-codamol
Co-trimoxazole (Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole)
CoAmoxiclav (Augmentin)
Coagulopathy
Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
Coarctation of the Aorta
Cobalt Cardiomyopathy
Cocaine Toxicity and Chest pain
Cocaine abuse
Cocaine toxicity
Coccidioidomycosis
Codeine
Coding
Coeliac disease
Cogan Syndrome
Colchicine
Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD/AIHA)
Collagen
Colles’ fracture of the Radius
Colloid cyst in the third ventricle
Colloids vs Crystalloids
Colonic (Large bowel) Obstruction
Colonoscopy
Colorectal polyps
Colorectal tumours
Colposcopy
Combined Oral contraceptive pill (COCP)
Common Chromosomal Defects
Common Peroneal Nerve (CPN)
Common Problems in Elderly
Common Psychiatric Emergencies
Common variable immunodeficiency
Commotio cordis
Community Acquired Pneumonia and Differentials
Comparing Groups
Compilers
Complement
Components of a Eukaryotic Gene
Comprehensive Clinical Microbiology Tutorial for Medical Students
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA)
Computer Networking
Computer Security
Concurrent Programming
Confirming Death
Confusion
Congenital Acyanotic Heart Disease
Congenital Adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital Complete Heart Block
Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease (Children)
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus - Clubfoot
Congenital abnormalities
Conjunctivitis
Constipation (Adults)
Constipation (Children)
Constipation in the Elderly
Constrictive Pericarditis
Contact Dermatitis
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
Continuous Positive Airways Pressure (CPAP)
Contraception request/advice
Conus Medullaris syndrome
Cor Pulmonale
Cord Prolapse
Corneal Abrasion
Coronary Artery Anatomy
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery
Corticobasal degeneration (Dementia)
Corticospinal Tract
Corticosteroid-related psychosis 💊
Corticosteroids : Uses and Cautions
Cotard's Syndrome
Cough (Adult)
Cough (Child)
Cowden Syndrome / PTEN Hamartoma Tumour Syndrome
Cowpox (Orthopoxvirus)
Coxiella Burnetii Q fever
Cramps
Craniopharyngioma
Creatinine Clearance
Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Cri du Chat Syndrome
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever
Critical Illness Neuromuscular Weakness (CINMW)
Critical care Crib Sheets
Crohn's disease
Croup
Crying baby
Cryoprecipitate
Cryptococcus neoformans infections (Cryptococcal Infections)
Cryptogenic Organising Pneumonia (COP-BOOP)
Cryptogenic stroke
Cryptography
Cryptosporidiosis
Crystal arthropathy
Cushing disease
Cushing syndrome
Cushing's Syndrome due to Ectopic ACTH
Cutaneous Warts
Cutaneous fungal infections
Cyanide toxicity
Cyanosis
Cyclizine
Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes
Cyclophosphamide
Cycloserine
Cys leukotriene receptor antagonists
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystinosis
Cystinuria
Cystitis and Urethritis (UTI)
Cystoscopy
Cytokine Physiology
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections
D Dimer
D-lactic acidosis or D-lactate encephalopathy
DNA and RNA short notes
DNA replication
DNACPR in the Older Person
Dabigatran
Dalteparin
Dandy Walker syndrome
Dantrolene
Dapagliflozin
Darier’s disease (Keratosis Follicularis)
Darunavir
Data Security and Protection
Data Structures
Data security awareness
Database Management
DeQuervain's thyroiditis
Death Certificates and Cremation UK
Death and dying
Decision Making by Clinicians
Decompressive Hemicraniectomy
Decreased appetite
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep brain stimulation
Dehydration (Child)
Dehydration Adult
Delirium in the Elderly
Delusions
Demeclocycline
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementias
Demyelinating Diseases
Dengue Fever
Denosumab (Prolia)
Dental Caries
Dentatorubral Pallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA)
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatology Emergencies
Dermatology terms
Dermatomes
Dermatomyositis
Dermoid cysts
Desferrioxamine
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Desogestrel (Progestogen Only Pill) 💊
Developmental Delay & Abnormal Development in Children
Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) of the Hip (DDH)
Dexamethasone
DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome)
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and DKA (children)
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy
Diabetes Variable Rate Insulin Infusion
Diabetes and Hypertension
Diabetes and Pregnancy
Diabetes in Children
Diabetes: (Autonomic) Neuropathy (DAN)
Diabetes: Criteria US and UK
Diabetes: Eye Disease
Diabetes: Foot Problems
Diabetes:Complications
Diabetic Amyotrophy
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Adults
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Children
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic neuropathy
Diamond-Blackfan anaemia
Diamorphine
Diaphragmatic disorders
Diarrhoea (Children)
Diazepam
Didanosine (ddI)
Diethylstilbestrol
Dieulafoy Lesion
Different Forms of Medical Trials and Studies
Differential Diagnosis of Malar Rash
Differentials of ABC
Differentials of Painful thigh
Differentiation syndrome
Difficulty Swallowing
Difficulty with breastfeeding 🍼
Diffuse Alveolar Haemorrhage (DAH)
Diffuse Oesophageal spasm
Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) or Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Diffusion Capacity
Digoxin
Digoxin Toxicity
Digoxin-specific antibody
Dihydrocodeine
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Diltiazem
Diphtheria (Corynebacterium diphtheriae)
Diplopia (Double Vision)
Dipyridamole
Discharges against advice
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE)
Disease prevention/screening
Diseases with associated cancers
Dislocation Sternoclaivcular joint
Disopyramide
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Distal Humerus Fracture
Distal Radius Fracture
Distributive Shock (Reduced SVR vasodilated)
Disulfiram (Antabuse)
Diuretics
Diverticular disease
Diving Physiology
Dizziness
Dobutamine
Dog Bites
Domestic Violence and Safeguarding NHS
Domperidone
Donepezil (Aricept)
Donovanosis
Dopamine Hydrochloride
Dopamine agonists
Dornase Alpha
Dosing Gentamicin
Downs syndrome
Doxapram
Doxazosin (Cardura)
Doxepin
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
Doxycycline
Driving Advice
Drug Induced Parkinson disease
Drug Metabolism
Drug Overdose Adults
Drug Reaction Eosinophilia Systemic Symptoms (DRESS syndrome)
Drug Toxicity Assessment and Management
Drug induced Lupus Erythematosus
Drug induced liver disease
Drug overdose children
Drugs
Drugs to Avoid in Acute Renal failure
Drugs to avoid Elderly
Drugs to avoid in Liver failure
Dry and Wet and Gas Gangrene
Dual X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Dulaglutide GLP-1 agonist
Duloxetine
Duodenal Atresia (Children)
Dupuytrens contracture
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
Dysmorphic child
Dysphagia / Swallowing Problems
ECG - Acute Coronary Syndrome
ECG - Artefact
ECG - Asystole and P wave Asystole
ECG - Bundle Branch Blocks
ECG - Calculate the electrical axis
ECG - Causes of a Dominant R wave in V1
ECG - Collection A
ECG - Collection B
ECG - Heart Block
ECG - Hyperkalaemia
ECG - Interpretation
ECG - Left Axis Deviation
ECG - Left Bundle Branch Block LBBB
ECG - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
ECG - Low Voltage Complexes
ECG - NSTEMI
ECG - Normal 12 Lead
ECG - Normal ECG basics
ECG - P wave
ECG - Pathological Q waves
ECG - Potential Errors
ECG - QT interval
ECG - Right Axis Deviation
ECG - Right Bundle Branch Block RBBB
ECG - Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
ECG - ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction STEMI
ECG - ST segment changes
ECG - ST-T T waves changes
ECG - Sinoatrial block
ECG - Sinus Bradycardia
ECG - The QRS complex
ECG - short PR interval
ECG Analysis
ECG/EKG Crib sheets
ECGs for the MLA
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
ENT emergencies
ENT infections
Ear Pain (Otalgia)
Ear and Nasal Discharge
Eating Disorders
Ebola Virus Disease
Ebstein anomaly
Echinocytes
Ecstasy toxicity
Ectopia lentis (subluxation of the lens)
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectropion
Eculizumab
Eczema/Dermatitis
Edoxaban (Lixiana)
Edward syndrome (trisomy 18 syndrome)
Efavirenz (Sustiva) EFV
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes
Ehrlichiosis
Eikenella corrodens
Eisenmenger's syndrome
Elation/elated mood
Elbow Dislocation
Elder Abuse and Safeguarding
Electrical Storm in Ventricular Tachycardia or Ventricular Fibrillation
Electrical injury
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Electron Transport Chain
Embryology of Blood and Immune System
Embryology of Limb Development
Embryology of Nervous system
Embryology of Organ Development
Emergency Contraception (EC)
Emergency Drug Antidotes
Emergency Drugs - Cardiac
Emergency Drugs Endocrine
Emergency Drugs Pain
Emergency Gastrointestinal Drugs
Emergency Haematology Drugs
Emergency Obstetric and Gynaecology Drugs
Emergency Respiratory Drugs
Emergency neuropsychiatric drugs
Emphysema
Empty sella syndrome
Emtricitabine (Emtriva) FTC
Enalapril
Encephalocoele
Encopresis in Children
End of Life Care Prescribing
Endocrine Emergencies
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
Endometriosis
Endophthalmitis
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Endothelins
Enfuvirtide
Enoxaparin Sodium (Clexane-Lovenox)
Enoximone
Entacapone
Enterococci
Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis
Entropion
Enuresis/Bedwetting in Children
Enzyme inducers and inhibitors
Enzymes in Humans
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis
Eosinophilic granulomatosis (Churg Strauss)
Ependymoma
Epididymitis and Orchitis (Children)
Epididymitis and Orchitis in Adults
Epidural Haematoma
Epidural Spinal abscess
Epilepsy
Epilepsy - Diagnosis
Epilepsy - Idiopathic Generalised Epilepsy
Epilepsy in Pregnancy
Episcleritis
Epistaxis
Eplerenone
Eponymous brainstem strokes
Epstein-Barr Virus infection
Equality Diversity and Human Rights
Equality Diversity and Inclusion
Erb Palsy
Erectile dysfunction
Ergocalciferol (Calciferol)
Erlotinib (Tarceva) 💊
Erysipelas
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Erythema Gyratum Repens
Erythema Multiforme
Erythema Nodosum
Erythema ab Igne
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Erythromycin
Escherichia coli (E. coli)
Escitalopram 💊
Esomeprazole
Essential Hypertension
Essential Thrombocythaemia (ET)
Essential Tremor
Etanercept
Ethambutol
Ethanol
Ethanol toxicity
Ethylene glycol toxicity
Etomidate
Etravirine (intelence) ETR
Euglycaemic Ketoacidosis (euDKA) with SGLT2 Inhibitors
Ewing sarcoma
Exenatide (Byetta) GLP1 agonist
Exercise Physiology
Exercise stress test
Exploding head syndrome
Extradural haemorrhage
Extramedullary plasmacytoma
Extrapyramidal symptoms
Extrinsic Allergic alveolitis (Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis)
Eye Collection
Eye Trauma
Eye infections
Eye pain/discomfort
Ezetimibe
Fabry disease
Facial Nerve (VII Cranial nerve)
Facial and Periorbital Swelling
Facial pain
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
Factor V Leiden Deficiency
Faecal Calprotectin
Faecal Incontinence
Fahr syndrome (Idiopathic basal ganglia calcification)
Failure to thrive or Faltering growth
Falls
Familial Adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Familial Hyperlipidaemias
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH)
Familial/Hereditary Amyloidosis
Family Tree (Pedigree)
Family history of possible genetic disorder
Famotidine
Fanconi Anaemia
Fanconi Syndrome
Farmer's lung
Fasciculation
Fast Atrial Fibrillation and Rate Control
Fat Metabolism
Fat embolism
Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI)
Fatty acids
Febrile convulsion
Felodipine (Dihydropyridine)
Female Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
Femoral Hernia
Femoral Vein Cannulation
Femoral nerve
Fentanyl - Fentanil
Ferritin
Ferrous Fumarate - Gluconate - Sulphate
Fertilisation and Formation of Zygote
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Fetal-type Posterior cerebral artery (FTP)
Fever - all ages
Fever in IV Drug User (PUO)
Fever in a traveller
Fever/Pyrexia of unknown origin (FUO PUO)
Fibrinogen
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Fibromyalgia
Fibrotic Lung Disease
Fidaxomicin
Fifth Disease (Erythrovirus B19 infection)
Finasteride (5 alpha-reductase inhibitor) 💊
Fire Safety for NHS Professionals
First Seizure
First degree AV Block
Fissure in Ano
Fistulo in Ano
Fit Notes in General Practice (UK)
Fits/seizures and Epilepsy (Children)
Fitz-Hugh Curtis Syndrome
Fixed Abnormal Beliefs (Delusions)
Flashes and Floaters in the Visual Field
Flecainide Acetate
Flexor sheath infection (flexor tenosynovitis)
Flow Cytometry
Flucloxacillin
Fluconazole
Flucytosine
Fludrocortisone
Fluid balance status and management
Flumazenil (Annexate - Romazicon)
Fluoxetine
Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD)
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Foix-Alajouanine syndrome
Folate (Folic) acid (B9)
Folate deficiency (B9)
Folinic acid (Leucovorin)
Follicular lymphoma
Folliculitis
Fomepizole
Fondaparinux
Food Intolerance in Children
Food borne disease
Foot Drop
Forearm Fractures
Foreign Body in Eye
Foscarnet Sodium
Fosfomycin
Foslevodopa / Foscarbidopa
Fosphenytoin
Foster Kennedy Syndrome
Fourniers gangrene
Fractured Clavicle
Fractured Neck of Femur/Femoral Neck
Fractured Pubic Ramus
Fractured Scapula
Fractured Shaft Femur
Fractured Tibia and Fibula
Fractures in Children
Fractures of Neck and Shaft of Upper humerus
Fragile X syndrome
Frailty an Overview
Fraser guidelines and Gillick Competence
Free Radicals
Fresh Frozen Plasma
Freshwater (River/Lake)/Saltwater (Sea/Ocean) Drowning
Friedreichs Ataxia
Frontotemporal dementia
Full or Complete Blood Count (FBC CBC)
Functional organization of a eukaryotic gene
Fungi and their infections
Furosemide (Frusemide)
Fusidic acid
Fusobacteria - Tropical ulcer
Fusobacterium
G protein-coupled receptors
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists
Gabapentin
Galantamine
Gallstone ileus
Gallstones and biliary colic
Gamete intra-fallopian tube transfer (GIFT)
Gametogenesis
Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
Gamma hydroxy butyrate (GHB) toxicity
Ganciclovir - Valganciclovir
Ganglion Cysts
Gardner's syndrome
Gardnerella vaginalis
Gas Gangrene (Clostridial Myonecrosis)
Gastric (MALT) Lymphoma
Gastric Cancer
Gastric Outlet obstruction (pyloric stenosis) in Adults
Gastrinoma
Gastro Intestinal Stromal Tumours (GIST)
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux (GORD)
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux (Paediatrics GORD)
Gastro-oesophageal reflux in Children
Gastroenteritis in Adults
Gastroenteritis in Children
Gastroenterology Examination
Gastroenterology Examination (OSCE)
Gastrointestinal Emergencies
Gastrointestinal tract Physiology
Gastrostomy (PEG) tube managment
Gaucher's disease
Gene components
General Anaesthetics
General Basic Fracture management
Genetic Diseases
Genetic Linkage
Genetic Mutations
Genital Ulcers
Genital Warts (HPV)
Gentamicin
Geriatric Medicine Emergencies
Geriatric Medicine Syllabus (For Resident Doctors in Training)
Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome (GSS)
Giardiasis
Gilbert's syndrome
Gingival (Gum) hyperplasia or hypertrophy
Gitelman's syndrome
Glasgow Coma scale
Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone)
Glibenclamide
Gliclazide
Glimepiride
Glioblastoma
Glipizide
Glomerulonephritis
Glossitis
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (Cranial Nerve IX)
Glucagon
Glucagonoma
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Glucose Metabolism
Glucose Tolerance Test
Glutamate
Glycated Haemoglobin HbA1c
Glyceryl Trinitrate (GTN)
Glycogen storage diseases
Glycolysis Krebs Electron Transport Chain
Glycopyrronium Bromide
Goitre
Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Golimumab (Simponi)
Gonorrhoea
Goodpasture's syndrome (Anti GBM disease)
Goserelin (Zoladex)
Government Benefits Available to People with Disabilities UK
Gradenigo's syndrome
Grades of Recommendation
Gradual change in or loss of vision
Gram Stain
Granuloma annulare
Granulomas
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis GPA (Wegeners)
Graves Disease (Thyrotoxicosis)
Griseofulvin
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Guillain Barre Syndrome
Gum hypertrophy
Gynaecological Examination (OSCE)
Gynaecological History Taking
Gynaecological emergencies
Gynaecomastia
HAS-BLED score
HIV and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
HIV and Pre-exposure prophylaxis
HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)
HIV disease New Diagnosis
HTLV-1 Associated myelopathy (Tropical Spastic Paraparesis)
Haematemesis
Haematology Emergencies
Haematology Laboratory Values
Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Previously Bone Marrow Transplantation)
Haematospermia
Haematuria
Haemoglobinopathies
Haemoglobins
Haemolytic Anaemia
Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (HUS)
Haemolytic disease of the newborn
Haemophilia
Haemophilia A
Haemophilia B
Haemophilus aegyptius
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Haemopoiesis
Haemoptysis
Haemorrhagic Transformation of Infarction
Haemorrhagic stroke
Haemorrhoids (Piles)
Hairy Cell Leukaemia
Hairy Leukoplakia
Hallervorden-Spatz disease (PKAN)
Haloperidol
Hamman-Rich syndrome
Hand foot and mouth disease
Hand fractures and Injuries
Hantavirus infections
Haptoglobins
Hartmann's procedure
Hartmanns solution (Ringers lactate)
Hartnup disease
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Head Impulse Test
Head Injury and Traumatic Brain Head Injury (TBI)
Head Lice
Head and Neck Cancers
Headache - Acute and Severe
Headache - Basilar Migraine
Headache - Cluster
Headache - Medication Overuse Headache
Headaches
Health Issues In Pregnancy
Health Safety and Manual Handling
Hearing Loss
Hearing aids
Heart Murmurs
Heart and Fetal circulation
Heat Stroke
Helicobacter pylori
Helvetica Spotted fever
Heme Synthesis, Biochemistry, and Physiology
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Heparin - General
Heparin - Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Heparin - Unfractionated Heparin
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatitis
Hepatitis (D) Delta Virus
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis E
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatology Emergencies
Hepatorenal syndromes
Hereditary Angio-Oedema
Hereditary Elliptocytosis
Hereditary Haemochromatosis
Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis
Hereditary Spherocytosis (HS)
Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies
Hereditary non polyposis coli (Lynch syndrome)
Hernias
Hernias (Children)
Herpes Gestationis
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSV)
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes Varicella-Zoster (Shingles) Infection
Herpes Virus 6 and 7
Herpes Viruses
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO) Shingles
Herpes simplex keratitis (HSK)
Herpetic Whitlow
Heterochromia Iridium
Heyde syndrome
Hiatus hernia
Hiccups (Singultus)
Hidradenitis suppurativa (Acne Inversa)
Hierarchy of Evidence-Based Trials
High Altitude Physiology
High Dose Insulin Euglycaemic Therapy (HIET)
High Output Stoma
Hip pain in children
