Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |

|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. | |
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Upper limb
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
Muscles of the Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically:
Abductor Digiti Minimi (Hand)
Origin: Pisiform
Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx of the 5th digit on its ulnar side
Action: Abducts the 5th digit
Innervation: Deep branch of the ulnar nerve
Artery: Ulnar a.
Notes: Located in the hypothenar compartment along with flexor digiti minimi brevis and opponens digiti minimi.
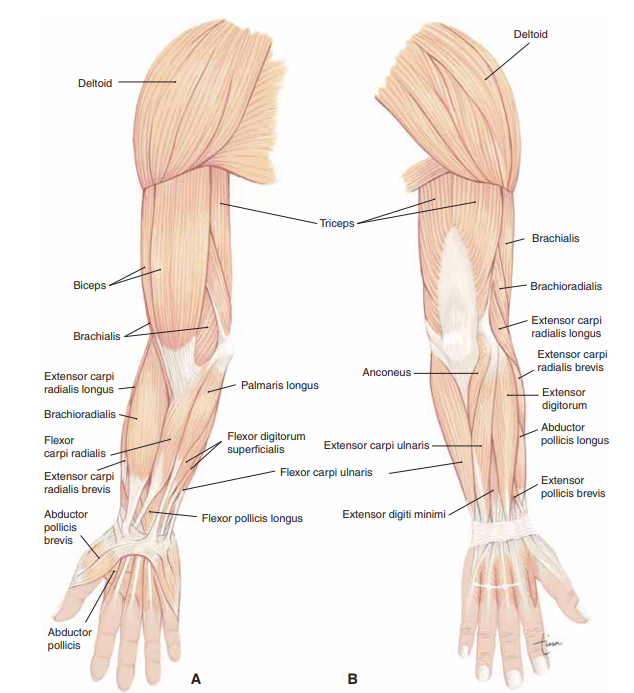
Abductor Pollicis Brevis
Origin: Flexor retinaculum, scaphoid, trapezium
Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx of the first digit
Action: Abducts the thumb
Innervation: Recurrent branch of the median nerve
Artery: Superficial palmar branch of the radial a.
Notes: Located in the thenar compartment with flexor pollicis brevis and opponens pollicis. (Latin, pollicis = the thumb)
Abductor Pollicis Longus
Origin: Middle one-third of the posterior surface of the radius, interosseous membrane, mid-portion of posterolateral ulna
Insertion: Radial side of the base of the first metacarpal
Action: Abducts the thumb at the carpometacarpal joint
Innervation: Radial nerve, deep branch
Artery: Posterior interosseous a.
Notes: Forms the lateral border of the anatomical snuffbox with extensor pollicis brevis. (Latin, pollicis = the thumb)
Adductor Pollicis
Origin: Oblique head: capitate, base of 2nd and 3rd metacarpals; transverse head: shaft of the 3rd metacarpal
Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx of the thumb
Action: Adducts the thumb
Innervation: Ulnar nerve, deep branch
Artery: Deep palmar arterial arch
Notes: Deep palmar arch and deep ulnar nerve pass between the two heads of adductor pollicis, in the adductor-interosseous compartment. (Latin, pollicis = the thumb)
Anconeus
Origin: Lateral epicondyle of the humerus
Insertion: Lateral side of the olecranon and upper one-fourth of the ulna
Action: Extends the forearm
Innervation: Nerve to anconeus, from the radial nerve
Artery: Interosseous recurrent a.
Notes: (Greek, anconeus = elbow)
Biceps Brachii
Origin: Short head: tip of the coracoid process of the scapula; long head: supraglenoid tubercle of the scapula
Insertion: Tuberosity of the radius
Action: Flexes the forearm, flexes the arm (long head), supinates
Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5,6)
Artery: Brachial a.
Notes: A powerful supinator, especially if the elbow is flexed.
Brachialis
Origin: Anterior surface of the lower one-half of the humerus and associated intermuscular septa
Insertion: Coronoid process of the ulna
Action: Flexes the forearm
Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5,6)
Artery: Brachial a., radial recurrent a.
Notes: A powerful flexor.
Brachioradialis
Origin: Upper two-thirds of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
Insertion: Lateral side of the base of the styloid process of the radius
Action: Flexes the elbow, assists in pronation & supination
Innervation: Radial nerve
Artery: Radial recurrent a.
Notes: Although innervated by the nerve for extensors (radial), its primary action is elbow flexion. Its neutral position is halfway between supination and pronation (elbow flexed, thumb up).
Coracobrachialis
Origin: Coracoid process of the scapula
Insertion: Medial side of the humerus at mid-shaft
Action: Flexes and adducts the arm
Innervation: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5,6)
Artery: Brachial a.
Notes: The musculocutaneous nerve passes through the coracobrachialis muscle to reach other arm flexor muscles (biceps brachii and brachialis).
Deltoid
Origin: Lateral one-third of the clavicle, acromion, lower lip of the crest of the spine of the scapula
Insertion: Deltoid tuberosity of the humerus
Action: Abducts arm; anterior fibers flex & medially rotate the arm; posterior fibers extend & laterally rotate the arm
Innervation: Axillary nerve (C5,6) from the posterior cord of the brachial plexus
Artery: Posterior circumflex humeral a.
Notes: Deltoid is the principal abductor of the arm, but it requires supraspinatus muscle to initiate this movement.
Dorsal Interosseous (Hand)
Origin: Four muscles, each arising from two adjacent metacarpal shafts
Insertion: Base of the proximal phalanx and extensor expansion on lateral side of the 2nd digit, lateral & medial sides of the 3rd digit, and medial side of the 4th digit
Action: Flexes the metacarpophalangeal joint, extends the proximal and distal interphalangeal joints of digits 2-4, abducts digits 2-4
Innervation: Ulnar nerve, deep branch
Artery: Dorsal and palmar metacarpal aa.
Notes: Bipennate muscles; remember DAB & PAD - Dorsal interosseous muscles ABduct, and Palmar interosseous muscles ADduct.
Extensor Carpi Radialis Brevis
Origin: Common extensor tendon (lateral epicondyle of the humerus)
Insertion: Dorsum of the third metacarpal bone (base)
Action: Extends the wrist, abducts the hand
Innervation: Deep radial nerve
Artery: Radial a.
Notes: Works with the extensor carpi radialis longus and flexor carpi radialis in abduction of the hand.
Extensor Carpi Radialis Longus
Origin: Lower one-third of the lateral supracondylar ridge of the humerus
Insertion: Dorsum of the second metacarpal bone (base)
Action: Extends the wrist, abducts the hand
Innervation: Radial nerve
Artery: Radial a.
Notes: Works with the extensor carpi radialis brevis and flexor carpi radialis in abduction of the hand.