Hirschsprung disease (congenital megacolon)
Hirsuitism XXX
Histones
Histoplasmosis
Hoarseness and voice change
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkins and Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma:
Holt-Oram syndrome
Holter monitor (tape) 24-72 h
Homocystinuria
Hookworm
Horner's syndrome
Horseshoe Kidney
Hospital acquired Pneumonia HAP (NICE 139)
Hospital-acquired infections
How does a CPU work
How to Read and Analyze a Medical Paper
Human Herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A)
Human Leukocyte Antigen and its Role in Disease Associations
Human Metabolism
Human albumin solution (HAS)
Human papilloma virus infection
Human prion diseases
Hunter's syndrome (MPS-2)
Huntingtons Disease/Chorea
Hurler's syndrome (MPS-1)
Hydatid disease (Echinococcus)
Hydatidiform mole
Hydralazine
Hydrocephalus and Stroke
Hydrocortisone
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen and other Bonds
Hydrops fetalis
Hydroxocobalamin
Hydroxocobalamin - Cyanocobalamin (B12)
Hydroxychloroquine 💊
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide)
Hyoscine (Buscopan)
Hyper IgM syndrome
Hyperacute Stroke Care Pathway
Hyperbaric Oxygen therapy
Hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia of Malignancy
Hypercholesterolaemia
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Hyperglycaemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)
Hyperinsulinaemic-euglycemic therapy (HIET)
Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemic and Hypokalaemic Periodic Paralysis
Hyperlipidaemia
Hypermagnesaemia
Hypernatraemia
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperphosphataemia (High phosphate)
Hyperprolactinaemia
Hypertension in Children
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Hyperthermia and Hypothermia
Hypertriglyceridaemia (HTG)
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM - HOCM)
Hyperuricaemia
Hyperventilation Syndrome
Hyperviscosity syndrome
Hyphaema (US Hyphema)
Hypocalcaemia
Hypoglossal Nerve (Cranial Nerve XII)
Hypoglycaemia
Hypogonadism (Female)
Hypokalaemia
Hypokalaemic Periodic Paralysis
Hypomagnesaemia
Hyponatraemia
Hypophosphataemia (Low phosphate)
Hypopituitarism (Pituitary Failure)
Hypospadias
Hypothermia
Hypothyroidism
Hypoxia - Reacting to Low Oxygen Saturations
Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy
ICH Classification and Severity Scores
IL-12 receptor deficiency
IV Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Ibandronic acid (Bisphosphonate)
Ibuprofen
Icatibant
Idarucizumab (Praxbind) 💊
Idiopathic Arthritis in Adults
Idiopathic Fascicular Left Ventricular Tachycardia
Idiopathic Intracranial hypertension
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia (IVT)
IgA Nephropathy (Berger's disease)
Ileostomy vs Colostomy
Iliopsoas Abscess
Images - Spot diagnoses
Imaging for the MLA#1
Imaging for the MLA#2
Imatinib mesylate
Imipenem (Primaxin) with Cilastin
Immediate management and assessment of the newborn
Immobility
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Immune response
Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
Immunoglobulins and their role in Immunity
Impetigo
Important Metabolic Pathways
Impulse control disorders
In Situ Thrombosis
Incidental Findings (Incidentalomas)
Inclusion Body Myositis
Incubation periods
Indapamide 💊
Index of Makindo
Indications for Irradiated Blood Products
Indinavir (IND)
Infant feeding issues
Infantile Spasms (West Syndrome)
Infection Associated Cancers
Infection Prevention Control for NHS Staff
Infection Prevention Control for NHS Staff
Infection screening in Septic patient
Infectious Colitis
Infectious Diarrhoea
Infectious Mononucleosis (EBV Most Often)
Infective Endocarditis
Infective Keratitis
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
Infertility & Subfertility
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease - Acute Severe Colitis
Infliximab
Influenza
Information Governance for NHS Staff
Inguinal Hernia
Injury Severity Score (ISS)
Insomnia - unable to sleep issues
Insulin Degludec (Tresiba)
Insulin Detemir (Levemir)
Insulin Glargine (Lantus, Abasaglar, Semglee, Toujeo)
Insulin Management in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Pumps
Insulinoma
Interferon Beta
Intermittent Claudication
Internal Capsule
Internal Jugular vein Cannulation
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
Interpreting Haematinics
Interstitial Keratitis
Interstitial Lung Disease
Intestinal Ischaemia
Intestinal obstruction (Children)
Intestinal obstruction and Ileus
Intra Aortic Balloon Pump
Intraabdominal abscess
Intrauterine death
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL)
Intravenous Iron Replacement
Intraventricular haemorrhage (neonates)
Introduction to Anaesthetics
Introduction to Cardiology
Introduction to ECGs
Introduction to Hormones
Introduction to Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Introduction to Psychiatry
Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation
Intussusception in Adults
Intussusception in Children
Iodine Physiology
Iodine deficiency Goitre
Ipratropium Bromide (Atrovent)
Irbesartan
Iritis (Anterior Uveitis)
Iron Salts
Iron Studies
Iron deficiency Anaemia
Iron toxicity
Irritable bowel syndrome
Ischaemic Colitis
Ischaemic Stroke
Ischaemic Strokes in the Pons
Ischaemic heart disease
Isoniazid
Isoprenaline
Isosorbide Dinitrate
Isosorbide mononitrate
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
Ispaghula Husk (Fybogel)
Ivabradine
Jansen Disease
Janus kinase 2
Jaundice
Java Programming
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
Job Syndrome (Hyper IgE syndrome)
Jugular Venous pressure
Junctional Tachycardia
Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (Stills Disease)
Juvenile Myoclonic epilepsy (JME)
Kallmanns syndrome
Kaposi sarcoma (KS)
Karnofsky performance status scale
Kawasaki disease
Keloids
Kennedy Syndrome (Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA))
Keratoacanthoma
Keratoconus
Kernicterus
Ketamine
Ketoconazole 💊
Ketones
Klebsiella pneumonia
Klinefelter Syndrome
Klumpke palsy
Koebner phenomenon
Kugelberg-Welander Syndrome (Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type III)
Kuru
Kwashiorkor
L-Thyroxine (T4)
Labetalol (Trandate)
Labour and Complications
Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuronitis
Lac operon
Lacerations
Lacerations
Lactate
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Lactic acidosis
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Lactose Intolerance
Lactulose
Lacunar Stroke Syndromes
Lady Windermere syndrome
Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LEMS)
Lamivudine (3TC)
Lamotrigine
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)
Language and Dysphasia
Lansoprazole
Lanthanum
Large for Gestational Age (LGA)
Lassa haemorrhagic fever (LHF)
Lateral Medullary Syndrome
Law and Mental Health (UK)
Law and Mental Health (USA)
Laxatives
Le Fort Fractures
Lead toxicity
Learning disability
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
Lecanemab (Leqembi)
Leflunomide (Arava)
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT) Tachycardia
Legal definition of Blindness
Legionella Pneumophila
Leishmaniasis (Cutanenous and Visceral)
Lemierre's syndrome
Lenalidomide (Revlimid)
Length Dependent Polyneuropathy
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Lenticulostriate branch occlusion
Leprosy (Hansen’s disease)
Leptin
Leptomeningeal Metastases
Leptospira interrogans
Leptospirosis (Weil's Disease) (Notifiable)
Leriche syndrome (aortoiliac occlusive disease)
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Leukaemia
Leukoariosis
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Leukotrienes
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
Levobupivacaine
Levodopa
Levomepromazine
Levosimendan 💊
Lhermitte Duclos Disease
Li Fraumeni syndrome
Lichen Planus
Liddle's syndrome
Lidocaine(Lignocaine)
Lightning strike
Limb Weakness
Limb girdle dystrophy
Limbic Encephalitis
Linagliptin (Trajenta)
Linezolid
Liothyronine Sodium L-Triiodothyronine (T3)
Lipid emulsion therapy - Intralipid
Lipoatrophy
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency
Liraglutide (Victoza)
Lisinopril
Listerial Meningitis
Listeriosis
Lithium
Lithium toxicity
Livedo Reticularis
Liver Biopsy
Liver Examination (OSCE)
Liver Physiology
Liver Transplantation
Liver abscess
Liver disease in Pregnancy
Local Anaesthetics for Suturing or other Procedures
Localisation of cortical function
Locked in Syndrome
Lofepramine
Loffler's syndrome (Pulmonary Eosinophilia)
Loin Pain
Long COVID
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Congenital
Long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
Long term Oxygen therapy (LTOT)
Loop diuretics
Loperamide
Lopinavir
Loratadine
Lorazepam
Losartan
Loss of Libido
Loss of red reflex
Louse-Borne vs Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever
Louse-borne relapsing fever
Low CSF pressure Headache
Low mood/affective/depression problems
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Lower Limb Fractures
Lower Limb Fractures and Injuries
Lower Limb Neurology (OSCE)
Lower Limb Soft Tissue Injuries
Lower respiratory tract infection (Child)
Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome (LGL) AVRT
Lugol iodine
Lumbar and Sacrum anatomy and function
Lumbar puncture
Lumbrosacral Radiculopathy
Lump in Groin
Lung Abscess
Lung Cancer
Lung Compliance
Lung Empyema
Lung Transplant
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus Vulgaris
Lyme disease
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytic Hypophysitis
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Lyonization (X-Inactivation)
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) Toxicity
Lysosomal storage diseases
MELAS
MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Macrocytic anaemia
Macroglossia
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)
Magnesium Physiology
Magnesium Sulphate - Sulfate
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance imaging
Major Disaster Plan
Major Histocompatibility complex
Malabsorption - small intestine
Malaria
Malaria Falciparum (Includes Cerebral Malaria)
Malaria in Children
Male Urethral Catheterisation
Malignant Ascites
Malignant Hyperparathyroidism due to PTHrP
Malignant Hyperpyrexia (Malignant Hyperthermia)
Malignant Hypertension
Malignant MCA syndrome
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant pleural mesothelioma
Mallet Finger
Mallory-Weiss Tear
Malnutrition Adults and the Elderly
Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool
Malnutrition universal screening tool (MUST)
Management of Bites
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Management of Unprotected Sex and Emergency Contraception (EC)
Managing Chronic Heart Failure
Mania
Mannitol
Mantle cell lymphoma
Marantic Endocarditis
Marasmus
Maraviroc (Celsentri)
Marburg virus disease
Marchiafava Bignami syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marginal Keratitis
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Maskne
Massive Haemorrhage and Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
Maths and Physics Crib Sheets
Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
McArdles disease (type V)
McCune Albright syndrome
Measles (notifiable)
Mebeverine
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Ischaemic Stroke
Meckel diverticulum
Meconium
Median Nerve
Medical Licensing Assessment Content Map (GMC)
Medical Tweetorial Links
Medical conditions affecting the Teeth
Medullary Sponge kidney
Medulloblastoma
Mefenamic acid
Mefloquine (Larium)
Megaloblastic anaemia
Melaena
Melatonin
Melioidosis (Burkholderia pseudomallei)
Memantine Hydrochloride
Membranous Glomerulonephritis
Memory Loss
Menetrier disease
Menieres disease
Meningioma
Menkes Disease
Menopause
Menopause and Menopausal Problems
Menstrual cycle
Menstrual problems
Mental Capacity Act 2005
Mental Health Act 1983
Mental capacity concerns
Mental health problems in pregnancy or postpartum 🤰
Mercaptopurine 💊
Meropenem
Mesalazine (Aminosalicylate)
Mesangiocapillary Glomerulonephritis
Mesenteric Ischaemia
Mesenteric adenitis
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
Metabolic Syndrome X
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Metachromic leukodystrophy
Metastatic Adenocarcinoma
Metastatic Calcification
Metastatic bone disease
Metastatic disease
Metformin
Methaemoglobinaemia
Methanol Toxicity
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Methodone
Methods to reduce toxin absorption
Methotrexate
Methylcellulose
Methylprednisolone
Methylthioninium chloride (Methylene blue)
Metoclopramide
Metolazone 💊
Metoprolol
Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Metyrapone (Metopirone) 💊
Miconazole
Microangiopathic Haemolytic anaemia
Microbiology and Assessment of Streptococcus
Microcytic anaemia
Microscopic Polyangiitis
Microscopic colitis
Microstomia
Microtubules
Midazolam
Middle East Resp Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus
Midodrine
Mifepristone
Migraine
Miller-Fisher syndrome
Milrinone
Milwaukee shoulder syndrome
Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE)
Minimal Change Disease Glomerulonephritis
Minocycline
Minoxidil
Mirabegron
Mirizzi syndrome
Mirtazapine
Mirvetuximab soravtansine (Elahere)
Miscarriage
Misoprostol
Misplaced Nasogastric tube insertion
Mitochondria
Mitochondrial diseases
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitral Regurgitation (Incompetence)
Mitral Stenosis
Mitral Stenosis vs Regurgitation
Mitral Valve prolapse
Mittelschmerz
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)
Mobility aids
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale (MOHS)
Modified Rankin Score
Modified Valsalva
Molecular Structures for Medicine
Molluscum contagiosum
MonkeyPox (MPOX)
Monoclonal gammopathy Undetermined significance
Monocytes
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) syndrome
Montelukast
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA)
Moraxella catarrhalis
Morphine Sulphate
Morphological Blood film abnormalities and variants
Mosquito borne diseases
Motor End Plate
Motor Neuron Disease (MND-ALS)
Moyamoya disease
Muckle Wells syndrome
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Conduction block
Multiple Antithrombotics Anticoagulants
Multiple Crib sheets
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1)
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type II (MEN2)
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome
Multiple Pregnancy
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
Mumps (Notifiable)
Muscle Pain Myalgia
Muscular Dystrophies
Musculocutaneous nerve
Musculoskeletal deformities
Musculoskeletal deformities
Myasthenia Gravis
Mycophenolate mofetil
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasmas
Mycosis Fungoides (Sezary Syndrome)
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG) & MOG Antibody-Associated Disease (MOGAD)
Myelodysplastic syndrome (Myelodysplasia)
Myelofibrosis
Myelopathy (Disorder of Spinal cord)
Myeloproliferative disorders
Myeloproliferative vs Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Myobacterium avium Complex Infection
Myocardial perfusion
Myoclonus
Myoglobin
Myotomes
Myotonic dystrophy - Dystrophia myotonica
Myxoedema coma
N-Acetylcysteine (Parvolex)
NICE and other guidelines links
NSAID toxicity
Nail disorders
Naloxone (Narcan) Opiate antagonist
Naproxen
Narcolepsy
Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Nasal Discharge
Nasal Obstruction
Nasal polyps
Natalizumab (Tysabri)
National Early Warning Score NEWS 2 Score
Natural Language processing
Neck swellings and lumps
Necrotising Enterocolitis
Necrotising fasciitis
Needlestick injury and PEP
Nefopam 💊
Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus)
Nelson Syndrome
Nemaline myopathy
Neomycin
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome NAS
Neonatal Jaundice
Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus
Neonatal death or cot death
Neonatal death or cot death
Neonatal meningitis
Neostigmine 💊
Nephritic vs Nephrotic syndrome
Nephroblastoma (Wilm's tumour)
Nephrotic Syndrome in Children
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotoxic drugs
Nerve conduction studies
Nerve fibres types
Neuroanatomy Images
Neuroblastoma
Neurocysticercosis (Taenia solium a pork parasite)
Neuroferrinopathy
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neurological - Vision and Eye movements
Neurological Examination - Cortical Functions
Neurological Examination - Motor
Neurological Examination - Speech&Language
Neurological Sensory Examination (OSCE)
Neurological examination - Eyes
Neurological or ENT Examination - Nystagmus
Neurology Chapter
Neuromuscular weakness
Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic's disease)
Neuropathic Pain Management
Neuropathic pain
Neuroscience of Memory
Neurosurgery
Neurotransmitters
Neutropenia
Neutropenic Sepsis
Neutrophil Alkaline Phosphatase
Neutrophils
Nevirapine (Viramune) NEV-NVP
Newborn Bloodspot (Heel Prick) Screening
Niacin deficiency (Pellagra Vitamin B3)
Nicardipine (Cardene)
Nicorandil
Niemann-Pick disease
Nifedipine
Night sweats
Nikolsky's sign
Nimodipine (Nimotop)
Nipple Discharge
Nirsevimab (Beyfortus)
Nitrates
Nitric Oxide
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrous oxide use and abuse
Nizatidine
Nocardia
Noise induced hearing loss
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease MASLD and MASH
Non Convulsive Status Epilepticus
Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non gonococcal urethritis
Non invasive ventilation (NIV)
Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy
Non-accidental injury
Non-accidental injury (children)
Noonan syndrome
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Normal Distribution
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Normal Saline 0.9%
Normal pregnancy and Antenatal care
Normocytic anaemia
Norovirus
Nortriptyline
Nosocomial infections
Notifiable disease and organisms UK
Nucleotides
Nutrition in Infants Breastfeeding
Nystatin
OSCE New Headache
OSCE Abdominal Examination
OSCE Acute Abdominal Pain
OSCE Acute Appendicitis
OSCE Acute Right-Sided Weakness
OSCE Ascites Examination
OSCE Blood pressure
OSCE Breast Anatomy Exam
OSCE Cardiac History Taking
OSCE Causes of Male Infertility
OSCE Chest Pain in the Emergency Department
OSCE Chronic Visual Loss
OSCE Comatose Patient
OSCE Cranial nerves and examination
OSCE Dyspepsia
OSCE Dysphagia Swallowing
OSCE Ear Examination
OSCE Examination of Visual Fields
OSCE Examining for Finger Clubbing
OSCE Examining the Arterial Pulse
OSCE Examining the Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP)
OSCE Eye Examination
OSCE Failure to Thrive
OSCE First Seizure
OSCE Gastroenterology History taking
OSCE Hip Pain
OSCE Inguinal Examination
OSCE Jaundice
OSCE Leg Pain & Swelling
OSCE Lower Limb Neurological Examination
OSCE Male Genital exam
OSCE Monocular loss of vision
OSCE Neurological Examination - Cognition
OSCE Neurological Examination Face
OSCE Neurology - History taking
OSCE New Onset Weakness (Stroke Assessment)
OSCE Polyuria and Thirst (Diabetes)
OSCE Postmenopausal Bleeding
OSCE Rectal Bleeding
OSCE Respiratory - History Taking
OSCE Shortness of Breath History
OSCE Shoulder exam
OSCE Station Hearing Loss
OSCE Station – Melaena
OSCE Testicular/Scrotal Examination
OSCE Thyroid Exam
OSCE Unintentional Weight Loss
OSCE Upper Limb Neurology Examination
Obesity
Obesity and Pregnancy
Object orientated programming
Obsessive-Compulsive disorder
Obstetric definitions
Obstetrics Emergencies
Obstructive Lung Diseases
Obstructive Shock (Mechanical Obstruction)
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Occupational Lung Disease
Octreotide
Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
Oesophageal Carcinoma
Oesophageal Perforation - Rupture
Oesophageal Variceal Bleeding
Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD/EGD)
Olanzapine
Older Patient with Swallowing Problems
Olecranon Fracture
Olfactory Nerve (Cranial Nerve I)
Oligodendroglioma
Olmersartan
Olsalazine (Aminosalicylate)
Omalizumab
Omeprazole
Onchocerciasis
Oncogenic viruses
Ondansetron
Ophthalmic Emergencies
Ophthalmic Nerve
Ophthalmology Exam Lists
Opiates
Opicapone
Opioid/Opiate toxicity
Opsonisation
Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II) and tract
Optic Neuritis
Optic atrophy
Optics Pathway
Oral Aphthous Ulcers
Oral Candidiasis
Oral Leukoplakia
Orbital Cellulitis vs Preorbital Cellulitis
Orf (Contagious Ecthyma)
Organism and sensitivities
Organomegaly
Organophosphate (OP) Toxicity
Orphenadrine
Orthostatic Hypotension
Oseltamivir - Tamiflu
Osteoarthritis
Osteochondroma
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenic sarcoma (Osteosarcoma)
Osteomalacia
Osteomyelitis
Osteonecrosis of the jaw
Osteopetrosis
Osteoporosis
Otitis Externa (Malignant)
Otitis Media
Otosclerosis
Ottawa rules for ankle and foot x-ray
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian Cyst
Overlap Syndrome
Overview of Cardiac Electrophysiology
Oxford / Bamford Classification
Oxford community stroke project (Bamford)
Oxidation and Reduction for Medical Students
Oxybutynin (Ditropan)
Oxycodone (Oxycontin-Oxynorm)
Oxygen delivery devices
Oxytetracycline
POEMS syndrome
Pabrinex
Pacemakers and Indications for Pacing
Paediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections
Paediatric emergencies
Pagets (Bone) disease
Pain Management : Acute & Chronic
Pain on inspiration
Painful Sexual Intercourse (Dyspareunia)
Painful Shoulder syndromes
Painful swollen leg
Palliation - Nausea Dyspnoea Secretions Pain
Palliation prescribing
Pallor
Palpitations
Pamidronate (Bisphosphonate)
Panayiotopoulos Syndrome in Children
Pancoast tumour (Cancer)
Pancreas Physiology and Anatomy
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancytopenia
Panic Disorder
Panton-Valentine leucocidin toxin
Pantoprazole
Pantothenate Kinase–Associated Neurodegeneratio
Papilloedema
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) toxicity
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paradoxical embolisation
Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis (Dementia)
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
Paraphimosis (urological emergency)
Paraquat toxicity
Parathyroid Physiology
Parkinson Hyperpyrexia Syndrome
Parkinson Plus syndromes
Parkinson disease
Parkinsonism and Tremors
Paronychia
Parotitis
Paroxetine
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria
Pasteurella multocida
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
Patellar Bursitis
Patent Ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
Pathological Gaits 🚶♂️
Pathological bone fracture
Patient on Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy
Patients who refuse treatment or lack capacity
Patiromer
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Pectus Excavatum
Pegvisomant 💊
Pelvic Anatomy
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Mass
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic fractures
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Penetrating Abdominal Trauma
Penicillamine
Penicillin Allergy
Penicillins
Penile Cancer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) and gastritis in Children
Peptic ulcer disease and Gastritis in Adults
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) procedure:
Pergolide
Perianal abscesses and fistulae
Perianal symptoms
Pericardial Disease
Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade
Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid haemorrhage
Perindopril
Perinephric abscess
Perioperative Anticoagulation
Peripartum cardiomyopathy
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Nerve Palsies
Peripheral nerve injuries/palsies (Children)
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral oedema and ankle swelling
Peripheral vascular disease
Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC)
Peritonitis
Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy)
Pernicious anaemia
Personality Disorders
Perthes disease (Osteochondritis of the Hip)
Petechial Rash in Adult or Child
Pethidine
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Peyronie’s Disease
Phaeochromocytoma
Phagocytes
Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacology in the Elderly
Pharyngeal anatomy
Pharyngeal arch derivatives
Pharyngitis
Phenobarbital sodium
Phenoxymethylpenicillin (Penicillin V)
Phentolamine
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Philadelphia chromosome
Phimosis
Phobic disorders
Phocomelia and Thalidomide
Phosphorus/Phosphate
Physics of flow for Medical students
Physiology of vision
Picolax - Citrafleet
Pilonidal Abscess (sinus)
Pinta (Treponema carateum)
Pioglitazone (Thiazolidinediones)
Pituitary Anatomy and Physiology
Pituitary Apoplexy
Pituitary Tumours
Pityriasis or Tinea versicolor infections
Pityriasis rosea
Pivmecillinam (a penicillin antibiotic)
Placenta praevia
Placental abruption
Plantar fasciitis
Plasmapheresis
Plasmids
Platelets
Pleural effusion
Pleural tap (thoracentesis)
Pneumococcal meningitis
Pneumoconiosis
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
Pneumonia in Children
Pneumonia 🩺
Poisoning
Poisons eliminated Haemodialysis - perfusion
Poliomyelitis
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
Polyarticular arthritis
Polycystic Ovary syndrome
Polycythaemia
Polycythaemia Vera (Primary Polycythaemia)
Polydipsia (thirst)
Polymerase chain reaction
Polymorphic light eruption
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyositis
Polypharmacy and STOPP/START criteria
Polyuria
Pontiac fever (Legionella Pneumophila)
Pontine-Midbrain haemorrhage
Popliteal Artery Aneurysm
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
Porphyria Testing
Portal Hypertension
Positron and Single photon Emission Tomography
Post Menopausal Bleeding
Post Partum Thyroiditis
Post Polio Syndrome (PPS)
Post Streptococcal/Infectious Glomerulonephritis
Post Stroke Epilepsy (PSE)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Immunoglobulins
Post-operative surgical care and complications
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs)
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
Posterior circulation
Postpartum / Postnatal Psychosis
Postpartum/Postnatal Depression
Postprandial hypotension
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
Post‑fall management: Concerns for the On‑Call Team
Potassium Physiology
Pralidoxime
Pramipexole (Mirapexin)
Prasugrel
Pravastatin
Praziquantel
Prazosin
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-eclampsia, Gestational Hypertension
Prednisolone
Prednisone
Pregabalin
Pregnancy risk assessment
Premature Menopause
Prematurity
Presbyacusis(Presbycusis)
Prescribing in Pregnancy
Pressure sores or ulcers
Preterm labour
Prevotella (Bacteroides) melaninogenica
Priapism
Primaquine
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL)
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG)
Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Primary and Secondary Hypoparathyroidism
Primary ciliary dyskinesia and Kartagener's syndrome
Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome)
Primary progressive aphasia (Dementia)
Probenecid
Prochlorperazine (Stemetil)
Procyclidine
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP)
Prolactinoma
Propafenone
Propantheline
Propionibacterium
Propofol
Propranolol
Propylthiouracil
Prostate cancer
Prosthetic Metal and Tissue Valves
Protamine Sulfate
Protein C Deficiency
Protein S Deficiency
Protein Synthesis
Protein losing enteropathy
Protein metabolism
Protein p53
Proteus
Prothrombin 20210A mutation
Prothrombin Complex Concentrates (Octaplex and Beriplex)
Prothrombin time and Coagulation
Prothrombotic Hypercoagulable disorders
Proximal Humeral Fracture
Proximal myopathy
Prucalopride
Pruritis
Pruritis ani
Psammoma bodies 🌀
Pseudo(pseudo)hypoparathyroidism
Pseudomonas infection (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
Psoriasis
Psoriatic arthritis
Psychogenic Polydipsia
Pubertal Development
Pubic Lice (Pediculosis Pubis)
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
Pulmonary Arteriovenous malformation
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Pulmonary Eosinophilia and CXR changes
Pulmonary Haemorrhage
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary Physiology
Pulmonary Regurgitation
Pulmonary Stenosis
Pulse oximetry
Pupils : Relative Afferent pupillary defect (RAPD)
Purpura
Purpura Fulminans
Putamen and Globus Pallidus
Putaminal Haemorrhage
Pyloric Stenosis Children
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Pyonephrosis
Pyrazinamide
Pyridostigmine 💊
Pyroglutamic acidosis
Pyruvate Kinase deficiency
Python Programming
Quetiapine
Quinine
Quinine toxicity
RFS Rib fracture score
Rabies
Radial Head and Neck Fractures
Radial Ulnar and Median Palsy of the Hand
Radial nerve
Radiation exposure
Radicular syndromes
Radiculopathies
Radioactive iodine (I 131)
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy (RIG) Procedure
Radiology for finals
Raised intracranial pressure
Raloxifene
Raltegravir
Ramipril
Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Ranitidine
Ranolazine
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI)
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
Rasagiline
Rasburicase
Rate limiting steps in metabolism
Raynaud's Phenomenon Primary and Secondary
Reactive Arthritis
Rectal Foreign Body
Rectal Pain (Proctalgia)
Rectal Prolapse
Rectal examination (OSCE)
Red Blood Cell Maturation
Red Blood Cells
Red cell aplasia
Reduced/change in fetal movements
Refeeding syndrome
Referring to Level 2 or 3 care (ITU ICU HDU)
Reflex anoxic attacks in Children
Refractive Errors
Refsum disease
Regular Broad Complex Tachycardia
Relapsing Polychondritis
Remdesvir (Veklury)
Renal Anatomy
Renal Artery Stenosis Renovascular Disease
Renal Papillary Necrosis
Renal Physiology
Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
Renal Top Tips
Renal Transplantation
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA)
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Renal and Urology Emergencies
Renal cell carcinoma
Renal syndromes
Renin and Aldosterone Renin ratio (ARR)
Renin-angiotensin system
Respiratory Examination (OSCE)
Respiratory Acidosis
Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Arrest
Respiratory Arrest
Respiratory Disease Investigations
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Neonates)
Respiratory Emergencies
Respiratory Failure
Respiratory Spirometry and Flow Volume Loops
Restless legs syndrome
Restriction enzymes
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
Resus: Septic Shock and Sepsis
Resuscitation - Acute Haemorrhage
Resuscitation - Adult Bradycardia Algorithm
Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm
Resuscitation - Advanced Life Support
Resuscitation - Basic Life Support ABCDE
Resuscitation - Choking Algorithm
Resuscitation - Newborns and Children
Resuscitation - Post Resuscitation Algorithm
Reteplase
Reticulocytes
Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
Retinal detachment
Retinitis pigmentosa
Retinoblastoma
Retinoids
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Rett Syndrome
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome
Reye syndrome
Rhesus haemolytic disease
Rheumatic fever
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatology Autoantibodies
Rheumatology Drugs
Rheumatology Lab values
Rhino-Orbital-Cerebral Mucormycosis
Rhinosinusitis
Rhodococcus equi
Ribavirin
Ribosomes
Ricin Toxicity
Rickettsia (General Principles)
Rickettsia africae (Tick Bite Fever)
Rickettsia akari (Rickettsial pox)
Rickettsia conorii (Mediterranean Spotted Fever)
Rickettsia prowazekii (Epidemi/Louse-borne Typhus)
Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain spotted fever)
Rickettsia tsutsugamushi (Scrub typhus)
Rickettsia typhi (Murine/Endemic typhus)
Rifampicin (Rifabutin Rifampin)
Rifaximin
Right Iliac Fossa Pain
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Tachycardia (RVOT)
Right Ventricular ST Elevation MI (RVMI)
Right heart valve disease
Rilipivirine (Edurant) RVP
Riluzole (Rilutek)
Risedronate (Bisphosphonate)
Risperidone
Ritonavir (Norvir) RTV
Rituximab (Mabthera)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocuronium
Role of Secondary Messengers
Role of Urinary Catheters in the Elderly
Rotavirus
Rotigotine
Rubella (German Measles) Notifiable
Rust Programming
SCL70 Antibody
SQL programming
Saccular Berry Cerebral Aneurysms
Sacubitril with Valsartan
Safeguarding Adults and Children
Safety Surgical checklist WHO
Salivary Gland Disease
Salivary glands
Salmonella enterica
Salmonella typhi
Sampling in Medical Statistics
Saquinavir (Invirase) SQV
Sarcoidosis
Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
Scabies
Scaphoid fracture
Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina)
Scarring
Schistosomiasis
Schizophrenia
Schmidts syndrome
Sciatic nerve
Sciatica
Scleritis
Scrotal/testicular pain/lump/swelling ⚠️
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Keratosis
Secondary Hypertension
Secondary Pulmonary hypertension - Cor pulmonale
Secondary dysmenorrhoea
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Secondary prevention Post Acute Coronary Syndrome
Sedation and Analgesia on ITU
Selective IgA deficiency
Selective Serotonin reuptake Inhibitor toxicity
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)
Selegiline
Selenium deficiency
Self assessment form
Self-harm
Senior Self Assessment
Senna
Septic arthritis
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
Serotonin syndrome
Serplulimab
Serratia
Sevelamer
Severe combined immunodeficiency disorders
Shaft of Ulna Fracture
Sheehans syndrome
Shigella characteristics
Shigellosis (Bacillary Dysentery)
Shock in Pregnancy
Short QT Syndrome
Short Synacthen test (SST)
Shoulder Anterior Dislocations
Shoulder: Posterior Dislocation
Sick Child/Neonate
Sick Euthyroid Syndrome
Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady syndrome)
Sickle Cell Disease
Sideroblastic Anaemia
Sigmoid and Caecal Volvulus Adults
Sildenafil (Viagra)
Silicosis
Simvastatin
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Node disease
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus arrhythmia
Sitagliptin
Sitosterolemia
Sjögren’s syndrome
Skin Pathology and Description and Examination
Skin Treatments
Skin Ulcers
Skin and soft tissue and bone infections
Skin or subcutaneous lump
Skull Anatomy
Sleep physiology
Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
Small Bowel Obstruction (Adults)
Small for Gestational Age (SGA)
Small vessel disease
Smallpox
Smoke Inhalation
Smoking and Its Consequence
Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smouldering Myeloma
Snake Bites
Sneddon Syndrome
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Sodium Nitroprusside
Sodium Physiology
Sodium Picosulfate
Sodium Potassium ATPase pump
Sodium Thiopental - Sodium Thiopentone
Sodium Valproate (Epilim Depakote)
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate (Lokelma)
Soft Tissue Injury
Soft tissue : Cut finger
Soft tissue injuries (sprains, strains)
Solifenacin
Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
Somatisation
Somatisation/ medically unexplained physical symptoms
Sore throat
Sotalol Hydrochloride
Speech and language problems
Spina Bifida
Spinal Cord Anatomy
Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations
Spinal Cord Compression
Spinal Cord Haematoma
Spinal Cord Infarction
Spinal Cord Injury / Malignant Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC)
Spinal Fracture
Spinal Fractures: assessment & management
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal Tracts
Spinal and Epidural Anaesthesia
Spironolactone
Splenectomy
Splenectomy and Hyposplenism
Splenic Rupture
Splenomegaly Examination (OSCE)
Spondylolisthesis
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Spontaneous Pneumothorax
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squint
St John's Wort 💊
Staphylococcal Infections
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Statin
Status Epilepticus (Epilepsy/Seizure)
Stavudine (Zerit) d4T
Stem Cell Transplantation
Sterno-Clavicular Joint Dislocation
Steroid-responsive encephalopathy associated with autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's Encephalopathy)
Stiff Person Syndrome
Strabismus (Lazy Eye)
Streptobacillus moniliformis
Streptococcal Infections
Streptococcus - anaerobes
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Pneumococcus)
Streptococcus agalactiae Group B
Streptococcus milleri
Streptococcus pyogenes Group A
Streptococcus viridans
Streptokinase
Streptomycin
Stridor
Stroke
Stroke - Epidemiology and risk factors
Stroke - General Management
Stroke Collaterals
Stroke MRI Basics
Stroke Mimics And Chameleons
Stroke Penumbra
Stroke Related Cerebral Perfusion
Stroke Risk Factors
Stroke Thrombolysis
Stroke Vascular Anatomy
Stroke and Vision
Stroke: The Brain and Function
Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm)
Strontium
Struggling to Cope at Home
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis
Subacute Thyroiditis
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Subclavian Steal Syndrome
Subclavian Vein Thrombosis (SCVT)
Subdural haematoma
Subfertility in Men
Subfertility in Women
Substance misuse
Substance use disorder
Sucralfate
Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing loss (SNHL)
Sugammadex
Suicidal thoughts
Suicide
Sulfasalazine - Sulphasalazine
Sumatriptan
Summary of Emergency Conditions in Oncology
Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA) Syndrome
Superior Sagittal Sinus Thrombosis
Superior Vena Caval Obstruction syndrome
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
Supracondylar Femur Fractures
Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
Supraspinatus tendonitis
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Surgical Cricothyroidotomy
Surgical Liaison in Older Patients Quality & Silver Trauma (UK)
Surgical Stomas
Surgical prophylaxis
Surgical site infection
Susac syndrome
Suxamethonium
Sweat Test
Swiss Cheese Model of Patient Harm
Sydenhams chorea
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Synchronised DC Cardioversion
Syncope
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH (SIADH) secretion
Syphilis
Syringobulbia
Syringomyelia
Systemic Amyloid in Pathology
Systemic Amyloidosis
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic Mastocytosis
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
T lymphocytes
TMN Staging tumours
TNF Blockade
TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome
TO DO
TORCH infections
TURP Hyponatraemia syndrome
Tabes dorsalis
Table showing Visual Field Changes for Examination
Tacrolimus 💊
Tafamidis
Takayasu arteritis (pulseless disease)
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Tamoxifen
Tamsulosin (Flomax)
Tangier Disease
Tardive Dyskinesias
Tay-Sachs disease
Tazocin (Tazobactam - Piperacillin)
Teicoplanin
Telogen Effluvium
Telomeres
Temazepam
Temozolomide (Temodal) 💊
Temporal (Giant Cell GCA) Arteritis
Tenecteplase
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Tensilon test
Tension Headache
Tension Pneumothorax
Teplizumab (Tzield)
Terbutaline
Teriparatide
Terlipressin
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Testicular Cancer
Testicular Torsion
Testing
Tests in Liver Disease: Usefulness and Interpretation
Tetrabenazine
Tetracosactide (Synacthen)
Tetracyclines
Tetralogy of Fallot
Thalamic Haemorrhage
Thalamic Pain Syndrome or Dejerine–Roussy Syndrome
Thalamic Strokes
Thalamus
Thalidomide
The Aorta
The Axillary Artery
The Brachial Artery
The Brachial plexus
The Carotid Artery
The Cell Nucleus
The Cell membrane
The Circle of Willis
The Deteriorating Patient
The Eye and Systemic Disease
The Femoral Artery
The Fetal Head and Vaginal Birth
The Iliac arteries
The Nephron – the Functional Unit of the Kidney
The Popliteal artery
The Radial and Ulnar Arteries
The Subclavian Artery
The Vertebral and Basilar Arteries
Theophylline
Theophylline toxicity
Thiamine
Third Degree (complete) Heart Block
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytosis (High Platelets)
Thrombophilia (Prothrombotic) testing
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Thyroglossal Cyst (Children)
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid Eye Disease
Thyroid Function Tests and antibodies
Thyroid Physiology
Thyroid Storm - Thyrotoxic crisis
Thyroid Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
Thyroid nodules
Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism
Tiagabine
Ticagrelor
Tick Paralysis
Tick-borne relapsing fever (Borrelia duttonii)
Timolol
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm)
Tinea capitis
Tinidazole
Tinnitus
Tinzaparin (Innohep)
Tiotropium (Spiriva)
Titre - Titer
Tocilizumab
Tolbutamide
Tolcapone
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Recognition Receptors and Triggers of Innate Immunity
Tolosa Hunt Syndrome
Tolterodine
Tolvaptan
Tongue tie - ankyloglossia (Children)
Tonsilitis
Tonsillectomy Adenoidectomy
Topiramate (Topamax)
Torsades de pointes TdP (Polymorphic VT)
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic Megacolon
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Toxicological Emergencies
Toxoplasmosis
Tramadol 💊
Tranexamic Acid
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation/replacement (TAVI/R)
Transcutaneous Pacing
Transfer Factor (TLCO / DLCO)
Transferrin
Transfers of folder frail or disabled patients
Transient Global Amnesia (TGA)
Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA)
Transient Monocular Blindness (TMB)
Transjugular Intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
Transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
Transvenous Pacing (Temporary)
Transverse myelitis
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) 💊
Trauma
Trauma : NICE Guidance Haemorrhage
Trauma Physiology
Trauma: Cardiac Arrest
Trauma: Epilepsy - Post Traumatic
Trauma: Flail Chest Rib fractures
Trauma: Initial Assessment and Management
Trauma: Post traumatic stress disorder
Trauma: Resuscitative Thoracotomy
Trauma: Silver Trauma in older patients
Trauma: Spinal Injury
Trauma: Thoracic Assessment and Management
Trauma:Prehospital
Traumatic Auricular Haematoma (Cauliflower ear)
Travel health advice
Travellers Diarrhoea
Trazodone 💊
Treatment Escalation Plans (TEP) in the Elderly
Treponema
Tretinoin (All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) )
Triangles of the neck
Trichinellosis
Trichomoniasis Vaginalis
Tricuspid Atresia
Tricuspid Regurgitation
Tricuspid Stenosis
Tricyclic Antidepressant Toxicity
Tricyclic antidepressants
Trigeminal Nerve (Vth Nerve)
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trihexyphenidyl (benzhexol)
Trimethoprim
Trinucleotide (triplet) Repeat Disorders
Trochlear Nerve (VIth nerve)
Tropheryma whipplei (Whipple disease)
Tropical Sprue
Truncus Arteriosus (Children)
Tuberculosis
Tuberculous Meningitis
Tuberous sclerosis
Tularaemia (Francisella tularensis)
Tumour Lysis Syndrome
Tumour Necrosis Factor
Tumour Suppressor Genes
Tumour markers
Turcot's syndrome (Brain tumor polyposis syndrome)
Turners syndrome (Children)
Twins
Tympanic (Eardrum) membrane perforation
Types of Hypersensitivity Reactions
Types of Joints
Types of Organ Transplant Rejection
Typhoid and Paratyphoid fever (Enteric Fever)
Tyrosine Kinase receptors
USMLE Lab Values
Ubiquitin
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulnar nerve
Ultrasound Physics & Imaging
Undifferentiated Inflammatory Arthritis (Children)
Unintentional weight loss (Adults)
Unsteadiness
Unwanted pregnancy and termination
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleed
Upper Limb fractures and injuries
Upper and Lower Limb Neurology (OSCE)
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron signs
Upper limb Soft Tissue Injuries
Upper respiratory tract infection
Urethral Discharge (Urethritis)
Urethral syndrome
Urinary Catheterisation
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Obstruction
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI Children)
Urinary Tract Obstruction
Urinary symptoms
Urinary tract calculi (stones)
Urothelial tumours/ Transitional cell carcinomas
Urticaria
Uterine fibroids
Uveitis
VIPomas
Vaccine in Older Patients
Vaginal Candidiasis
Vaginal Carcinoma
Vaginal Prolapse
Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve X)
Valaciclovir
Valsartan
Vancomycin
Variable rate intravenous insulin infusion VRIII
Variant (Prinzmetal) Angina
Variant Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Varicella Cerebral Vasculopathy
Varicose veins
Variegate Porphyria
Vasa Praevia
Vascular Anatomy
Vascular Dementia
Vascular access for haemodialysis
Vasculitis - General Issues and Classification
Vasopressin (AVP) Antidiuretic hormone
Vasovagal syncope
Vaughan-Williams Classification
Vecuronium
Vedolizumab (Entyvio)
Venepuncture (Blood tests)
Venlafaxine
Venous Insufficiency and Leg Ulcers
Venous Supply of the leg
Venous Thromboembolism Pregnancy and Puerperium
Venous access Cannulas OSCE
Venous and Arterial Ulcers and Other Lower Limb Ulcers
Venous and Arterial and Pressure Ulcers
Ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Septal defect (VSD)
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Ventricular ectopic beats
Verapamil
Vertebral artery dissection
Vesicoureteric reflux (VUR) (Children)
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (Cranial Nerve VIII)
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio vulnificus
Vibrio vulnificus
Vigabatrin (Sabril)
Vinblastine
Vincent's angina
Vincristine
Violence Aggression and Conflict Resolution
Viral Gastroenteritis and other causes
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers (VHF)
Viral Meningitis
Viral exanthema
Viral hepatitides
Viruses and their infections
Visual Basic Programming
Visual Hallucinations in the elderly
Visual acuity
Vitamin A Deficiency
Vitamin B1 Thiamine deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 excess
Vitamin C deficiency (Scurvy)
Vitamin D (1,25 OH2)
Vitamin D 25 (OH) D Testing
Vitamin D Physiology
Vitamin D Replacement
Vitamin D resistant rickets (Children)
Vitamin K (Phytomenadione)
Vitamin K deficiency
Vitiligo
Voltarol (Diclofenac)
Volvulus (Children)
Vomiting
Von Gierke Disease (Children)
Von Hippel Lindau
Von Willebrand Disease
Vulval itching/lesion
Vulval/vaginal lump
Waardenburg's syndrome
Waldenstrom Macroglobulinaemia
Warfarin
Water Physiology
Watershed Infarcts
Waveform CO₂ capnography
Weight Gain Adults
Wellbeing Checks in General Practice for GPs
Wellens Syndrome
Werdnig–Hoffman Disease (SMA Type 1)
Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome
Wheeze: Clinical Approach and Considerations
White Blood Cells
Williams Syndrome (Children)
Wilson disease
Windows Powershell
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (Children)
Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome (WPW) AVRT
Wolfram syndrome (DIDMOAD)
Wound Management
Wound healing
Wrist Injury: Smith’s Fracture
X linked Agammaglobulinaemia (Bruton)
X linked Hypophosphataemic rickets
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance
X-linked Ichthyosis
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (Children)
Xanthelasma
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Yaws (Frambesia) Treponema pertenue
Yellow Fever
Yellow Nail Syndrome
Yersinia enterocolitica
Yersinia pestis - Bubonic Plague
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
ZZ_Abnormal char
Zidovudine (Retrovir) AZT - ZDV
Zieve's syndrome
Zika virus
Zinc deficiency
Zolbetuximab (Vyloy)
Zoledronic acid (Zoledronate)
Zollinger Ellison syndrome
Zolpidem
Zopiclone
eGFR
zNecrobiosis
️Causes of a Limp in Adults
🍽️ Malnutrition in Children
📊 Thromboelastography (TEG)
🔄 ROTEM - Rotational Thromboelastometry
🦠 Skin Infections due to Fungi
🧑⚕️ Weakness in Adults – Causes, Features, and Diagnosis<
🩺 Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
🩺 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) OSCE
@Contributers
@Developer and Author
@Privacy and Data Policy
ACTH (Adrenocorticotropic hormone)
AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein) Testing
AIDS (HIV) Neurological Disease
AIDS (HIV) Respiratory disease
AIDS Dementia Complex (HIV)
AIDS HAART Antiretroviral Drugs
AIDS HIV Infection
AIDS(HIV) Gastrointestinal Disease
APGAR Scoring (Children)
APTT and Coagulation
Abacavir
Abatacept
Abbreviated Mental Test Score (AMTS)
Abciximab
Abdominal Anatomy and Physiology
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA)
Abdominal Distension
Abdominal Mass (Child health)
Abdominal Masses: Clinical Approach and Considerations
Abdominal X Ray Collections
Abdominal X-Ray (AXR)*
Abdominal paracentesis for ascites
Abducent Nerve (Cranial Nerve VI)
Abetalipoproteinemia (Bassen-Kornzweig Syndrome)
Abnormal Cervical Smear Results
Abnormal Involuntary Movements
Abnormal eating exercising behaviour (Children)
Abnormal urinalysis
Abscess - General
Absence Seizure
Acamprosate
Acanthocytes
Acanthosis Nigricans
Acarbose
Accelerated Idioventricular Rhythm
Accessory Nerve (Cranial Nerve XI)
Acetazolamide
Acetylcholine Receptor Antibodies
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Achalasia
Achenbach’s syndrome
Achilles Tendon rupture
Achondroplasia
Aciclovir
Acid Base Abnormality
Acid maltase deficiency (Pompe disease)
Acne Rosacea
Acne Vulgaris
Acoustic Neuroma
Acquired Long QT syndrome (LQTS)
Acrodermatitis enteropathica (Children)
Acromegaly and Giantism
Acromio-clavicular joint
Actinic Keratosis
Actinomyces israeli
Action Potential Neuron Versus Cardiac Ventricular Myocyte
Activated Charcoal
Active Proctitis
Actrapid (Insulin)
Acute (Ascending) Cholangitis
Acute Abdomen - Perforation of a Viscus
Acute Abdominal Pain - Adults
Acute Abdominal Pain - Children
Acute Acalculous Cholecystitis
Acute Airway Obstruction
Acute Anaphylactoid Reactions
Acute Anaphylaxis
Acute Appendicitis
Acute Appendicitis in Children
Acute Bacterial Meningitis (Adults)
Acute Bacterial Meningitis in Children
Acute Bacterial Prostatitis
Acute Blepharitis
Acute Bronchitis
Acute Change in Vision or Vision Loss
Acute Chest Syndrome (Sickle Cell)
Acute Colonic Pseudo-obstruction
Acute Compartment Syndrome
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS)
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) NSTEMI USA
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS) STEMI
Acute Coronary Syndrome (ACS): Complications
Acute Coronary Syndrome (Cardiac Troponins)
Acute Coronary Syndrome Arrhythmias
Acute Coronary Syndrome Grace score
Acute Coronary Syndrome TIMI Score
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Cardiac Thrombolysis
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Myocardial infarction
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Sgarbossa Criteria
Acute Coronary Syndrome: Unstable Angina
Acute Coronary: Percutaneous Coronary Intervention
Acute Disc Prolapse
Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis
Acute Dystonic Reaction
Acute Encephalitis
Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia
Acute Epiglottitis
Acute Exacerbation of COPD
Acute Fatty Liver of Pregnancy
Acute Glaucoma
Acute Glomerulonephritis in Children
Acute Heart Failure and Pulmonary Oedema
Acute Hydrocephalus
Acute Hypotension
Acute Inflammation
Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)
Acute Interstitial nephritis
Acute Joint Pain and Swelling (Children)
Acute Kidney Injury
Acute Limb Ischaemia
Acute Liver Disease
Acute Liver Failure
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (ALL)
Acute Mastoiditis
Acute Monoarthritis
Acute Myeloblastic Leukaemia (AML)
Acute Myocarditis
Acute Neck Injury (no fracture)
Acute Necrotizing Ulcerative Gingivitis
Acute Pancreatitis
Acute Pericarditis
Acute Phase reactants
Acute Porphyrias
Acute Promyelocytic Leukaemia (APML)
Acute Psychosis
Acute Pyelonephritis and Urosepsis (UTI)
Acute Radiation Syndromes
Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS)
Acute Retroviral Syndrome (HIV)
Acute Rhabdomyolysis
Acute Rotator Cuff Tear
Acute Severe Asthma (Status Asthmaticus)
Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS)
Acute Stroke Care Guidance UK Ireland 2023
Acute Tracheitis
Acute Urinary Retention
Acute and Chronic Diarrhoea
Acute and Chronic Gout
Acute on Chronic Liver Disease Decompensation
Acute rash (Child Health)
Acutely Ill Patient
Acutely Ill Patient with Parkinson's disease
Adalimumab
Addenbrooke's Cognitive Examination-Revised (ACER)
Addison Disease (Adrenal Insufficiency)
Adefovir
Adenocarcinoma of the Ampulla of vater
Adenosine
Adenosine deaminase deficiency
Adhesive Capsulitis (Frozen Shoulder)
Administer IV Injection
Adrenal Adenomas
Adrenal Cancer
Adrenal Masses Incidentalomas
Adrenal Physiology
Adrenaline (Epinephrine)
Adrenocortical crises (Babies)
Adrenoleukodystrophy
Adrenomyeloneuropathy
Adult Onset Stills Disease
Adult Polycystic kidney disease
Adverse Drug Effects
African Trypanosomiasis (Sleeping sickness)
Age-Related Macular Degeneration (ARMD)
Aicardi syndrome
Air Embolism
Alberta Stroke program Early CT score (ASPECT) scoring system
Albumin
Albumin-Protein Creatinine Ratio (PCR)
Alcohol Metabolism
Alcohol Withdrawal (Delirium Tremens)
Alcoholic Hepatitis
Alcoholic Ketoacidosis
Aldosterone Physiology
Alendronate (Alendronic acid)
Alfacalcidol
Algorithms
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP)
Alkalinisation of urine
Alkaptonuria
Allergic Bronchopulmonary Aspergillosis
Allergic Rhinitis
Allergic disorders
Allergies
Allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Allopurinol
Alogliptin (Vipidia)
Alopecia
Alopecia Areata
Alpha Thalassaemia
Alpha subunit (ASU) of TSH
Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency
Alport's Syndrome
Alteplase
Altitude sickness / Acute Mountain sickness
Aluminium and Magnesium Antacids
Alveolar Gas Equation
Alzheimer disease (Dementia)
Amantadine
Amaurosis fugax
Amblyopia
Ameloblastoma
Amenorrhoea
American Trypanosomiasis (Chagas Disease)
Amiloride
Amino acids
Aminoglycosides
Aminophylline
Aminosalicylates
Amiodarone
Amiodarone and Thyroid disease
Amitriptyline
Amlodipine
Ammonia Encephalopathy
Amnestic syndromes and Memory Disorders
Amoebiasis Amoebic (Entamoeba histolytica)
Amoxicillin
Amphetamine toxicity
Amphotericin B
Ampicillin
Amputations
Anaemia (Child Health)
Anaemia (Pregnancy)
Anaemia in Chronic Kidney Disease
Anaemia of Chronic Disease
Anaemia: Assessment
Anagrelide 💊
Anakinra
Anal Cancer
Anal Fissure
Analgesic Nephropathy
Anatomy and Physiology of the Bone Marrow
Anatomy of Arteries
Anatomy of Cells and Physiology
Anatomy of Dentistry
Anatomy of Large Bowel
Anatomy of Male Genitalia
Anatomy of Neurons
Anatomy of Small Bowel
Anatomy of Spinal Column
Anatomy of the Basal Ganglia
Anatomy of the Biliary system
Anatomy of the Bladder
Anatomy of the Breast
Anatomy of the Cerebrum
Anatomy of the Cervical Spine Vertebrae C1 (Atlas) and C2 (Axis)
Anatomy of the Diaphragm
Anatomy of the Ear
Anatomy of the Eye
Anatomy of the Glomerulus
Anatomy of the Hand
Anatomy of the Inguinal and Femoral canal
Anatomy of the Larynx
Anatomy of the Liver
Anatomy of the Muscles
Anatomy of the Nose
Anatomy of the Oesophagus
Anatomy of the Ovary
Anatomy of the Pharynx
Anatomy of the Rectum
Anatomy of the Skin
Anatomy of the Spleen
Anatomy of the Stomach
Anatomy of the Thorax
Anatomy of the Uterus and Fallopian Tubes
Andexanet alfa
Androgen insensitivity syndrome
Aneurysms, ischaemic limb and occlusions
Angina bullosa haemorrhagica
Angiodysplasia
Angiomyolipoma
Angioneurotic Oedema
Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors
Angiotensin Converting enzyme (ACE)
Angular Stomatitis - Cheilitis
Anion Gap
Ankylosing spondylitis
Anomalous Coronary Arteries
Anorexia Nervosa
Anosmia
Antacid medication
Anterior / Medial Medullary Infarct (Dejerine Syndrome)
Anterior Cruciate ligament injury
Anterior Horn Cell diseases
Anterior Spinal Cord syndrome
Anterior circulation Brain
Anthrax (Bacillus anthracis)
Anti-Citrullinated Protein Antibody (ACPA)
Anti-D immunoglobulin
Anti-Hu antibodies
Anti-NMDA (NMDAR) receptor encephalitis
Anti-OKT3 antibodies
Anti-RNP Antibody
Anti-Yo antibodies
Anti-neutrophilic cytoplasmic antibodies (ANCA)
Antiarrhythmic agents
Antibiotic Guidelines
Antibiotics Mechanisms
Antibiotics for Abdominal Infections
Anticholinergic Burden
Anticholinergic syndrome
Anticipation
Anticoagulation and Antithrombotic
Antidiuretic hormone (Vasopressin)
Antigen presenting cells
Antimicrobial Choices
Antimicrobial agents
Antimuscarinic drugs
Antiphospholipid Syndrome
Antithrombin III deficiency (AT3)
Anuria and Oliguria
Anxiety Phobias and OCD
Anxiety disorder: generalised (GAD)
Aortic Dissection
Aortic Regurgitation
Aortic Sclerosis
Aortic Stenosis
Aortoenteric fistula
Apathetic thyrotoxicosis
Apixaban
Aplastic anaemia
Apomorphine
Apoptosis
Appendix Cancer Tumours
Approach to the Child with Respiratory Distress
Apraxia
Arnold Chiari malformation
Arrhythmias
Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Cardiomyopathy
Artemisinins
Arterial blood gas sampling
Arterial thrombosis
Arteriovenous Malformations
Artery of Percheron stroke
Artery-to-artery embolic stroke
Artesunate
Arthrocentesis and Synovial fluid analysis
Asbestos Related Lung disease
Ascites
Aspergilloma
Aspergillus fumigatus
Aspirin
Aspirin/Salicylate Toxicity
Assesment of Causes of Pain on inspiration
Assesment of the causes of Chronic Abdominal Pain
Assessing Abdominal Pain
Assessing Coma/Consciousness
Assessing Hearing Loss
Assessing Significance
Assessing a Patient who is Shocked
Assessing and Painful Red eye
Assessment of Causes of Nausea
Assessment of causes of Vaginal Discharge
Asteatotic eczema
Asthma
Asthma COPD overlap syndrome
Astigmatism
Astrocytomas
Ataxia Telangiectasia
Atazanavir
Atenolol
Atherosclerosis
Atorvastatin
Atracurium
Atrial Ectopic beats
Atrial Fibrillation (AF)
Atrial Fibrillation and Anticoagulation
Atrial Fibrillation and Rhythm Control
Atrial Natriuretic Peptide (ANP)
Atrial flutter
Atrial myxoma
Atrial septal defect (ASD)
Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia AVNRT
Atrophic vaginitis
Atropine Sulfate
Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Auditory hallucinations
Autism spectrum disorder
Autism spectrum disorder
Autoimmune Haemolytic anaemia (AIHA)
Autoimmune Hepatitis
Autoimmune Liver Disease
Autoimmune Polyendocrine Syndromes
Automatic Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (AICD)
Autonomic Nervous System
Autonomic neuropathy
Autosomal Dominant
Autosomal Recessive
Avascular Necrosis of Femoral head
Axillary Nerve
Azathioprine
Azithromycin
B lymphocytes
BRASH syndrome
BRCA genes (Familial Breast Cancer)
Bacillary Dysentery
Bacillus cereus poisoning
Back pain
Backpain / Backache
Baclofen
Bacteria and their Infections
Bacterial Vaginosis
Bacteroides fragilis
Baker's (Popliteal) Cyst
Balanitis (Adults)
Balanitis (Children)
Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN)
Balsalazide (Aminosalicylate)
Barrett's oesophagus
Barthel Index
Bartonella
Bartonella henselae (Cat Scratch Disease)
Bartters syndrome
Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basic Anatomy: An overview
Basic Chemistry for Medicine
Basic Concepts of Pregnancy
Basic Neuroscience
Basic Physics for Medicine
Basic Statistics
Basilar artery thrombosis
Bayes' Theorem
Becker Muscular dystrophy
Beclometasone (Beclomethasone)
Beer Potomania
Behaviour/personality change
Behavioural and Psychological Symptoms of Dementia
Behavioural difficulties in Adults
Behavioural difficulties in childhood
Behcet's Syndrome
Bejel ( Treponema pallidum subspecies endemicum)
Belantamab mafodotin (Blenrep)
Bell's Palsy (Facial nerve palsy)
Bendroflumethiazide (Bendrofluazide) 💊
Benign Eyelid Conditions
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV)
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Benign recurrent intrahepatic cholestasis
Benzodiazepine Toxicity
Benzodiazepines
Benzylpenicillin Sodium (Penicillin G)
Berg Balance Scale
Beriplex
Berylliosis
Beta Agonists
Beta Antagonists/Blockers
Beta Blocker toxicity
Beta Thalassaemia
Beta-2 Microglobulin
Beta-lactamases
Betahistine (Serc)
Bezafibrate
Bezafibrate
Biceps rupture
Bile salt malabsorption (BAM)
Biliary atresia
Bilirubin
Biochemical Lab values
Biochemistry and Physiology of Globins
Biological Agents
Bioterrorism
Birt-Hogg-Dubé Syndrome
Bisacodyl
Bisoprolol
Bisphosphonates
Bites and stings
Blackouts and faints (TLOC)
Bladder Cancer
Bladder Stones
Blank Templates
Bleeding Antepartum
Bleeding Postpartum
Bleeding or High INR on Warfarin or other Anticoagulation
Bleomycin
Blindness - global causes
Blood
Blood Pressure
Blood Transfusion Reactions
Blood cultures
Blood film interpretation
Blood transfusion
Blotting Techniques: Gel Electrophoresis
Body Mass Index
Bone Pain
Bone Physiology
Bone disease Lab results
Bone metabolism RANK RANKL OPG pathway
Bone scintigraphy (Bone scan)
Bordetella pertussis (Whooping cough)
Borrelia burgdorferi
Borrelia recurrentis
Bortezomib
Botulism
Boxer's fracture
Brachial neuritis (neuralgic amyotrophy)
Brain Abscess
Brain CT Collection
Brain Embryology
Brain Herniation syndromes
Brain MRI
Brain MRI Collection
Brain Metastases
Brain Natriuretic Peptide (BNP)
Brain Physiology
Brain Tumours
Brain Tumours in Children
Brainstem Anatomy
Branchial cleft cyst
Breaking Bad News (OSCE)
Breast Cancer
Breast Cysts
Breast Fibroadenoma
Breast Lump
Breast abscess and Mastitis
Breast tenderness/pain
Breathlessness
Bretylium
Broad Complex Tachycardia
Bromocriptine
Bronchial adenoma
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiolitis
Bronchoscopy
Brown-Sequard Spinal Cord syndrome
Brucella
Brucellosis
Brugada syndrome
Bruising
Budd-Chiari syndrome
Budesonide
Buerger disease (Thromboangiitis obliterans )
Bulbar vs Pseudobulbar palsy
Bulimia Nervosa
Bullous Pemphigoid
Bumetanide
Bunions
Buprenorphine
Bupropion
Burkholderia cepacia
Burkitt's lymphoma
Burns Management Guide
Busulphan (Busulfan)
Byssinosis
C Programming
C# programming
C++ Programming
CADASIL
CARASIL
CHADS2 - VASc score
CMV retinitis
CNS fungal Infections
CNS infections
COVID 19
CSF Interpretation
CSF Rhinorrhoea
CT Basics for Stroke
CT Pulmonary angiogram (CTPA)
Cabergoline
Caesarean Section (CS)
Café-au-lait spots
Caisson Disease Decompression sickness (The Bends)
Calcific Uraemic Arteriolopathy (Calciphyalxis)
Calcitonin
Calcitriol (1,25 Dihydroxycholecalciferol)
Calcium Channel Blockers
Calcium Chloride or Gluconate
Calcium Physiology
Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition (Pseudogout)
Calcium Resonium
Calcium channel blockers toxicity
Calot's triangle
Campylobacter jejuni
Canaliculitis
Cancer Frequency and Red flags
Cancer Pathology
Cancer and Stroke
Cancer of Unknown Primary
Candesartan
Candidiasis
Cannabis toxicity
Cannonball Metastases
Capacity in Older Adult
Capecitabine 💊
Caplacizumab
Capnocytophaga canimorsus
Capnography
Capreomycin
Capsular and Pontine Warning Syndromes
Captopri
Carbamazepine
Carbapenemase-producing Enterobacteriaceae
Carbimazole
Carbohydrates
Carbon Monoxide Toxicity
Carbon Tetrachloride Toxicity
Carbon dioxide embolism
Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
Carcinoid Heart Disease
Carcinoid Tumour Syndrome
Carcinoma of the Bile Duct
Carcinoma of the Gallbladder
Cardiac Amyloid heart disease
Cardiac Anatomy and Physiology
Cardiac Arrest in Pregnancy
Cardiac Catheter ablation
Cardiac Echocardiography: Basics and Uses
Cardiac Electrophysiology
Cardiac Embryology
Cardiac Failure
Cardiac MRI
Cardiac Physiology
Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT) Pacemaker
Cardiac Syndrome X (Microvascular Angina)
Cardiac Troponins
Cardiac and Respiratory Rehabilitation
Cardioembolic stroke
Cardiogenic shock
Cardiological Emergencies
Cardiology Examination (OSCE)
Cardiopulmonary bypass
Cardiorespiratory Arrest
Caring for Patients with Dementia
Carmustine
Caroticocavernous Fistula
Carotid Artery Dissection
Carotid Body Tumour
Carotid Endarterectomy
Carotid Sinus Syncope
Carotid Web
Carotid sinus massage
Carpal tunnel syndrome
Carvedilol
Caspases
Castleman's disease
Cataract
Catheter Related UTI
Catheter related Blood stream infection
Cauda Equina Syndrome (CES)
Cauda equina
Caudate Nucleus
Causes of Chronic Hepatitis
Causes of Eosinophila
Causes of Fatigue
Causes of Galactorrhoea
Causes of Gradual Visual Loss over weeks and months
Causes of Hypogonadism
Causes of Limp in Children
Causes of Neck Pain/Stiffness
Causes of Precious Puberty in Children
Causes of Ptosis
Causes of Short Stature in Children
Causes of Stroke
Causes of Tall Stature in Children
Causes of Tremor
Causes of Vertigo
Causes of a high Erythrocyte Sedimentation rate (ESR)
Causes of abnormal Vaginal bleeding
Causes of delayed Onset of Puberty in Children
Causes of high C reactive protein (CRP)
Cavernous angiomas (Cavernomas)
Cavernous sinus
Cavernous sinus thrombosis
Cefaclor
Cefalexin
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Ceftriaxone
Cefuroxime
Celecoxib
Cell Adhesion Molecules
Cell Biology
Cell Cycle
Cell Response to Injury
Cellulitis
Central Pontine Myelinolysis (Osmotic Demyelination Syndrome)
Central Retinal Arterial Occlusion (CRAO)
Central Spinal Cord Syndrome
Central Venous line Insertion
Centronuclear Myopathy (CNM)
Cerebellar Examination (OSCE)
Cerebellar Haemorrhage
Cerebellar Ischaemic Stroke
Cerebellar Structure, Function, Physiology and Disease
Cerebral Amyloid angiopathy (CAA)
Cerebral Angiitis
Cerebral Angiography
Cerebral Angiography and Perfusion
Cerebral Arterial Perfusion and Clinical Correlates
Cerebral Atrophy vs Hydrocephalus
Cerebral Cortex
Cerebral Palsy & HIE
Cerebral Radiation Vasculopathy
Cerebral Salt Wasting
Cerebral Vasculitis
Cerebral Veins 🧠
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (CVT)
Cerebral arteritis
Cerebral microbleeds
Cervical Cancer screening
Cervical Spine Immobilisation and Management
Cervical cancer
Cervical screening (HPV)
Cervical spondylosis
Cetirizine
Chalazion
Chancroid
Change in Bowel habit
Change in stool colour
Charcot Foot Syndrome (CFS)
Charcot Marie Tooth (CMT) disease
Chediak Higashi syndrome
Chemical Pathology
Chemosis
Chemotherapeutic Agents
Chest Abdomen anatomy
Chest Pain
Chest X Ray Collection
Chest X Ray Examples selection
Chest X Ray Interpretation
Chest drain Insertion
Chickenpox Varicella Infection
Child Abuse and Safeguarding NHS
Child abuse
Childhood Vaccination in the UK
Childhood Vaccination in the USA
Chlamydia Infections
Chlamydia psittaci
Chlamydia trachomatis
Chlamydophila pneumoniae
Chlorambucil
Chloramphenicol
Chlordiazepoxide
Chloroquine
Chlorphenamine(Chlorpheniramine)
Chlorpromazine
Cholangiocarcinoma
Cholecystitis
Cholera (Vibrio cholera)
Cholestatic Jaundice
Cholesteatoma
Cholesterol - Lipids
Cholesterol Embolisation Syndrome
Cholinergic crisis-syndrome
Chondrocalcinosis
Chorea - Ballismus
Choreoacanthocytosis
Chorioamnionitis
Choriocarcinoma - Malignant Gestational Trophoblastic Disease
Chromatin
Chronic Bronchitis
Chronic Fatigue Syndrome
Chronic Glaucoma
Chronic Granulomatous Disease
Chronic Inflammation
Chronic Inflammatory Demyelinating polyneuropathy
Chronic Interstitial Nephritis
Chronic Kidney Disease
Chronic Lymphocytic leukaemia (CLL)
Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML)
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic Pancreatitis
Chronic Peritonitis
Chronic Radiation Enteritis
Chronic Rash (Adult/Child)
Chronic Urinary Retention
Chronic Vision Uni-Bilateral loss (Blindness)
Chronic abdominal pain
Chronic and recurrent Meningitis
Chronic joint pain/stiffness 🦴
Chronic mucocutaneous candidiasis
Chronic stable angina
Ciclosporin
Cilia structure and function
Cimetidine
Cinacalcet
Ciprofloxacin
Circulatory Shock (Volume loss)
Cirrhosis
Cisatracurium
Cisplatin
Citalopram
Cladribine
Clarithromycin
Cleft lip or palate
Clindamycin
Clinical Appearance Collections
Clinically Isolated Syndrome (CIS) – First Demyelinating Event
Clonidine
Clopidogrel
Clostridioides difficile Infection
Clostridium botulinum Infection
Clostridium perfringens
Clostridium tetani - Tetanus
Clotrimazole cream
Clotting pathways
Clozapine
Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats CRISPR
Co Careldopa (Sinemet)
Co-Beneldopa (Madopar)
Co-codamol
Co-trimoxazole (Trimethoprim + Sulfamethoxazole)
CoAmoxiclav (Augmentin)
Coagulopathy
Coal Worker's Pneumoconiosis
Coarctation of the Aorta
Cobalt Cardiomyopathy
Cocaine Toxicity and Chest pain
Cocaine abuse
Cocaine toxicity
Coccidioidomycosis
Codeine
Coding
Coeliac disease
Cogan Syndrome
Colchicine
Cold Agglutinin Disease (CAD/AIHA)
Collagen
Colles’ fracture of the Radius
Colloid cyst in the third ventricle
Colloids vs Crystalloids
Colonic (Large bowel) Obstruction
Colonoscopy
Colorectal polyps
Colorectal tumours
Colposcopy
Combined Oral contraceptive pill (COCP)
Common Chromosomal Defects
Common Peroneal Nerve (CPN)
Common Problems in Elderly
Common Psychiatric Emergencies
Common variable immunodeficiency
Commotio cordis
Community Acquired Pneumonia and Differentials
Comparing Groups
Compilers
Complement
Components of a Eukaryotic Gene
Comprehensive Clinical Microbiology Tutorial for Medical Students
Comprehensive Geriatric Assessment (CGA)
Computer Networking
Computer Security
Concurrent Programming
Confirming Death
Confusion
Congenital Acyanotic Heart Disease
Congenital Adrenal hyperplasia
Congenital Complete Heart Block
Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease (Children)
Congenital Hypothyroidism
Congenital Talipes Equinovarus - Clubfoot
Congenital abnormalities
Conjunctivitis
Constipation (Adults)
Constipation (Children)
Constipation in the Elderly
Constrictive Pericarditis
Contact Dermatitis
Continuous Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis (CAPD)
Continuous Positive Airways Pressure (CPAP)
Contraception request/advice
Conus Medullaris syndrome
Cor Pulmonale
Cord Prolapse
Corneal Abrasion
Coronary Artery Anatomy
Coronary artery bypass graft surgery
Corticobasal degeneration (Dementia)
Corticospinal Tract
Corticosteroid-related psychosis 💊
Corticosteroids : Uses and Cautions
Cotard's Syndrome
Cough (Adult)
Cough (Child)
Cowden Syndrome / PTEN Hamartoma Tumour Syndrome
Cowpox (Orthopoxvirus)
Coxiella Burnetii Q fever
Cramps
Craniopharyngioma
Creatinine Clearance
Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Cri du Chat Syndrome
Crimean-Congo haemorrhagic fever
Critical Illness Neuromuscular Weakness (CINMW)
Critical care Crib Sheets
Crohn's disease
Croup
Crying baby
Cryoprecipitate
Cryptococcus neoformans infections (Cryptococcal Infections)
Cryptogenic Organising Pneumonia (COP-BOOP)
Cryptogenic stroke
Cryptography
Cryptosporidiosis
Crystal arthropathy
Cushing disease
Cushing syndrome
Cushing's Syndrome due to Ectopic ACTH
Cutaneous Warts
Cutaneous fungal infections
Cyanide toxicity
Cyanosis
Cyclizine
Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) enzymes
Cyclophosphamide
Cycloserine
Cys leukotriene receptor antagonists
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystinosis
Cystinuria
Cystitis and Urethritis (UTI)
Cystoscopy
Cytokine Physiology
Cytomegalovirus (CMV) infections
D Dimer
D-lactic acidosis or D-lactate encephalopathy
DNA and RNA short notes
DNA replication
DNACPR in the Older Person
Dabigatran
Dalteparin
Dandy Walker syndrome
Dantrolene
Dapagliflozin
Darier’s disease (Keratosis Follicularis)
Darunavir
Data Security and Protection
Data Structures
Data security awareness
Database Management
DeQuervain's thyroiditis
Death Certificates and Cremation UK
Death and dying
Decision Making by Clinicians
Decompressive Hemicraniectomy
Decreased appetite
Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Deep brain stimulation
Dehydration (Child)
Dehydration Adult
Delirium in the Elderly
Delusions
Demeclocycline
Dementia with Lewy bodies
Dementias
Demyelinating Diseases
Dengue Fever
Denosumab (Prolia)
Dental Caries
Dentatorubral Pallidoluysian Atrophy (DRPLA)
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatology Emergencies
Dermatology terms
Dermatomes
Dermatomyositis
Dermoid cysts
Desferrioxamine
Desmopressin (DDAVP)
Desogestrel (Progestogen Only Pill) 💊
Developmental Delay & Abnormal Development in Children
Developmental Dislocation (Dysplasia) of the Hip (DDH)
Dexamethasone
DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion syndrome)
Diabetes Insipidus
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1
Diabetes Mellitus Type 1 and DKA (children)
Diabetes Mellitus Type 2
Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy
Diabetes Variable Rate Insulin Infusion
Diabetes and Hypertension
Diabetes and Pregnancy
Diabetes in Children
Diabetes: (Autonomic) Neuropathy (DAN)
Diabetes: Criteria US and UK
Diabetes: Eye Disease
Diabetes: Foot Problems
Diabetes:Complications
Diabetic Amyotrophy
Diabetic Eye Disease
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Adults
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA) Children
Diabetic nephropathy
Diabetic neuropathy
Diamond-Blackfan anaemia
Diamorphine
Diaphragmatic disorders
Diarrhoea (Children)
Diazepam
Didanosine (ddI)
Diethylstilbestrol
Dieulafoy Lesion
Different Forms of Medical Trials and Studies
Differential Diagnosis of Malar Rash
Differentials of ABC
Differentials of Painful thigh
Differentiation syndrome
Difficulty Swallowing
Difficulty with breastfeeding 🍼
Diffuse Alveolar Haemorrhage (DAH)
Diffuse Oesophageal spasm
Diffuse Parenchymal Lung Disease (DPLD) or Interstitial Lung Disease (ILD)
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Diffusion Capacity
Digoxin
Digoxin Toxicity
Digoxin-specific antibody
Dihydrocodeine
Dilated Cardiomyopathy
Diltiazem
Diphtheria (Corynebacterium diphtheriae)
Diplopia (Double Vision)
Dipyridamole
Discharges against advice
Discoid lupus erythematosus (DLE)
Disease prevention/screening
Diseases with associated cancers
Dislocation Sternoclaivcular joint
Disopyramide
Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Distal Humerus Fracture
Distal Radius Fracture
Distributive Shock (Reduced SVR vasodilated)
Disulfiram (Antabuse)
Diuretics
Diverticular disease
Diving Physiology
Dizziness
Dobutamine
Dog Bites
Domestic Violence and Safeguarding NHS
Domperidone
Donepezil (Aricept)
Donovanosis
Dopamine Hydrochloride
Dopamine agonists
Dornase Alpha
Dosing Gentamicin
Downs syndrome
Doxapram
Doxazosin (Cardura)
Doxepin
Doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
Doxycycline
Driving Advice
Drug Induced Parkinson disease
Drug Metabolism
Drug Overdose Adults
Drug Reaction Eosinophilia Systemic Symptoms (DRESS syndrome)
Drug Toxicity Assessment and Management
Drug induced Lupus Erythematosus
Drug induced liver disease
Drug overdose children
Drugs
Drugs to Avoid in Acute Renal failure
Drugs to avoid Elderly
Drugs to avoid in Liver failure
Dry and Wet and Gas Gangrene
Dual X-ray absorptiometry (DEXA)
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Dulaglutide GLP-1 agonist
Duloxetine
Duodenal Atresia (Children)
Dupuytrens contracture
Dural Arteriovenous Malformations
Dysmorphic child
Dysphagia / Swallowing Problems
ECG - Acute Coronary Syndrome
ECG - Artefact
ECG - Asystole and P wave Asystole
ECG - Bundle Branch Blocks
ECG - Calculate the electrical axis
ECG - Causes of a Dominant R wave in V1
ECG - Collection A
ECG - Collection B
ECG - Heart Block
ECG - Hyperkalaemia
ECG - Interpretation
ECG - Left Axis Deviation
ECG - Left Bundle Branch Block LBBB
ECG - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy
ECG - Low Voltage Complexes
ECG - NSTEMI
ECG - Normal 12 Lead
ECG - Normal ECG basics
ECG - P wave
ECG - Pathological Q waves
ECG - Potential Errors
ECG - QT interval
ECG - Right Axis Deviation
ECG - Right Bundle Branch Block RBBB
ECG - Right Ventricular Hypertrophy
ECG - ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction STEMI
ECG - ST segment changes
ECG - ST-T T waves changes
ECG - Sinoatrial block
ECG - Sinus Bradycardia
ECG - The QRS complex
ECG - short PR interval
ECG Analysis
ECG/EKG Crib sheets
ECGs for the MLA
EEG (Electroencephalogram)
ENT emergencies
ENT infections
Ear Pain (Otalgia)
Ear and Nasal Discharge
Eating Disorders
Ebola Virus Disease
Ebstein anomaly
Echinocytes
Ecstasy toxicity
Ectopia lentis (subluxation of the lens)
Ectopic Pregnancy
Ectropion
Eculizumab
Eczema/Dermatitis
Edoxaban (Lixiana)
Edward syndrome (trisomy 18 syndrome)
Efavirenz (Sustiva) EFV
Ehlers-Danlos syndromes
Ehrlichiosis
Eikenella corrodens
Eisenmenger's syndrome
Elation/elated mood
Elbow Dislocation
Elder Abuse and Safeguarding
Electrical Storm in Ventricular Tachycardia or Ventricular Fibrillation
Electrical injury
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Electron Transport Chain
Embryology of Blood and Immune System
Embryology of Limb Development
Embryology of Nervous system
Embryology of Organ Development
Emergency Contraception (EC)
Emergency Drug Antidotes
Emergency Drugs - Cardiac
Emergency Drugs Endocrine
Emergency Drugs Pain
Emergency Gastrointestinal Drugs
Emergency Haematology Drugs
Emergency Obstetric and Gynaecology Drugs
Emergency Respiratory Drugs
Emergency neuropsychiatric drugs
Emphysema
Empty sella syndrome
Emtricitabine (Emtriva) FTC
Enalapril
Encephalocoele
Encopresis in Children
End of Life Care Prescribing
Endocrine Emergencies
Endometrial (Uterine) Cancer
Endometriosis
Endophthalmitis
Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
Endothelins
Enfuvirtide
Enoxaparin Sodium (Clexane-Lovenox)
Enoximone
Entacapone
Enterococci
Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis
Entropion
Enuresis/Bedwetting in Children
Enzyme inducers and inhibitors
Enzymes in Humans
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis
Eosinophilic granulomatosis (Churg Strauss)
Ependymoma
Epididymitis and Orchitis (Children)
Epididymitis and Orchitis in Adults
Epidural Haematoma
Epidural Spinal abscess
Epilepsy
Epilepsy - Diagnosis
Epilepsy - Idiopathic Generalised Epilepsy
Epilepsy in Pregnancy
Episcleritis
Epistaxis
Eplerenone
Eponymous brainstem strokes
Epstein-Barr Virus infection
Equality Diversity and Human Rights
Equality Diversity and Inclusion
Erb Palsy
Erectile dysfunction
Ergocalciferol (Calciferol)
Erlotinib (Tarceva) 💊
Erysipelas
Erysipelothrix rhusiopathiae
Erythema Gyratum Repens
Erythema Multiforme
Erythema Nodosum
Erythema ab Igne
Erythrodermic Psoriasis
Erythromycin
Escherichia coli (E. coli)
Escitalopram 💊
Esomeprazole
Essential Hypertension
Essential Thrombocythaemia (ET)
Essential Tremor
Etanercept
Ethambutol
Ethanol
Ethanol toxicity
Ethylene glycol toxicity
Etomidate
Etravirine (intelence) ETR
Euglycaemic Ketoacidosis (euDKA) with SGLT2 Inhibitors
Ewing sarcoma
Exenatide (Byetta) GLP1 agonist
Exercise Physiology
Exercise stress test
Exploding head syndrome
Extradural haemorrhage
Extramedullary plasmacytoma
Extrapyramidal symptoms
Extrinsic Allergic alveolitis (Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis)
Eye Collection
Eye Trauma
Eye infections
Eye pain/discomfort
Ezetimibe
Fabry disease
Facial Nerve (VII Cranial nerve)
Facial and Periorbital Swelling
Facial pain
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
Factor V Leiden Deficiency
Faecal Calprotectin
Faecal Incontinence
Fahr syndrome (Idiopathic basal ganglia calcification)
Failure to thrive or Faltering growth
Falls
Familial Adenomatous polyposis (FAP)
Familial Hyperlipidaemias
Familial Mediterranean Fever (FMF)
Familial hypocalciuric hypercalcaemia (FHH)
Familial/Hereditary Amyloidosis
Family Tree (Pedigree)
Family history of possible genetic disorder
Famotidine
Fanconi Anaemia
Fanconi Syndrome
Farmer's lung
Fasciculation
Fast Atrial Fibrillation and Rate Control
Fat Metabolism
Fat embolism
Fatal Familial Insomnia (FFI)
Fatty acids
Febrile convulsion
Felodipine (Dihydropyridine)
Female Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology
Femoral Hernia
Femoral Vein Cannulation
Femoral nerve
Fentanyl - Fentanil
Ferritin
Ferrous Fumarate - Gluconate - Sulphate
Fertilisation and Formation of Zygote
Fetal Alcohol Syndrome
Fetal-type Posterior cerebral artery (FTP)
Fever - all ages
Fever in IV Drug User (PUO)
Fever in a traveller
Fever/Pyrexia of unknown origin (FUO PUO)
Fibrinogen
Fibromuscular Dysplasia
Fibromyalgia
Fibrotic Lung Disease
Fidaxomicin
Fifth Disease (Erythrovirus B19 infection)
Finasteride (5 alpha-reductase inhibitor) 💊
Fire Safety for NHS Professionals
First Seizure
First degree AV Block
Fissure in Ano
Fistulo in Ano
Fit Notes in General Practice (UK)
Fits/seizures and Epilepsy (Children)
Fitz-Hugh Curtis Syndrome
Fixed Abnormal Beliefs (Delusions)
Flashes and Floaters in the Visual Field
Flecainide Acetate
Flexor sheath infection (flexor tenosynovitis)
Flow Cytometry
Flucloxacillin
Fluconazole
Flucytosine
Fludrocortisone
Fluid balance status and management
Flumazenil (Annexate - Romazicon)
Fluoxetine
Focal Cortical Dysplasia (FCD)
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Foix-Alajouanine syndrome
Folate (Folic) acid (B9)
Folate deficiency (B9)
Folinic acid (Leucovorin)
Follicular lymphoma
Folliculitis
Fomepizole
Fondaparinux
Food Intolerance in Children
Food borne disease
Foot Drop
Forearm Fractures
Foreign Body in Eye
Foscarnet Sodium
Fosfomycin
Foslevodopa / Foscarbidopa
Fosphenytoin
Foster Kennedy Syndrome
Fourniers gangrene
Fractured Clavicle
Fractured Neck of Femur/Femoral Neck
Fractured Pubic Ramus
Fractured Scapula
Fractured Shaft Femur
Fractured Tibia and Fibula
Fractures in Children
Fractures of Neck and Shaft of Upper humerus
Fragile X syndrome
Frailty an Overview
Fraser guidelines and Gillick Competence
Free Radicals
Fresh Frozen Plasma
Freshwater (River/Lake)/Saltwater (Sea/Ocean) Drowning
Friedreichs Ataxia
Frontotemporal dementia
Full or Complete Blood Count (FBC CBC)
Functional organization of a eukaryotic gene
Fungi and their infections
Furosemide (Frusemide)
Fusidic acid
Fusobacteria - Tropical ulcer
Fusobacterium
G protein-coupled receptors
GLP-1 Receptor Agonists
GLP-1 receptor agonists
Gabapentin
Galantamine
Gallstone ileus
Gallstones and biliary colic
Gamete intra-fallopian tube transfer (GIFT)
Gametogenesis
Gamma Glutamyl Transferase (GGT)
Gamma hydroxy butyrate (GHB) toxicity
Ganciclovir - Valganciclovir
Ganglion Cysts
Gardner's syndrome
Gardnerella vaginalis
Gas Gangrene (Clostridial Myonecrosis)
Gastric (MALT) Lymphoma
Gastric Cancer
Gastric Outlet obstruction (pyloric stenosis) in Adults
Gastrinoma
Gastro Intestinal Stromal Tumours (GIST)
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux (GORD)
Gastro-Oesophageal Reflux (Paediatrics GORD)
Gastro-oesophageal reflux in Children
Gastroenteritis in Adults
Gastroenteritis in Children
Gastroenterology Examination
Gastroenterology Examination (OSCE)
Gastrointestinal Emergencies
Gastrointestinal tract Physiology
Gastrostomy (PEG) tube managment
Gaucher's disease
Gene components
General Anaesthetics
General Basic Fracture management
Genetic Diseases
Genetic Linkage
Genetic Mutations
Genital Ulcers
Genital Warts (HPV)
Gentamicin
Geriatric Medicine Emergencies
Geriatric Medicine Syllabus (For Resident Doctors in Training)
Gerstmann-Straussler-Scheinker Syndrome (GSS)
Giardiasis
Gilbert's syndrome
Gingival (Gum) hyperplasia or hypertrophy
Gitelman's syndrome
Glasgow Coma scale
Glatiramer acetate (Copaxone)
Glibenclamide
Gliclazide
Glimepiride
Glioblastoma
Glipizide
Glomerulonephritis
Glossitis
Glossopharyngeal Nerve (Cranial Nerve IX)
Glucagon
Glucagonoma
Glucose 6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency
Glucose Metabolism
Glucose Tolerance Test
Glutamate
Glycated Haemoglobin HbA1c
Glyceryl Trinitrate (GTN)
Glycogen storage diseases
Glycolysis Krebs Electron Transport Chain
Glycopyrronium Bromide
Goitre
Golfer's Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Golimumab (Simponi)
Gonorrhoea
Goodpasture's syndrome (Anti GBM disease)
Goserelin (Zoladex)
Government Benefits Available to People with Disabilities UK
Gradenigo's syndrome
Grades of Recommendation
Gradual change in or loss of vision
Gram Stain
Granuloma annulare
Granulomas
Granulomatosis with Polyangiitis GPA (Wegeners)
Graves Disease (Thyrotoxicosis)
Griseofulvin
Growth Hormone Deficiency
Guillain Barre Syndrome
Gum hypertrophy
Gynaecological Examination (OSCE)
Gynaecological History Taking
Gynaecological emergencies
Gynaecomastia
HAS-BLED score
HIV and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis (PEP)
HIV and Pre-exposure prophylaxis
HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)
HIV disease New Diagnosis
HTLV-1 Associated myelopathy (Tropical Spastic Paraparesis)
Haematemesis
Haematology Emergencies
Haematology Laboratory Values
Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (Previously Bone Marrow Transplantation)
Haematospermia
Haematuria
Haemoglobinopathies
Haemoglobins
Haemolytic Anaemia
Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (HUS)
Haemolytic disease of the newborn
Haemophilia
Haemophilia A
Haemophilia B
Haemophilus aegyptius
Haemophilus ducreyi
Haemophilus influenzae
Haemophilus parainfluenzae
Haemopoiesis
Haemoptysis
Haemorrhagic Transformation of Infarction
Haemorrhagic stroke
Haemorrhoids (Piles)
Hairy Cell Leukaemia
Hairy Leukoplakia
Hallervorden-Spatz disease (PKAN)
Haloperidol
Hamman-Rich syndrome
Hand foot and mouth disease
Hand fractures and Injuries
Hantavirus infections
Haptoglobins
Hartmann's procedure
Hartmanns solution (Ringers lactate)
Hartnup disease
Hashimoto's thyroiditis
Head Impulse Test
Head Injury and Traumatic Brain Head Injury (TBI)
Head Lice
Head and Neck Cancers
Headache - Acute and Severe
Headache - Basilar Migraine
Headache - Cluster
Headache - Medication Overuse Headache
Headaches
Health Issues In Pregnancy
Health Safety and Manual Handling
Hearing Loss
Hearing aids
Heart Murmurs
Heart and Fetal circulation
Heat Stroke
Helicobacter pylori
Helvetica Spotted fever
Heme Synthesis, Biochemistry, and Physiology
Henoch-Schonlein purpura
Heparin - General
Heparin - Low Molecular Weight Heparin
Heparin - Unfractionated Heparin
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT)
Hepatic Encephalopathy
Hepatitis
Hepatitis (D) Delta Virus
Hepatitis A
Hepatitis B
Hepatitis C
Hepatitis E
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Hepatology Emergencies
Hepatorenal syndromes
Hereditary Angio-Oedema
Hereditary Elliptocytosis
Hereditary Haemochromatosis
Hereditary Haemorrhagic Telangiectasia (HHT)
Hereditary Spastic Paraparesis
Hereditary Spherocytosis (HS)
Hereditary neuropathy with pressure palsies
Hereditary non polyposis coli (Lynch syndrome)
Hernias
Hernias (Children)
Herpes Gestationis
Herpes Simplex Encephalitis (HSV)
Herpes Simplex Virus
Herpes Varicella-Zoster (Shingles) Infection
Herpes Virus 6 and 7
Herpes Viruses
Herpes Zoster Ophthalmicus (HZO) Shingles
Herpes simplex keratitis (HSK)
Herpetic Whitlow
Heterochromia Iridium
Heyde syndrome
Hiatus hernia
Hiccups (Singultus)
Hidradenitis suppurativa (Acne Inversa)
Hierarchy of Evidence-Based Trials
High Altitude Physiology
High Dose Insulin Euglycaemic Therapy (HIET)
High Output Stoma
Hip pain in children
Hirschsprung disease (congenital megacolon)
Hirsuitism XXX
Histones
Histoplasmosis
Hoarseness and voice change
Hodgkin Lymphoma
Hodgkins and Non-Hodgkins Lymphoma:
Holt-Oram syndrome
Holter monitor (tape) 24-72 h
Homocystinuria
Hookworm
Horner's syndrome
Horseshoe Kidney
Hospital acquired Pneumonia HAP (NICE 139)
Hospital-acquired infections
How does a CPU work
How to Read and Analyze a Medical Paper
Human Herpesvirus 6A (HHV-6A)
Human Leukocyte Antigen and its Role in Disease Associations
Human Metabolism
Human albumin solution (HAS)
Human papilloma virus infection
Human prion diseases
Hunter's syndrome (MPS-2)
Huntingtons Disease/Chorea
Hurler's syndrome (MPS-1)
Hydatid disease (Echinococcus)
Hydatidiform mole
Hydralazine
Hydrocephalus and Stroke
Hydrocortisone
Hydrogen Bonds
Hydrogen and other Bonds
Hydrops fetalis
Hydroxocobalamin
Hydroxocobalamin - Cyanocobalamin (B12)
Hydroxychloroquine 💊
Hydroxyurea (Hydroxycarbamide)
Hyoscine (Buscopan)
Hyper IgM syndrome
Hyperacute Stroke Care Pathway
Hyperbaric Oxygen therapy
Hypercalcaemia
Hypercalcaemia of Malignancy
Hypercholesterolaemia
Hyperemesis Gravidarum
Hyperglycaemic Hyperosmolar State (HHS)
Hyperinsulinaemic-euglycemic therapy (HIET)
Hyperkalaemia
Hyperkalaemic and Hypokalaemic Periodic Paralysis
Hyperlipidaemia
Hypermagnesaemia
Hypernatraemia
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperphosphataemia (High phosphate)
Hyperprolactinaemia
Hypertension in Children
Hypertension in Pregnancy
Hyperthermia and Hypothermia
Hypertriglyceridaemia (HTG)
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM - HOCM)
Hyperuricaemia
Hyperventilation Syndrome
Hyperviscosity syndrome
Hyphaema (US Hyphema)
Hypocalcaemia
Hypoglossal Nerve (Cranial Nerve XII)
Hypoglycaemia
Hypogonadism (Female)
Hypokalaemia
Hypokalaemic Periodic Paralysis
Hypomagnesaemia
Hyponatraemia
Hypophosphataemia (Low phosphate)
Hypopituitarism (Pituitary Failure)
Hypospadias
Hypothermia
Hypothyroidism
Hypoxia - Reacting to Low Oxygen Saturations
Hypoxic-Ischaemic Encephalopathy
ICH Classification and Severity Scores
IL-12 receptor deficiency
IV Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
Ibandronic acid (Bisphosphonate)
Ibuprofen
Icatibant
Idarucizumab (Praxbind) 💊
Idiopathic Arthritis in Adults
Idiopathic Fascicular Left Ventricular Tachycardia
Idiopathic Intracranial hypertension
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Idiopathic Ventricular Tachycardia (IVT)
IgA Nephropathy (Berger's disease)
Ileostomy vs Colostomy
Iliopsoas Abscess
Images - Spot diagnoses
Imaging for the MLA#1
Imaging for the MLA#2
Imatinib mesylate
Imipenem (Primaxin) with Cilastin
Immediate management and assessment of the newborn
Immobility
Immune Reconstitution Syndrome
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Immune response
Immune-Mediated Necrotizing Myopathy
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD)
Immunoglobulins and their role in Immunity
Impetigo
Important Metabolic Pathways
Impulse control disorders
In Situ Thrombosis
Incidental Findings (Incidentalomas)
Inclusion Body Myositis
Incubation periods
Indapamide 💊
Index of Makindo
Indications for Irradiated Blood Products
Indinavir (IND)
Infant feeding issues
Infantile Spasms (West Syndrome)
Infection Associated Cancers
Infection Prevention Control for NHS Staff
Infection Prevention Control for NHS Staff
Infection screening in Septic patient
Infectious Colitis
Infectious Diarrhoea
Infectious Mononucleosis (EBV Most Often)
Infective Endocarditis
Infective Keratitis
Inferior Vena Cava Filter
Infertility & Subfertility
Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease - Acute Severe Colitis
Infliximab
Influenza
Information Governance for NHS Staff
Inguinal Hernia
Injury Severity Score (ISS)
Insomnia - unable to sleep issues
Insulin Degludec (Tresiba)
Insulin Detemir (Levemir)
Insulin Glargine (Lantus, Abasaglar, Semglee, Toujeo)
Insulin Management in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes
Insulin Pumps
Insulinoma
Interferon Beta
Intermittent Claudication
Internal Capsule
Internal Jugular vein Cannulation
Internuclear Ophthalmoplegia
Interpreting Haematinics
Interstitial Keratitis
Interstitial Lung Disease
Intestinal Ischaemia
Intestinal obstruction (Children)
Intestinal obstruction and Ileus
Intra Aortic Balloon Pump
Intraabdominal abscess
Intrauterine death
Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma (IVLBCL)
Intravenous Iron Replacement
Intraventricular haemorrhage (neonates)
Introduction to Anaesthetics
Introduction to Cardiology
Introduction to ECGs
Introduction to Hormones
Introduction to Obstetrics and Gynaecology
Introduction to Psychiatry
Intubation and Mechanical Ventilation
Intussusception in Adults
Intussusception in Children
Iodine Physiology
Iodine deficiency Goitre
Ipratropium Bromide (Atrovent)
Irbesartan
Iritis (Anterior Uveitis)
Iron Salts
Iron Studies
Iron deficiency Anaemia
Iron toxicity
Irritable bowel syndrome
Ischaemic Colitis
Ischaemic Stroke
Ischaemic Strokes in the Pons
Ischaemic heart disease
Isoniazid
Isoprenaline
Isosorbide Dinitrate
Isosorbide mononitrate
Isotretinoin (Accutane)
Ispaghula Husk (Fybogel)
Ivabradine
Jansen Disease
Janus kinase 2
Jaundice
Java Programming
Jervell and Lange-Nielsen syndrome
Job Syndrome (Hyper IgE syndrome)
Jugular Venous pressure
Junctional Tachycardia
Juvenile Dermatomyositis
Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (Stills Disease)
Juvenile Myoclonic epilepsy (JME)
Kallmanns syndrome
Kaposi sarcoma (KS)
Karnofsky performance status scale
Kawasaki disease
Keloids
Kennedy Syndrome (Spinal and Bulbar Muscular Atrophy (SBMA))
Keratoacanthoma
Keratoconus
Kernicterus
Ketamine
Ketoconazole 💊
Ketones
Klebsiella pneumonia
Klinefelter Syndrome
Klumpke palsy
Koebner phenomenon
Kugelberg-Welander Syndrome (Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type III)
Kuru
Kwashiorkor
L-Thyroxine (T4)
Labetalol (Trandate)
Labour and Complications
Labyrinthitis and Vestibular Neuronitis
Lac operon
Lacerations
Lacerations
Lactate
Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)
Lactic acidosis
Lactobacillus acidophilus
Lactose Intolerance
Lactulose
Lacunar Stroke Syndromes
Lady Windermere syndrome
Lambert-Eaton syndrome (LEMS)
Lamivudine (3TC)
Lamotrigine
Langerhans cell histiocytosis (LCH)
Language and Dysphasia
Lansoprazole
Lanthanum
Large for Gestational Age (LGA)
Lassa haemorrhagic fever (LHF)
Lateral Medullary Syndrome
Law and Mental Health (UK)
Law and Mental Health (USA)
Laxatives
Le Fort Fractures
Lead toxicity
Learning disability
Leber hereditary optic neuropathy (LHON)
Lecanemab (Leqembi)
Leflunomide (Arava)
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT) Tachycardia
Legal definition of Blindness
Legionella Pneumophila
Leishmaniasis (Cutanenous and Visceral)
Lemierre's syndrome
Lenalidomide (Revlimid)
Length Dependent Polyneuropathy
Lennox-Gastaut syndrome
Lenticulostriate branch occlusion
Leprosy (Hansen’s disease)
Leptin
Leptomeningeal Metastases
Leptospira interrogans
Leptospirosis (Weil's Disease) (Notifiable)
Leriche syndrome (aortoiliac occlusive disease)
Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
Leukaemia
Leukoariosis
Leukocyte alkaline phosphatase
Leukocytoclastic vasculitis
Leukotrienes
Levetiracetam (Keppra)
Levobupivacaine
Levodopa
Levomepromazine
Levosimendan 💊
Lhermitte Duclos Disease
Li Fraumeni syndrome
Lichen Planus
Liddle's syndrome
Lidocaine(Lignocaine)
Lightning strike
Limb Weakness
Limb girdle dystrophy
Limbic Encephalitis
Linagliptin (Trajenta)
Linezolid
Liothyronine Sodium L-Triiodothyronine (T3)
Lipid emulsion therapy - Intralipid
Lipoatrophy
Lipoprotein lipase deficiency
Liraglutide (Victoza)
Lisinopril
Listerial Meningitis
Listeriosis
Lithium
Lithium toxicity
Livedo Reticularis
Liver Biopsy
Liver Examination (OSCE)
Liver Physiology
Liver Transplantation
Liver abscess
Liver disease in Pregnancy
Local Anaesthetics for Suturing or other Procedures
Localisation of cortical function
Locked in Syndrome
Lofepramine
Loffler's syndrome (Pulmonary Eosinophilia)
Loin Pain
Long COVID
Long QT syndrome (LQTS) Congenital
Long chain acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency
Long term Oxygen therapy (LTOT)
Loop diuretics
Loperamide
Lopinavir
Loratadine
Lorazepam
Losartan
Loss of Libido
Loss of red reflex
Louse-Borne vs Tick-Borne Relapsing Fever
Louse-borne relapsing fever
Low CSF pressure Headache
Low mood/affective/depression problems
Lower Gastrointestinal Bleeding
Lower Limb Fractures
Lower Limb Fractures and Injuries
Lower Limb Neurology (OSCE)
Lower Limb Soft Tissue Injuries
Lower respiratory tract infection (Child)
Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome (LGL) AVRT
Lugol iodine
Lumbar and Sacrum anatomy and function
Lumbar puncture
Lumbrosacral Radiculopathy
Lump in Groin
Lung Abscess
Lung Cancer
Lung Compliance
Lung Empyema
Lung Transplant
Lupus Nephritis
Lupus Vulgaris
Lyme disease
Lymphadenopathy
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytic Hypophysitis
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (LGV)
Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Lyonization (X-Inactivation)
Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) Toxicity
Lysosomal storage diseases
MELAS
MR cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
Macrocytic anaemia
Macroglossia
Macrophage activation syndrome (MAS)
Magnesium Physiology
Magnesium Sulphate - Sulfate
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
Magnetic resonance imaging
Major Disaster Plan
Major Histocompatibility complex
Malabsorption - small intestine
Malaria
Malaria Falciparum (Includes Cerebral Malaria)
Malaria in Children
Male Urethral Catheterisation
Malignant Ascites
Malignant Hyperparathyroidism due to PTHrP
Malignant Hyperpyrexia (Malignant Hyperthermia)
Malignant Hypertension
Malignant MCA syndrome
Malignant Melanoma
Malignant pleural mesothelioma
Mallet Finger
Mallory-Weiss Tear
Malnutrition Adults and the Elderly
Malnutrition Universal Screening Tool
Malnutrition universal screening tool (MUST)
Management of Bites
Management of Type 2 Diabetes
Management of Unprotected Sex and Emergency Contraception (EC)
Managing Chronic Heart Failure
Mania
Mannitol
Mantle cell lymphoma
Marantic Endocarditis
Marasmus
Maraviroc (Celsentri)
Marburg virus disease
Marchiafava Bignami syndrome
Marfan syndrome
Marginal Keratitis
Marginal Zone Lymphoma
Maskne
Massive Haemorrhage and Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
Maths and Physics Crib Sheets
Maturity Onset Diabetes of the Young (MODY)
McArdles disease (type V)
McCune Albright syndrome
Measles (notifiable)
Mebeverine
Mechanical Thrombectomy for Ischaemic Stroke
Meckel diverticulum
Meconium
Median Nerve
Medical Licensing Assessment Content Map (GMC)
Medical Tweetorial Links
Medical conditions affecting the Teeth
Medullary Sponge kidney
Medulloblastoma
Mefenamic acid
Mefloquine (Larium)
Megaloblastic anaemia
Melaena
Melatonin
Melioidosis (Burkholderia pseudomallei)
Memantine Hydrochloride
Membranous Glomerulonephritis
Memory Loss
Menetrier disease
Menieres disease
Meningioma
Menkes Disease
Menopause
Menopause and Menopausal Problems
Menstrual cycle
Menstrual problems
Mental Capacity Act 2005
Mental Health Act 1983
Mental capacity concerns
Mental health problems in pregnancy or postpartum 🤰
Mercaptopurine 💊
Meropenem
Mesalazine (Aminosalicylate)
Mesangiocapillary Glomerulonephritis
Mesenteric Ischaemia
Mesenteric adenitis
Mesial temporal lobe epilepsy
Metabolic Syndrome X
Metabolic acidosis
Metabolic alkalosis
Metachromic leukodystrophy
Metastatic Adenocarcinoma
Metastatic Calcification
Metastatic bone disease
Metastatic disease
Metformin
Methaemoglobinaemia
Methanol Toxicity
Methicillin Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
Methodone
Methods to reduce toxin absorption
Methotrexate
Methylcellulose
Methylprednisolone
Methylthioninium chloride (Methylene blue)
Metoclopramide
Metolazone 💊
Metoprolol
Metronidazole (Flagyl)
Metyrapone (Metopirone) 💊
Miconazole
Microangiopathic Haemolytic anaemia
Microbiology and Assessment of Streptococcus
Microcytic anaemia
Microscopic Polyangiitis
Microscopic colitis
Microstomia
Microtubules
Midazolam
Middle East Resp Syndrome (MERS) Coronavirus
Midodrine
Mifepristone
Migraine
Miller-Fisher syndrome
Milrinone
Milwaukee shoulder syndrome
Mini Mental State Examination (MMSE)
Minimal Change Disease Glomerulonephritis
Minocycline
Minoxidil
Mirabegron
Mirizzi syndrome
Mirtazapine
Mirvetuximab soravtansine (Elahere)
Miscarriage
Misoprostol
Misplaced Nasogastric tube insertion
Mitochondria
Mitochondrial diseases
Mitosis and Meiosis
Mitral Regurgitation (Incompetence)
Mitral Stenosis
Mitral Stenosis vs Regurgitation
Mitral Valve prolapse
Mittelschmerz
Mixed Connective Tissue Disease (MCTD)
Mobility aids
Modified Oxford Handicap Scale (MOHS)
Modified Rankin Score
Modified Valsalva
Molecular Structures for Medicine
Molluscum contagiosum
MonkeyPox (MPOX)
Monoclonal gammopathy Undetermined significance
Monocytes
Monosodium glutamate (MSG) syndrome
Montelukast
Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MOCA)
Moraxella catarrhalis
Morphine Sulphate
Morphological Blood film abnormalities and variants
Mosquito borne diseases
Motor End Plate
Motor Neuron Disease (MND-ALS)
Moyamoya disease
Muckle Wells syndrome
Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia
Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Conduction block
Multiple Antithrombotics Anticoagulants
Multiple Crib sheets
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type 1 (MEN1)
Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia type II (MEN2)
Multiple Myeloma
Multiple Organ Dysfunction Syndrome
Multiple Pregnancy
Multiple Sclerosis (MS)
Multiple System Atrophy (MSA)
Mumps (Notifiable)
Muscle Pain Myalgia
Muscular Dystrophies
Musculocutaneous nerve
Musculoskeletal deformities
Musculoskeletal deformities
Myasthenia Gravis
Mycophenolate mofetil
Mycoplasma pneumoniae
Mycoplasmas
Mycosis Fungoides (Sezary Syndrome)
Myelin Oligodendrocyte Glycoprotein (MOG) & MOG Antibody-Associated Disease (MOGAD)
Myelodysplastic syndrome (Myelodysplasia)
Myelofibrosis
Myelopathy (Disorder of Spinal cord)
Myeloproliferative disorders
Myeloproliferative vs Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Myobacterium avium Complex Infection
Myocardial perfusion
Myoclonus
Myoglobin
Myotomes
Myotonic dystrophy - Dystrophia myotonica
Myxoedema coma
N-Acetylcysteine (Parvolex)
NICE and other guidelines links
NSAID toxicity
Nail disorders
Naloxone (Narcan) Opiate antagonist
Naproxen
Narcolepsy
Narrow Complex Tachycardia
Nasal Discharge
Nasal Obstruction
Nasal polyps
Natalizumab (Tysabri)
National Early Warning Score NEWS 2 Score
Natural Language processing
Neck swellings and lumps
Necrotising Enterocolitis
Necrotising fasciitis
Needlestick injury and PEP
Nefopam 💊
Neisseria meningitidis (Meningococcus)
Nelson Syndrome
Nemaline myopathy
Neomycin
Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome NAS
Neonatal Jaundice
Neonatal Lupus Erythematosus
Neonatal death or cot death
Neonatal death or cot death
Neonatal meningitis
Neostigmine 💊
Nephritic vs Nephrotic syndrome
Nephroblastoma (Wilm's tumour)
Nephrotic Syndrome in Children
Nephrotic syndrome
Nephrotoxic drugs
Nerve conduction studies
Nerve fibres types
Neuroanatomy Images
Neuroblastoma
Neurocysticercosis (Taenia solium a pork parasite)
Neuroferrinopathy
Neurofibromatosis Type 1
Neurofibromatosis Type 2
Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome
Neurological - Vision and Eye movements
Neurological Examination - Cortical Functions
Neurological Examination - Motor
Neurological Examination - Speech&Language
Neurological Sensory Examination (OSCE)
Neurological examination - Eyes
Neurological or ENT Examination - Nystagmus
Neurology Chapter
Neuromuscular weakness
Neuromyelitis Optica (Devic's disease)
Neuropathic Pain Management
Neuropathic pain
Neuroscience of Memory
Neurosurgery
Neurotransmitters
Neutropenia
Neutropenic Sepsis
Neutrophil Alkaline Phosphatase
Neutrophils
Nevirapine (Viramune) NEV-NVP
Newborn Bloodspot (Heel Prick) Screening
Niacin deficiency (Pellagra Vitamin B3)
Nicardipine (Cardene)
Nicorandil
Niemann-Pick disease
Nifedipine
Night sweats
Nikolsky's sign
Nimodipine (Nimotop)
Nipple Discharge
Nirsevimab (Beyfortus)
Nitrates
Nitric Oxide
Nitrofurantoin
Nitrous oxide use and abuse
Nizatidine
Nocardia
Noise induced hearing loss
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease MASLD and MASH
Non Convulsive Status Epilepticus
Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
Non gonococcal urethritis
Non invasive ventilation (NIV)
Non steroidal anti inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs)
Non-Arteritic Anterior Ischaemic Optic Neuropathy
Non-accidental injury
Non-accidental injury (children)
Noonan syndrome
Noradrenaline (Norepinephrine)
Normal Distribution
Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus
Normal Saline 0.9%
Normal pregnancy and Antenatal care
Normocytic anaemia
Norovirus
Nortriptyline
Nosocomial infections
Notifiable disease and organisms UK
Nucleotides
Nutrition in Infants Breastfeeding
Nystatin
OSCE New Headache
OSCE Abdominal Examination
OSCE Acute Abdominal Pain
OSCE Acute Appendicitis
OSCE Acute Right-Sided Weakness
OSCE Ascites Examination
OSCE Blood pressure
OSCE Breast Anatomy Exam
OSCE Cardiac History Taking
OSCE Causes of Male Infertility
OSCE Chest Pain in the Emergency Department
OSCE Chronic Visual Loss
OSCE Comatose Patient
OSCE Cranial nerves and examination
OSCE Dyspepsia
OSCE Dysphagia Swallowing
OSCE Ear Examination
OSCE Examination of Visual Fields
OSCE Examining for Finger Clubbing
OSCE Examining the Arterial Pulse
OSCE Examining the Jugular Venous Pressure (JVP)
OSCE Eye Examination
OSCE Failure to Thrive
OSCE First Seizure
OSCE Gastroenterology History taking
OSCE Hip Pain
OSCE Inguinal Examination
OSCE Jaundice
OSCE Leg Pain & Swelling
OSCE Lower Limb Neurological Examination
OSCE Male Genital exam
OSCE Monocular loss of vision
OSCE Neurological Examination - Cognition
OSCE Neurological Examination Face
OSCE Neurology - History taking
OSCE New Onset Weakness (Stroke Assessment)
OSCE Polyuria and Thirst (Diabetes)
OSCE Postmenopausal Bleeding
OSCE Rectal Bleeding
OSCE Respiratory - History Taking
OSCE Shortness of Breath History
OSCE Shoulder exam
OSCE Station Hearing Loss
OSCE Station – Melaena
OSCE Testicular/Scrotal Examination
OSCE Thyroid Exam
OSCE Unintentional Weight Loss
OSCE Upper Limb Neurology Examination
Obesity
Obesity and Pregnancy
Object orientated programming
Obsessive-Compulsive disorder
Obstetric definitions
Obstetrics Emergencies
Obstructive Lung Diseases
Obstructive Shock (Mechanical Obstruction)
Obstructive Sleep Apnoea
Occupational Lung Disease
Octreotide
Oculomotor Nerve (Cranial Nerve III)
Oesophageal Carcinoma
Oesophageal Perforation - Rupture
Oesophageal Variceal Bleeding
Oesophagogastroduodenoscopy (OGD/EGD)
Olanzapine
Older Patient with Swallowing Problems
Olecranon Fracture
Olfactory Nerve (Cranial Nerve I)
Oligodendroglioma
Olmersartan
Olsalazine (Aminosalicylate)
Omalizumab
Omeprazole
Onchocerciasis
Oncogenic viruses
Ondansetron
Ophthalmic Emergencies
Ophthalmic Nerve
Ophthalmology Exam Lists
Opiates
Opicapone
Opioid/Opiate toxicity
Opsonisation
Optic Nerve (Cranial Nerve II) and tract
Optic Neuritis
Optic atrophy
Optics Pathway
Oral Aphthous Ulcers
Oral Candidiasis
Oral Leukoplakia
Orbital Cellulitis vs Preorbital Cellulitis
Orf (Contagious Ecthyma)
Organism and sensitivities
Organomegaly
Organophosphate (OP) Toxicity
Orphenadrine
Orthostatic Hypotension
Oseltamivir - Tamiflu
Osteoarthritis
Osteochondroma
Osteogenesis Imperfecta
Osteogenic sarcoma (Osteosarcoma)
Osteomalacia
Osteomyelitis
Osteonecrosis of the jaw
Osteopetrosis
Osteoporosis
Otitis Externa (Malignant)
Otitis Media
Otosclerosis
Ottawa rules for ankle and foot x-ray
Ovarian Cancer
Ovarian Cyst
Overlap Syndrome
Overview of Cardiac Electrophysiology
Oxford / Bamford Classification
Oxford community stroke project (Bamford)
Oxidation and Reduction for Medical Students
Oxybutynin (Ditropan)
Oxycodone (Oxycontin-Oxynorm)
Oxygen delivery devices
Oxytetracycline
POEMS syndrome
Pabrinex
Pacemakers and Indications for Pacing
Paediatric Autoimmune Neuropsychiatric Disorders Associated with Streptococcal Infections
Paediatric emergencies
Pagets (Bone) disease
Pain Management : Acute & Chronic
Pain on inspiration
Painful Sexual Intercourse (Dyspareunia)
Painful Shoulder syndromes
Painful swollen leg
Palliation - Nausea Dyspnoea Secretions Pain
Palliation prescribing
Pallor
Palpitations
Pamidronate (Bisphosphonate)
Panayiotopoulos Syndrome in Children
Pancoast tumour (Cancer)
Pancreas Physiology and Anatomy
Pancreatic Cancer
Pancytopenia
Panic Disorder
Panton-Valentine leucocidin toxin
Pantoprazole
Pantothenate Kinase–Associated Neurodegeneratio
Papilloedema
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen)
Paracetamol (Acetaminophen) toxicity
Paracoccidioidomycosis
Paradoxical embolisation
Paraneoplastic Limbic Encephalitis (Dementia)
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
Paraphimosis (urological emergency)
Paraquat toxicity
Parathyroid Physiology
Parkinson Hyperpyrexia Syndrome
Parkinson Plus syndromes
Parkinson disease
Parkinsonism and Tremors
Paronychia
Parotitis
Paroxetine
Paroxysmal Nocturnal Haemoglobinuria
Pasteurella multocida
Patau syndrome (trisomy 13)
Patellar Bursitis
Patent Ductus arteriosus (PDA)
Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO)
Pathological Gaits 🚶♂️
Pathological bone fracture
Patient on Anticoagulant and Antiplatelet Therapy
Patients who refuse treatment or lack capacity
Patiromer
Pattern Recognition Receptors
Pectus Excavatum
Pegvisomant 💊
Pelvic Anatomy
Pelvic Inflammatory Disease
Pelvic Mass
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic fractures
Pemphigus Vulgaris
Penetrating Abdominal Trauma
Penicillamine
Penicillin Allergy
Penicillins
Penile Cancer
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) and gastritis in Children
Peptic ulcer disease and Gastritis in Adults
Percutaneous Endoscopic Gastrostomy (PEG) procedure:
Pergolide
Perianal abscesses and fistulae
Perianal symptoms
Pericardial Disease
Pericardial Effusion and Tamponade
Perimesencephalic Subarachnoid haemorrhage
Perindopril
Perinephric abscess
Perioperative Anticoagulation
Peripartum cardiomyopathy
Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD)
Peripheral Nerve Palsies
Peripheral nerve injuries/palsies (Children)
Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral oedema and ankle swelling
Peripheral vascular disease
Peripherally inserted central catheters (PICC)
Peritonitis
Peritonsillar Abscess (Quinsy)
Pernicious anaemia
Personality Disorders
Perthes disease (Osteochondritis of the Hip)
Petechial Rash in Adult or Child
Pethidine
Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
Peyronie’s Disease
Phaeochromocytoma
Phagocytes
Pharmacokinetic
Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacology in the Elderly
Pharyngeal anatomy
Pharyngeal arch derivatives
Pharyngitis
Phenobarbital sodium
Phenoxymethylpenicillin (Penicillin V)
Phentolamine
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
Phenytoin (Dilantin)
Philadelphia chromosome
Phimosis
Phobic disorders
Phocomelia and Thalidomide
Phosphorus/Phosphate
Physics of flow for Medical students
Physiology of vision
Picolax - Citrafleet
Pilonidal Abscess (sinus)
Pinta (Treponema carateum)
Pioglitazone (Thiazolidinediones)
Pituitary Anatomy and Physiology
Pituitary Apoplexy
Pituitary Tumours
Pityriasis or Tinea versicolor infections
Pityriasis rosea
Pivmecillinam (a penicillin antibiotic)
Placenta praevia
Placental abruption
Plantar fasciitis
Plasmapheresis
Plasmids
Platelets
Pleural effusion
Pleural tap (thoracentesis)
Pneumococcal meningitis
Pneumoconiosis
Pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia
Pneumonia in Children
Pneumonia 🩺
Poisoning
Poisons eliminated Haemodialysis - perfusion
Poliomyelitis
Polyarteritis nodosa (PAN)
Polyarticular arthritis
Polycystic Ovary syndrome
Polycythaemia
Polycythaemia Vera (Primary Polycythaemia)
Polydipsia (thirst)
Polymerase chain reaction
Polymorphic light eruption
Polymyalgia Rheumatica
Polymyositis
Polypharmacy and STOPP/START criteria
Polyuria
Pontiac fever (Legionella Pneumophila)
Pontine-Midbrain haemorrhage
Popliteal Artery Aneurysm
Porphyria Cutanea Tarda (PCT)
Porphyria Testing
Portal Hypertension
Positron and Single photon Emission Tomography
Post Menopausal Bleeding
Post Partum Thyroiditis
Post Polio Syndrome (PPS)
Post Streptococcal/Infectious Glomerulonephritis
Post Stroke Epilepsy (PSE)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-exposure prophylaxis with Immunoglobulins
Post-operative surgical care and complications
Post-transplant lymphoproliferative disorders (PTLDs)
Posterior Reversible Encephalopathy Syndrome (PRES)
Posterior circulation
Postpartum / Postnatal Psychosis
Postpartum/Postnatal Depression
Postprandial hypotension
Postural Orthostatic Tachycardia Syndrome (POTS)
Post‑fall management: Concerns for the On‑Call Team
Potassium Physiology
Pralidoxime
Pramipexole (Mirapexin)
Prasugrel
Pravastatin
Praziquantel
Prazosin
Pre-Operative Assessment
Pre-eclampsia, Gestational Hypertension
Prednisolone
Prednisone
Pregabalin
Pregnancy risk assessment
Premature Menopause
Prematurity
Presbyacusis(Presbycusis)
Prescribing in Pregnancy
Pressure sores or ulcers
Preterm labour
Prevotella (Bacteroides) melaninogenica
Priapism
Primaquine
Primary Biliary Cholangitis
Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL)
Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma (POAG)
Primary Pulmonary Hypertension
Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis
Primary amoebic meningoencephalitis (PAM)
Primary and Secondary Hypoparathyroidism
Primary ciliary dyskinesia and Kartagener's syndrome
Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn's syndrome)
Primary progressive aphasia (Dementia)
Probenecid
Prochlorperazine (Stemetil)
Procyclidine
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Progressive Supranuclear Palsy (PSP)
Prolactinoma
Propafenone
Propantheline
Propionibacterium
Propofol
Propranolol
Propylthiouracil
Prostate cancer
Prosthetic Metal and Tissue Valves
Protamine Sulfate
Protein C Deficiency
Protein S Deficiency
Protein Synthesis
Protein losing enteropathy
Protein metabolism
Protein p53
Proteus
Prothrombin 20210A mutation
Prothrombin Complex Concentrates (Octaplex and Beriplex)
Prothrombin time and Coagulation
Prothrombotic Hypercoagulable disorders
Proximal Humeral Fracture
Proximal myopathy
Prucalopride
Pruritis
Pruritis ani
Psammoma bodies 🌀
Pseudo(pseudo)hypoparathyroidism
Pseudomonas infection (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
Psoriasis
Psoriatic arthritis
Psychogenic Polydipsia
Pubertal Development
Pubic Lice (Pediculosis Pubis)
Pulmonary Alveolar Proteinosis
Pulmonary Arteriovenous malformation
Pulmonary Embolism (PE)
Pulmonary Eosinophilia and CXR changes
Pulmonary Haemorrhage
Pulmonary Hypertension
Pulmonary Physiology
Pulmonary Regurgitation
Pulmonary Stenosis
Pulse oximetry
Pupils : Relative Afferent pupillary defect (RAPD)
Purpura
Purpura Fulminans
Putamen and Globus Pallidus
Putaminal Haemorrhage
Pyloric Stenosis Children
Pyoderma gangrenosum
Pyonephrosis
Pyrazinamide
Pyridostigmine 💊
Pyroglutamic acidosis
Pyruvate Kinase deficiency
Python Programming
Quetiapine
Quinine
Quinine toxicity
RFS Rib fracture score
Rabies
Radial Head and Neck Fractures
Radial Ulnar and Median Palsy of the Hand
Radial nerve
Radiation exposure
Radicular syndromes
Radiculopathies
Radioactive iodine (I 131)
Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
Radiologically Inserted Gastrostomy (RIG) Procedure
Radiology for finals
Raised intracranial pressure
Raloxifene
Raltegravir
Ramipril
Ramsay Hunt syndrome
Ranitidine
Ranolazine
Rapid Sequence Intubation (RSI)
Rapidly Progressive Glomerulonephritis (RPGN)
Rasagiline
Rasburicase
Rate limiting steps in metabolism
Raynaud's Phenomenon Primary and Secondary
Reactive Arthritis
Rectal Foreign Body
Rectal Pain (Proctalgia)
Rectal Prolapse
Rectal examination (OSCE)
Red Blood Cell Maturation
Red Blood Cells
Red cell aplasia
Reduced/change in fetal movements
Refeeding syndrome
Referring to Level 2 or 3 care (ITU ICU HDU)
Reflex anoxic attacks in Children
Refractive Errors
Refsum disease
Regular Broad Complex Tachycardia
Relapsing Polychondritis
Remdesvir (Veklury)
Renal Anatomy
Renal Artery Stenosis Renovascular Disease
Renal Papillary Necrosis
Renal Physiology
Renal Replacement Therapy (RRT)
Renal Top Tips
Renal Transplantation
Renal Tubular Acidosis (RTA)
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Renal and Urology Emergencies
Renal cell carcinoma
Renal syndromes
Renin and Aldosterone Renin ratio (ARR)
Renin-angiotensin system
Respiratory Examination (OSCE)
Respiratory Acidosis
Respiratory Alkalosis
Respiratory Anatomy and Physiology
Respiratory Arrest
Respiratory Arrest
Respiratory Disease Investigations
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (Neonates)
Respiratory Emergencies
Respiratory Failure
Respiratory Spirometry and Flow Volume Loops
Restless legs syndrome
Restriction enzymes
Restrictive Cardiomyopathy
Resus: Septic Shock and Sepsis
Resuscitation - Acute Haemorrhage
Resuscitation - Adult Bradycardia Algorithm
Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm
Resuscitation - Advanced Life Support
Resuscitation - Basic Life Support ABCDE
Resuscitation - Choking Algorithm
Resuscitation - Newborns and Children
Resuscitation - Post Resuscitation Algorithm
Reteplase
Reticulocytes
Retinal Vein Occlusion (CRVO)
Retinal detachment
Retinitis pigmentosa
Retinoblastoma
Retinoids
Retinopathy of Prematurity (ROP)
Retroperitoneal fibrosis
Rett Syndrome
Reversible cerebral vasoconstriction syndrome
Reye syndrome
Rhesus haemolytic disease
Rheumatic fever
Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatology Autoantibodies
Rheumatology Drugs
Rheumatology Lab values
Rhino-Orbital-Cerebral Mucormycosis
Rhinosinusitis
Rhodococcus equi
Ribavirin
Ribosomes
Ricin Toxicity
Rickettsia (General Principles)
Rickettsia africae (Tick Bite Fever)
Rickettsia akari (Rickettsial pox)
Rickettsia conorii (Mediterranean Spotted Fever)
Rickettsia prowazekii (Epidemi/Louse-borne Typhus)
Rickettsia rickettsii (Rocky Mountain spotted fever)
Rickettsia tsutsugamushi (Scrub typhus)
Rickettsia typhi (Murine/Endemic typhus)
Rifampicin (Rifabutin Rifampin)
Rifaximin
Right Iliac Fossa Pain
Right Ventricular Outflow Tract Tachycardia (RVOT)
Right Ventricular ST Elevation MI (RVMI)
Right heart valve disease
Rilipivirine (Edurant) RVP
Riluzole (Rilutek)
Risedronate (Bisphosphonate)
Risperidone
Ritonavir (Norvir) RTV
Rituximab (Mabthera)
Rivaroxaban (Xarelto)
Rivastigmine (Exelon)
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Rocuronium
Role of Secondary Messengers
Role of Urinary Catheters in the Elderly
Rotavirus
Rotigotine
Rubella (German Measles) Notifiable
Rust Programming
SCL70 Antibody
SQL programming
Saccular Berry Cerebral Aneurysms
Sacubitril with Valsartan
Safeguarding Adults and Children
Safety Surgical checklist WHO
Salivary Gland Disease
Salivary glands
Salmonella enterica
Salmonella typhi
Sampling in Medical Statistics
Saquinavir (Invirase) SQV
Sarcoidosis
Saxagliptin (Onglyza)
Scabies
Scaphoid fracture
Scarlet Fever (Scarlatina)
Scarring
Schistosomiasis
Schizophrenia
Schmidts syndrome
Sciatic nerve
Sciatica
Scleritis
Scrotal/testicular pain/lump/swelling ⚠️
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic Keratosis
Secondary Hypertension
Secondary Pulmonary hypertension - Cor pulmonale
Secondary dysmenorrhoea
Secondary hyperparathyroidism
Secondary prevention Post Acute Coronary Syndrome
Sedation and Analgesia on ITU
Selective IgA deficiency
Selective Serotonin reuptake Inhibitor toxicity
Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRI)
Selegiline
Selenium deficiency
Self assessment form
Self-harm
Senior Self Assessment
Senna
Septic arthritis
Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies
Serotonin syndrome
Serplulimab
Serratia
Sevelamer
Severe combined immunodeficiency disorders
Shaft of Ulna Fracture
Sheehans syndrome
Shigella characteristics
Shigellosis (Bacillary Dysentery)
Shock in Pregnancy
Short QT Syndrome
Short Synacthen test (SST)
Shoulder Anterior Dislocations
Shoulder: Posterior Dislocation
Sick Child/Neonate
Sick Euthyroid Syndrome
Sick Sinus Syndrome (Tachy-Brady syndrome)
Sickle Cell Disease
Sideroblastic Anaemia
Sigmoid and Caecal Volvulus Adults
Sildenafil (Viagra)
Silicosis
Simvastatin
Sinus Bradycardia
Sinus Node disease
Sinus Tachycardia
Sinus arrhythmia
Sitagliptin
Sitosterolemia
Sjögren’s syndrome
Skin Pathology and Description and Examination
Skin Treatments
Skin Ulcers
Skin and soft tissue and bone infections
Skin or subcutaneous lump
Skull Anatomy
Sleep physiology
Slipped Upper Femoral Epiphysis (SUFE)
Small Bowel Obstruction (Adults)
Small for Gestational Age (SGA)
Small vessel disease
Smallpox
Smoke Inhalation
Smoking and Its Consequence
Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
Smouldering Myeloma
Snake Bites
Sneddon Syndrome
Sodium Bicarbonate (NaHCO3)
Sodium Nitroprusside
Sodium Physiology
Sodium Picosulfate
Sodium Potassium ATPase pump
Sodium Thiopental - Sodium Thiopentone
Sodium Valproate (Epilim Depakote)
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate
Sodium Zirconium Cyclosilicate (Lokelma)
Soft Tissue Injury
Soft tissue : Cut finger
Soft tissue injuries (sprains, strains)
Solifenacin
Solitary Pulmonary Nodule
Somatisation
Somatisation/ medically unexplained physical symptoms
Sore throat
Sotalol Hydrochloride
Speech and language problems
Spina Bifida
Spinal Cord Anatomy
Spinal Cord Arteriovenous Malformations
Spinal Cord Compression
Spinal Cord Haematoma
Spinal Cord Infarction
Spinal Cord Injury / Malignant Spinal Cord Compression (MSCC)
Spinal Fracture
Spinal Fractures: assessment & management
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA)
Spinal Stenosis
Spinal Tracts
Spinal and Epidural Anaesthesia
Spironolactone
Splenectomy
Splenectomy and Hyposplenism
Splenic Rupture
Splenomegaly Examination (OSCE)
Spondylolisthesis
Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis
Spontaneous Pneumothorax
Spontaneous intracranial hypotension
Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Squint
St John's Wort 💊
Staphylococcal Infections
Staphylococcus aureus
Staphylococcus epidermidis
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Statin
Status Epilepticus (Epilepsy/Seizure)
Stavudine (Zerit) d4T
Stem Cell Transplantation
Sterno-Clavicular Joint Dislocation
Steroid-responsive encephalopathy associated with autoimmune thyroiditis (Hashimoto's Encephalopathy)
Stiff Person Syndrome
Strabismus (Lazy Eye)
Streptobacillus moniliformis
Streptococcal Infections
Streptococcus - anaerobes
Streptococcus Pneumoniae (Pneumococcus)
Streptococcus agalactiae Group B
Streptococcus milleri
Streptococcus pyogenes Group A
Streptococcus viridans
Streptokinase
Streptomycin
Stridor
Stroke
Stroke - Epidemiology and risk factors
Stroke - General Management
Stroke Collaterals
Stroke MRI Basics
Stroke Mimics And Chameleons
Stroke Penumbra
Stroke Related Cerebral Perfusion
Stroke Risk Factors
Stroke Thrombolysis
Stroke Vascular Anatomy
Stroke and Vision
Stroke: The Brain and Function
Strongyloides stercoralis (threadworm)
Strontium
Struggling to Cope at Home
Subacute Sclerosing Panencephalitis
Subacute Thyroiditis
Subarachnoid Haemorrhage
Subclavian Steal Syndrome
Subclavian Vein Thrombosis (SCVT)
Subdural haematoma
Subfertility in Men
Subfertility in Women
Substance misuse
Substance use disorder
Sucralfate
Sudden Cardiac Death (SCD)
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing loss (SNHL)
Sugammadex
Suicidal thoughts
Suicide
Sulfasalazine - Sulphasalazine
Sumatriptan
Summary of Emergency Conditions in Oncology
Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA) Syndrome
Superior Sagittal Sinus Thrombosis
Superior Vena Caval Obstruction syndrome
Superior and Inferior Vena Cava
Supracondylar Femur Fractures
Supracondylar Humerus Fractures
Supraspinatus tendonitis
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Surgical Cricothyroidotomy
Surgical Liaison in Older Patients Quality & Silver Trauma (UK)
Surgical Stomas
Surgical prophylaxis
Surgical site infection
Susac syndrome
Suxamethonium
Sweat Test
Swiss Cheese Model of Patient Harm
Sydenhams chorea
Sympathetic Ophthalmia
Synchronised DC Cardioversion
Syncope
Syndrome of Inappropriate ADH (SIADH) secretion
Syphilis
Syringobulbia
Syringomyelia
Systemic Amyloid in Pathology
Systemic Amyloidosis
Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE)
Systemic Mastocytosis
Systemic Sclerosis (Scleroderma)
T lymphocytes
TMN Staging tumours
TNF Blockade
TNF receptor-associated periodic syndrome
TO DO
TORCH infections
TURP Hyponatraemia syndrome
Tabes dorsalis
Table showing Visual Field Changes for Examination
Tacrolimus 💊
Tafamidis
Takayasu arteritis (pulseless disease)
Takotsubo Cardiomyopathy
Tamoxifen
Tamsulosin (Flomax)
Tangier Disease
Tardive Dyskinesias
Tay-Sachs disease
Tazocin (Tazobactam - Piperacillin)
Teicoplanin
Telogen Effluvium
Telomeres
Temazepam
Temozolomide (Temodal) 💊
Temporal (Giant Cell GCA) Arteritis
Tenecteplase
Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Tensilon test
Tension Headache
Tension Pneumothorax
Teplizumab (Tzield)
Terbutaline
Teriparatide
Terlipressin
Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
Testicular Cancer
Testicular Torsion
Testing
Tests in Liver Disease: Usefulness and Interpretation
Tetrabenazine
Tetracosactide (Synacthen)
Tetracyclines
Tetralogy of Fallot
Thalamic Haemorrhage
Thalamic Pain Syndrome or Dejerine–Roussy Syndrome
Thalamic Strokes
Thalamus
Thalidomide
The Aorta
The Axillary Artery
The Brachial Artery
The Brachial plexus
The Carotid Artery
The Cell Nucleus
The Cell membrane
The Circle of Willis
The Deteriorating Patient
The Eye and Systemic Disease
The Femoral Artery
The Fetal Head and Vaginal Birth
The Iliac arteries
The Nephron – the Functional Unit of the Kidney
The Popliteal artery
The Radial and Ulnar Arteries
The Subclavian Artery
The Vertebral and Basilar Arteries
Theophylline
Theophylline toxicity
Thiamine
Third Degree (complete) Heart Block
Thoracic outlet syndrome
Thrombocytopenia
Thrombocytosis (High Platelets)
Thrombophilia (Prothrombotic) testing
Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP)
Thyroglossal Cyst (Children)
Thyroid Cancer
Thyroid Eye Disease
Thyroid Function Tests and antibodies
Thyroid Physiology
Thyroid Storm - Thyrotoxic crisis
Thyroid Surgery (Thyroidectomy)
Thyroid nodules
Thyrotoxicosis and Hyperthyroidism
Tiagabine
Ticagrelor
Tick Paralysis
Tick-borne relapsing fever (Borrelia duttonii)
Timolol
Tinea Corporis (Ringworm)
Tinea capitis
Tinidazole
Tinnitus
Tinzaparin (Innohep)
Tiotropium (Spiriva)
Titre - Titer
Tocilizumab
Tolbutamide
Tolcapone
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs): Recognition Receptors and Triggers of Innate Immunity
Tolosa Hunt Syndrome
Tolterodine
Tolvaptan
Tongue tie - ankyloglossia (Children)
Tonsilitis
Tonsillectomy Adenoidectomy
Topiramate (Topamax)
Torsades de pointes TdP (Polymorphic VT)
Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Drainage
Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens-Johnson syndrome
Toxic Megacolon
Toxic Shock Syndrome
Toxicological Emergencies
Toxoplasmosis
Tramadol 💊
Tranexamic Acid
Transcatheter aortic valve implantation/replacement (TAVI/R)
Transcutaneous Pacing
Transfer Factor (TLCO / DLCO)
Transferrin
Transfers of folder frail or disabled patients
Transient Global Amnesia (TGA)
Transient Ischaemic Attack (TIA)
Transient Monocular Blindness (TMB)
Transjugular Intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
Transposition of the great arteries (TGA)
Transvenous Pacing (Temporary)
Transverse myelitis
Trastuzumab (Herceptin) 💊
Trauma
Trauma : NICE Guidance Haemorrhage
Trauma Physiology
Trauma: Cardiac Arrest
Trauma: Epilepsy - Post Traumatic
Trauma: Flail Chest Rib fractures
Trauma: Initial Assessment and Management
Trauma: Post traumatic stress disorder
Trauma: Resuscitative Thoracotomy
Trauma: Silver Trauma in older patients
Trauma: Spinal Injury
Trauma: Thoracic Assessment and Management
Trauma:Prehospital
Traumatic Auricular Haematoma (Cauliflower ear)
Travel health advice
Travellers Diarrhoea
Trazodone 💊
Treatment Escalation Plans (TEP) in the Elderly
Treponema
Tretinoin (All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA) )
Triangles of the neck
Trichinellosis
Trichomoniasis Vaginalis
Tricuspid Atresia
Tricuspid Regurgitation
Tricuspid Stenosis
Tricyclic Antidepressant Toxicity
Tricyclic antidepressants
Trigeminal Nerve (Vth Nerve)
Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trihexyphenidyl (benzhexol)
Trimethoprim
Trinucleotide (triplet) Repeat Disorders
Trochlear Nerve (VIth nerve)
Tropheryma whipplei (Whipple disease)
Tropical Sprue
Truncus Arteriosus (Children)
Tuberculosis
Tuberculous Meningitis
Tuberous sclerosis
Tularaemia (Francisella tularensis)
Tumour Lysis Syndrome
Tumour Necrosis Factor
Tumour Suppressor Genes
Tumour markers
Turcot's syndrome (Brain tumor polyposis syndrome)
Turners syndrome (Children)
Twins
Tympanic (Eardrum) membrane perforation
Types of Hypersensitivity Reactions
Types of Joints
Types of Organ Transplant Rejection
Typhoid and Paratyphoid fever (Enteric Fever)
Tyrosine Kinase receptors
USMLE Lab Values
Ubiquitin
Ulcerative Colitis
Ulnar nerve
Ultrasound Physics & Imaging
Undifferentiated Inflammatory Arthritis (Children)
Unintentional weight loss (Adults)
Unsteadiness
Unwanted pregnancy and termination
Upper Gastrointestinal Bleed
Upper Limb fractures and injuries
Upper and Lower Limb Neurology (OSCE)
Upper and Lower Motor Neuron signs
Upper limb Soft Tissue Injuries
Upper respiratory tract infection
Urethral Discharge (Urethritis)
Urethral syndrome
Urinary Catheterisation
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary Obstruction
Urinary Tract Infection (UTI Children)
Urinary Tract Obstruction
Urinary symptoms
Urinary tract calculi (stones)
Urothelial tumours/ Transitional cell carcinomas
Urticaria
Uterine fibroids
Uveitis
VIPomas
Vaccine in Older Patients
Vaginal Candidiasis
Vaginal Carcinoma
Vaginal Prolapse
Vagus Nerve (Cranial Nerve X)
Valaciclovir
Valsartan
Vancomycin
Variable rate intravenous insulin infusion VRIII
Variant (Prinzmetal) Angina
Variant Creutzfeldt Jakob disease
Varicella Cerebral Vasculopathy
Varicose veins
Variegate Porphyria
Vasa Praevia
Vascular Anatomy
Vascular Dementia
Vascular access for haemodialysis
Vasculitis - General Issues and Classification
Vasopressin (AVP) Antidiuretic hormone
Vasovagal syncope
Vaughan-Williams Classification
Vecuronium
Vedolizumab (Entyvio)
Venepuncture (Blood tests)
Venlafaxine
Venous Insufficiency and Leg Ulcers
Venous Supply of the leg
Venous Thromboembolism Pregnancy and Puerperium
Venous access Cannulas OSCE
Venous and Arterial Ulcers and Other Lower Limb Ulcers
Venous and Arterial and Pressure Ulcers
Ventilator associated pneumonia (VAP)
Ventricular Fibrillation
Ventricular Septal defect (VSD)
Ventricular Tachycardia (VT)
Ventricular ectopic beats
Verapamil
Vertebral artery dissection
Vesicoureteric reflux (VUR) (Children)
Vestibulocochlear Nerve (Cranial Nerve VIII)
Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Vibrio vulnificus
Vibrio vulnificus
Vigabatrin (Sabril)
Vinblastine
Vincent's angina
Vincristine
Violence Aggression and Conflict Resolution
Viral Gastroenteritis and other causes
Viral Haemorrhagic Fevers (VHF)
Viral Meningitis
Viral exanthema
Viral hepatitides
Viruses and their infections
Visual Basic Programming
Visual Hallucinations in the elderly
Visual acuity
Vitamin A Deficiency
Vitamin B1 Thiamine deficiency
Vitamin B12 deficiency
Vitamin B12 excess
Vitamin C deficiency (Scurvy)
Vitamin D (1,25 OH2)
Vitamin D 25 (OH) D Testing
Vitamin D Physiology
Vitamin D Replacement
Vitamin D resistant rickets (Children)
Vitamin K (Phytomenadione)
Vitamin K deficiency
Vitiligo
Voltarol (Diclofenac)
Volvulus (Children)
Vomiting
Von Gierke Disease (Children)
Von Hippel Lindau
Von Willebrand Disease
Vulval itching/lesion
Vulval/vaginal lump
Waardenburg's syndrome
Waldenstrom Macroglobulinaemia
Warfarin
Water Physiology
Watershed Infarcts
Waveform CO₂ capnography
Weight Gain Adults
Wellbeing Checks in General Practice for GPs
Wellens Syndrome
Werdnig–Hoffman Disease (SMA Type 1)
Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome
Wheeze: Clinical Approach and Considerations
White Blood Cells
Williams Syndrome (Children)
Wilson disease
Windows Powershell
Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (Children)
Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome (WPW) AVRT
Wolfram syndrome (DIDMOAD)
Wound Management
Wound healing
Wrist Injury: Smith’s Fracture
X linked Agammaglobulinaemia (Bruton)
X linked Hypophosphataemic rickets
X-Linked Recessive Inheritance
X-linked Ichthyosis
X-linked lymphoproliferative disease (Children)
Xanthelasma
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Yaws (Frambesia) Treponema pertenue
Yellow Fever
Yellow Nail Syndrome
Yersinia enterocolitica
Yersinia pestis - Bubonic Plague
Yersinia pseudotuberculosis
ZZ_Abnormal char
Zidovudine (Retrovir) AZT - ZDV
Zieve's syndrome
Zika virus
Zinc deficiency
Zolbetuximab (Vyloy)
Zoledronic acid (Zoledronate)
Zollinger Ellison syndrome
Zolpidem
Zopiclone
eGFR
zNecrobiosis
️Causes of a Limp in Adults
🍽️ Malnutrition in Children
📊 Thromboelastography (TEG)
🔄 ROTEM - Rotational Thromboelastometry
🦠 Skin Infections due to Fungi
🧑⚕️ Weakness in Adults – Causes, Features, and Diagnosis<
🩺 Complex Regional Pain Syndrome (CRPS)
🩺 Urinary Tract Infection (UTI) OSCE
Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Pharyngeal anatomy
🧩 Anatomy of the Pharynx
The pharynx is a muscular tube (~12–14 cm long) connecting the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx and esophagus. It acts as a common pathway for both air and food. The pharynx is divided into three main regions: the nasopharynx, oropharynx, and laryngopharynx. It plays vital roles in breathing 🌬️, swallowing 🍽️, speech 🗣️, and immune defense 🛡️.
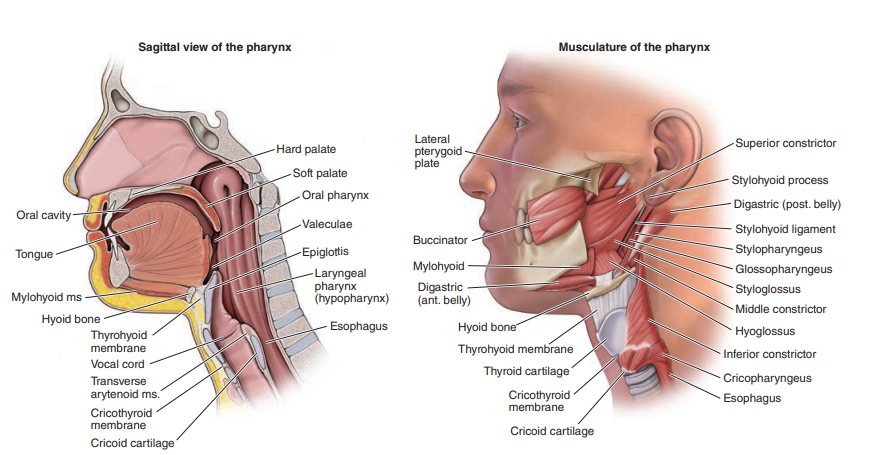
📍 Divisions of the Pharynx
- 👃 Nasopharynx:
- Posterior to the nasal cavity, superior to the soft palate.
- Passageway for air only.
- Contains pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) and openings of the Eustachian tubes ➝ pressure equalisation with the middle ear (important in otitis media in children).
- 👅 Oropharynx:
- Posterior to the oral cavity, extends from the soft palate to the hyoid bone.
- Pathway for both air and food.
- Contains palatine tonsils and lingual tonsils.
- Soft palate elevates during swallowing to prevent nasal regurgitation.
- 🎤 Laryngopharynx (Hypopharynx):
- Posterior to the larynx, extends from the hyoid bone to the esophagus.
- Food directed into esophagus; air directed into larynx.
- Epiglottis covers laryngeal inlet during swallowing ➝ protects against aspiration.
💪 Muscles of the Pharynx
The pharynx has constrictors (for propulsion) and longitudinal muscles (for elevation). They coordinate during swallowing (pharyngeal phase of deglutition).
- Constrictor Muscles:
- Superior: Contracts nasopharynx ➝ prevents regurgitation into nose.
- Middle: Narrows pharynx.
- Inferior: Pushes bolus into esophagus; contains the cricopharyngeus, forming the upper esophageal sphincter.
- Longitudinal Muscles:
- Stylopharyngeus: Elevates pharynx (CN IX).
- Palatopharyngeus: Elevates pharynx, narrows cavity.
- Salpingopharyngeus: Elevates pharynx, opens Eustachian tube.
🩸 Blood Supply of the Pharynx
- Arterial: Ascending pharyngeal, facial, maxillary (branches of external carotid).
- Venous: Pharyngeal venous plexus ➝ internal jugular vein.
🧠 Nerve Supply of the Pharynx
- Motor: All pharyngeal muscles by vagus nerve (CN X), except stylopharyngeus (CN IX).
- Sensory:
- Nasopharynx ➝ CN V2.
- Oropharynx ➝ CN IX (important in gag reflex afferent).
- Laryngopharynx ➝ CN X.
⚡ Functions of the Pharynx
- Swallowing (Deglutition): Sequential constrictor contractions propel food ➝ esophagus.
- Respiration: Conducts air ➝ larynx & trachea.
- Speech: Resonating chamber for phonation.
- Immune Defense: Waldeyer’s ring of tonsils traps pathogens at entry points.
💡 Clinical Pearls
- ❗ Killian’s dehiscence: Weak area between inferior constrictor fibers ➝ site of Zenker’s diverticulum.
- 👂 Recurrent otitis media in children often due to enlarged adenoids obstructing Eustachian tubes.
- 🤮 Gag Reflex: CN IX = afferent, CN X = efferent.
- 🫁 Aspiration risk increases with pharyngeal muscle weakness (e.g., post-stroke).
Categories
About
Acute Medicine
Anaesthetics
Anaesthetics and Critical Care
Anatomy
Biochemistry
Book
Cardiology
Collections
CompSci
Crib
Dental
Dermatology
Differentials
Drugs
Electrocardiogram
Embryology
Emergency Medicine
Endocrinology
ENT
Ethics
Foundation Doctors
Gastroenterology
General Practice
Genetics
Geriatric Medicine
Guidelines
Gynaecology
Haematology
Hepatology
Immunology
Infectious Disease
Infectious Diseases
Infographic
Investigations
Lists
Mandatory Training
Medical Students
Microbiology
Nephrology
Neurology
Neurosurgery
Nutrition
Obstetrics
Obstetrics Gynaecology
Oncology
Ophthalmology
Oral Medicine and Dentistry
Orthopaedics
OSCE
Paediatrics
Palliative
Pathology
Pharmacology
Physiology
Procedures
Psychiatry
Public Health
Radiology
Renal
Respiratory
Resuscitation
Rheumatology
Statistics and Research
Stroke
Surgery
Toxicology
Trauma and Orthopaedics
Urology
USMLE
|Biochemistry
|Embryology